Pharmacy Assistant Training: Role & Protocols
advertisement

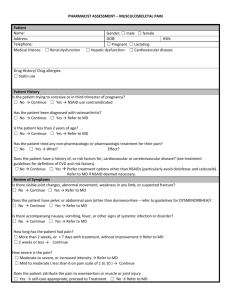
The Role of the Pharmacy Assistant It is not your role to provide customers with information on their medical condition or attempt to diagnose their symptoms. Your important role is to ask the customer questions, listen closely for their responses and then decide if you should refer them your pharmacist. Meet and Greet Pharmacy Customers Time the approach to greet the customer. Identify customers’ needs through appropriate questioning and active listening skills. Communication skills Speaking Listening Asking questions Use the right language Using Protocols Protocols are designed to act as standard operating procedures or rules to guide you when dealing with customers and selling Pharmacist Only and Pharmacy medicines. The two most commonly used protocols are the CARE and WHAT, STOP, GO protocols. Both are designed to ensure you have asked the right questions and have all the information you need to either: Refer to the pharmacist; or Recommend a product, and provide written or verbal information Communication skills Speaking Use a pleasant voice and sound friendly Speak slowly and clearly Be polite and respectful and use appropriate language Vary your tone Pause between phrases or sentences to ensure that the listener can absorb what you have said Don’t use jargon Be honest – it’s okay to say “I don’t know” Avoid talking to loudly, speaking to fast, mumbling or talking down to the customer The Pharmacy Assistant Is an important link between the customer and the pharmacist. Provides general product knowledge and advice to the customer. Refers customers with symptoms or medical conditions or queries about the medications to the pharmacist. Remember; The Pharmacist Is an important source of expert advice. Assesses customers’ clinical status and needs. Provides medication and health care advice. Assesses customers for product satisfaction and appropriate use. Refers customers as appropriate to a doctor. Records and follow up advice as appropriate. Listening Show interest Maintain appropriate eye contact Concentrate on feelings as well as facts Take notice of body language Listen carefully to what is being said Don’t interrupt Be patient Listen carefully to what the customer is saying and check you have understood the message Don’t pretend to understand if you don’t C A R E Check Assess Refer or recommend Explain Check - means asking your customer open and closed questions to find out: Who the patient is What other health conditions do they have What other medications do they use or have tried What symptoms they have and how long they have had them Has a medication worked on previous occasions Assess – deciding if the customer should be referred to the pharmacist or if you should recommend a product or supply the product requested. Customers should be referred to the pharmacist if: A request is made for a Pharmacist Only medicine The patient is a child under two years of age The customer appears to be under the influence of drugs or alcohol They request quantities of a particular medicine eg. Pseudoephedrine The customer is an aged person The customer is pregnant or breastfeeding The request is for treatment of specific symptoms The customer has used the product before and was not satisfied with the result The customer is taking other medications The customer has had the complaint for some time The customer has other health conditions (eg. asthma, diabetes, high blood pressure) The customer looks sick You are unsure Refer or Recommend The prompts for referral, listed above, are designed to make your role as a pharmacy assistant much clearer. You should be listening for them as soon as the customer begins to talk to you. That means listening actively and referring to the pharmacist as soon as you become aware of one of these prompts. This is as simple as saying “Many thanks; I will need to refer you to the pharmacist who will help you.” All you need to do then is let your pharmacist know that you are referring a customer to them. Explain – explain how to use the product if one is recommended. You should explain: The dosage and frequency Any side effects, hazards or precautions What to do if the condition does not improve or worsens Supply written health information such as Pharmacy Self Care fact cards to back up what you have told the customer WHAT, STOP, GO Protocol This protocol is also used to gather information to make sure the “right” medicine is provided. WHAT is the information you need from your customer W H A T Who is the patient? How long have they had the symptoms? Actual symptoms? Treatment STOP – when you have the information needed to decide the best course of action (provide a product or refer to the pharmacist), the following is needed: S T O P Symptoms? Totally sure? Overuse or abuse? Pharmacy only or Pharmacist referral? GO – once you have made your decision, you need to provide advice with the product or explain why you are referring to the pharmacist.