Earth Structure
advertisement

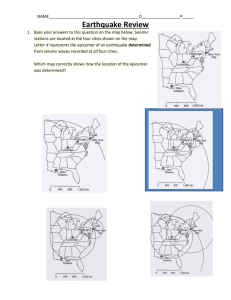
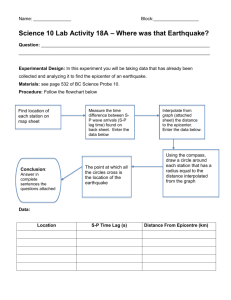
GEOLOGY STUDY GUIDE Module exam GL1 June 2005 EARTH’S STRUCTURE Geology Department, Greenhead College, Huddersfield. Your name .....……………………................................................. Date .........……………........... LEARNING TARGETS margin notes When you have completed this study guide, you will: ● know about the structure of the earth ● understand the movement of earthquake waves ● know about the evidence geologists use to find out about the earth ● have researched your own example of an earthquake ● learnt many useful geological terms. ______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ VC/Dept/Geol/009 page 1 GEOLOGY STUDY GUIDE Module exam GL1 June 2005 Resources Here is a choice of resources to use. You do not need to look at them all but clearly the more you read the better your knowledge of case studies will be. Tick the box once you have used the resource. If you read a photocopied extract then highlight it to help you reread it for revision. If you make notes from a video tape make sure that the notes are headed with the name of the tape so that you know the source of your information ES1 ES2 ES3 ES4 ES5 ES6 ES7 ES8 ES9 ES10 ES11 ES12 ES13 ES14 ES15 ES16 ES17 Understanding Geology David Webster p 9-13 Geoscience Edwards and King p.21-31 Geological Science by Andrew McLeish p.115-128 Earthquakes HMSO booklet in Thordur Centre – extract on Richter and Mercalli scales Handout on earthquake focus and epicentre Sheet 5 Isoseismal map Video Seismology at Work. Tapes 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 13 Alaskan earthquake 4.5 mins - watch twice Activity sheets 7 and 8 on refraction and reflection of earthquake waves Activity 28 and 31 on travel time curves – Plotting the Epicentre Summary Table on Earth composition and structure Earth Story Programme 8 A World Apart 50 mins Library video and Tape 41 Structure of the Earth. New Scientist Feb 1988 Graph of Velocity/Depth curves Hutchinson R. and Graham A. Meteorites HMSO Library Video Meteorites Tape 18 10 mins Diagram to show paths of earthquake waves Skinner, B.J. and Porter, S.C., The Dynamic Earth Chap 15 Library Websites www.geolsoc.org.uk/ Go to Teaching Resources www.gsrg.nmh.ac.uk/ www.earthquake.usgs.gov/ www.iris.washington.edu/seismic/60_2040_1_8.html www.gps.caltech.edu/~polet/events90-96.html www.geo.arizona.edu/saso/Earthquakes/Recent/ There are many other websites you could search. ______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ VC/Dept/Geol/009 page 2 GEOLOGY STUDY GUIDE margin notes Module exam GL1 June 2005 TASK 1 EARTH’S STRUCTURE The earth has a layered structure of crust (two main types), mantle, outer and inner core, each layer having a distinctive thickness, composition, density and physical state. Write notes using your textbooks (ES 1, ES 2 and ES 3) about each layer in the earth. TASK 2 EVIDENCE USED TO DISCOVER ABOUT THE EARTH Discuss with your group about how scientists can find out about what is inside the earth. Draw a spider diagram or mindmap in your group to show your ideas. TASK 3 EARTHQUAKE SCALES You will have established that earthquake (or seismic) waves are the most important evidence used by scientists. Using ES 1 and ES 4 describe the two scales which measure the magnitude and the intensity of earthquakes. What are the main differences between the two scales? TASK 4 FOCUS, EPICENTRE AND ISOSEISMALS Using the handout ES 5 label the focus, epicentre and isoseismals. Check your textbooks for definitions of each to make sure that you know what they are. Use ES6 to draw the isoseismal map for an earth quake. TASK 5 EARTHQUAKE WAVES Find a way of demonstrating how P, S and L waves move through the earth. Write a note to yourself to remind you about the differences between the three types of waves. You can use diagrams, tables or a written account of each type of wave. Draw a seismograph to show arrival times of P, S and L waves at a seismometer station TASK 6 ALASKAN EARTHQUAKE 1964 Watch ES 7 twice. Comment on the earthquake’s origin and the effects it had. What was the magnitude and intensity of the Alaskan earthquake? Make further notes from ES 4 if you would like to find out more. TASK 7 Research a specific earthquake using any resources you can find. The internet has proved to be very popular in the past to find out about recent earthquakes but there are many books and videos in the Library to borrow. Find out about the magnitude and intensity of the earthquake and the effects it had. Maps and photographs help with your explanation Use this box for notes ______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ VC/Dept/Geol/009 page 3 GEOLOGY STUDY GUIDE Module exam GL1 June 2005 margin notes TASK 8 MOVEMENT OF WAVES THROUGH THE EARTH Waves can be reflected and refracted as they travel through the earth. Carry out Activities 7 and 8 on ES 8 to show how these processes work. TASK 9 VELOCITY/DENSITY CHANGES AND THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH Draw the graph from ES 3 p.123 which shows how velocity of P and S waves changes as waves pass into the centre of the earth. Summarise in bullet points what the graph tells you about P and S waves. Identify and label the Low Velocity Zone (LVZ) which is also known as the asthenosphere. Use ES13 to label layers within the Earth. TASK 10 Draw the graph from ES 3 p.124 which shows how density of each layer changes. On your graph label the main layers and discontinuities within the earth. TASK 11 DISCONTINUITIES Find the best definition of a discontinuity by checking through your textbooks. There are two main discontinuities within the earth, so identify which layers they separate and the changes in densities and composition which take place at the discontinuity. Label the discontinuities on the graph you drew for Task 9. TASK 12 WHAT EARTHQUAKE WAVES DO AS THEY TRAVEL THROUGH THE EARTH Use ES16, which shows how earthquake waves curve as they pass through the earth, and explain how the P and S wave shadow zones occur. Draw a full page version with plenty of space for explanations in your own words. Label your diagram fully, including each layer in the earth, the Mohorovicic and Gutenberg discontinuities, the importance of the epicentral angles and the two shadow zones. TASK 13 TRAVEL TIME CURVES – PLOTTING THE EPICENTRE Complete the exercise ES 9 Activity 28 and 31 on travel time curves. You will need a drawing compass to finish this accurately. TASK 14 METEORITES Meteorites have provided very valuable information on the composition of the earth. Read about them in your textbooks. Learn about the two main types – stony meteorites and iron meteorites - and what they tell us about the composition of the mantle and the core. Use this box for notes ______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ VC/Dept/Geol/009 page 4 GEOLOGY STUDY GUIDE Module exam GL1 June 2005 margin notes TASK 15 OTHER EVIDENCE FOR EARTH STRUCTURE Make notes on the evidence given by hot springs, mantle rocks at surface, deep bore holes, volcanoes, the earth’s magnetic field and meteorites. TASK 16 SUMMARY OF EARTH STRUCTURE Now fill in the table ES 10 which summarises the thickness, composition, nature and density of each layer. This table is a way of reminding yourself what you know about earth layers and what evidence geoscientists can use in the study of the earth. TASK 17 GLOSSARY This topic contains plenty of geological jargon. Here is a list of words that you need to be familiar with. Write out their definitions to help with your long-term learning. Isoseismals Asthenosphere continental lithosphere iron meteorites shadow zone refraction outer core Richter Scale oceanic lithosphere time-travel curves discontinuity mantle reflection epicentre Mercalli Scale focus stony meteorites Mohorovicic discontinuity epicentral angles inner core Gutenberg discontinuity TASK 18 SUMMARY NOTES You need to learn this topic now. Summary notes deadline…………………………………… Use this box for notes ______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ VC/Dept/Geol/009 page 5