Contemporary Perspectives (Chapter 1)
advertisement

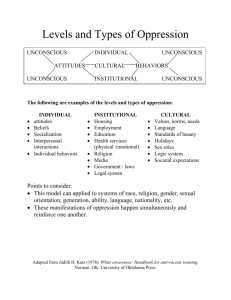
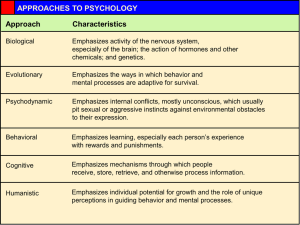
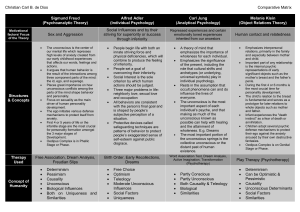
Contemporary Perspectives Today there are six main perspectives, or assumptions about the nature of human behavior and mental processes. BIOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE – Our mental processes are made possible by the nervous system, especially the brain. These psychologists look for the connections between events in the brain, such as the activity of brain cells, and behavior and mental processes. They are also interested in the influences of hormones and genes. COGNITIVE PERSPECTIVE – Emphasizes the role played by thoughts in determining behavior. Mental processes are studied in order to understand human nature. They investigate the ways in which people perceive information and make mental images of the world, solve problems, and dream and daydream. Information processing is compared to computer science. People’s behavior is influenced by their values, their interpretations, and their choices. HUMANISTIC PERSPECTIVE – Stresses the human capacity for self-fulfillment and the importance of consciousness, self-awareness, and the capacity to make choices. Consciousness shapes people’s personalities. Personal experience is the most important aspect of psychology. We are free to choose our own behavior, don’t act upon stimuli. People are basically good and helpful to others. PSYCHOANALYTIC PERSPECTIVE – Stresses the influence of unconscious forces on human behavior. Focus less today on unconscious sexual and aggressive impulses and more on conscious choices and self-direction. LEARNING PERSPECTIVE – Emphasizes the effects of experience on behavior. Learning is the essential factor in observing, describing, explaining, predicting, and controlling behavior. Behavior is learned either from direct experience or by observing other people. SOCIOCULTURAL PERSPECTIVE – Addresses such issues as ethnicity, gender, culture, and socio-economic status. These factors have a significant impact on human behavior and mental processes.