FileName
advertisement
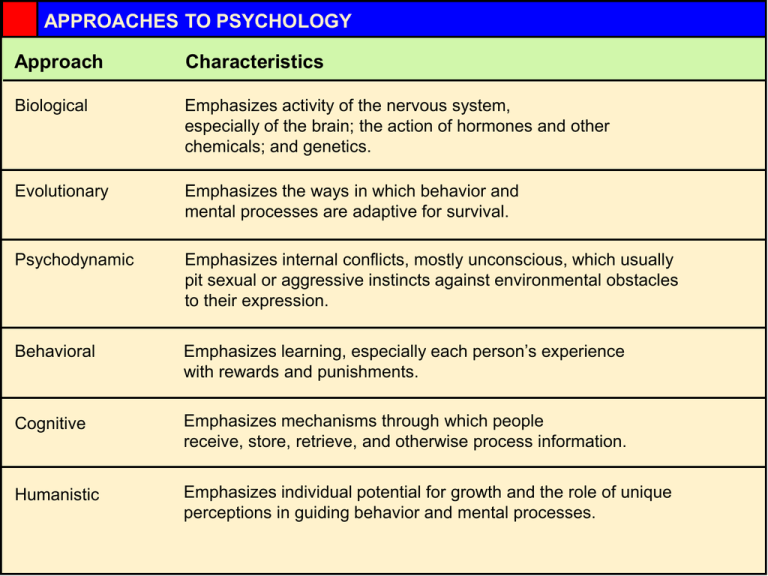
InRev1 APPROACHES TO PSYCHOLOGY Approach Characteristics Biological Emphasizes activity of the nervous system, especially of the brain; the action of hormones and other chemicals; and genetics. Evolutionary Emphasizes the ways in which behavior and mental processes are adaptive for survival. Psychodynamic Emphasizes internal conflicts, mostly unconscious, which usually pit sexual or aggressive instincts against environmental obstacles to their expression. Behavioral Emphasizes learning, especially each person’s experience with rewards and punishments. Cognitive Emphasizes mechanisms through which people receive, store, retrieve, and otherwise process information. Humanistic Emphasizes individual potential for growth and the role of unique perceptions in guiding behavior and mental processes. L1 LINKAGES to Introducing Psychology PERCEPTION Can subliminal messages help you lose weight (p.141) TREATMENT OF PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS Does psychotherapy work? (p. 582) SOCIAL INFLUENCE What makes some people so aggresive? (p. 647) Tab1_2 Variable Individualist Collectivist Personal identity Separate from others Connected to others Major goals Self-defined; be unique; realize your personal potential; compete with others Defined by others; belong; occupy your proper place; meet your obligations to others; be like others Criteria for self-esteem Ability to express unique aspects of the self; be self-assured Ability to restrain the self and be part of a social unit; be self- effacing Sources of success and failure Success comes from personal effort, failure from external factors Success due to help from others; failure due to personal faults Major frame of reference Personal attitudes, traits, and goals Family, work group











