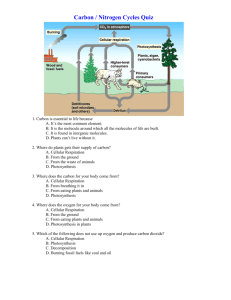
b) CAGCGATCGCTT e) Val-Ser-Arg-Ala-Leu
advertisement

BIOL 1114 EXAM 3 (No Star Form) 19 November 2001 Use a # 2 pencil to fill in the information portion of your NCS answer sheet including the appropriate circles (bubbles). Write “No Star” on the back of your NCS answer sheet. Read all questions and answers carefully before choosing the single BEST response for each question. Feel free to ask the instructor for clarification. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- --------------Use this information to answer QUESTIONS 1-9. Jake is considering getting a flu shot. The vaccine available in fall 2001 is designed to protect a person against 3 different strains of flu virus. This is possible because it contains three kinds of killed (dead) virus. A vaccine against any one of these viruses does not give protection against either of the others. Jake is afraid that getting a flu shot will “give him the flu” (that he will become ill with the flu from being injected with the vaccine). 1. You correctly tell Jake that he is _______________. a) right; the virus will multiply in his body and make him sick. b) wrong; the virus in the vaccine will multiply in his body, but his antibodies will protect him from illness. c) right; if he encounters someone else with the flu, the vaccine will have weakened him and he will become ill. d) wrong; the dead virus from the vaccine cannot multiply in his body. e) right; the vaccine contains antibodies to the virus, antibodies that will cause him to become ill with the flu. 2. The vaccine against flu contains ______________. a) at least three different antigens c) one antibody b) at least three different antibodies d) two different antigens e) only one antigen 3. If Jake gets a flu shot, his B cells (lymphocytes) will ____________. a) multiply and many of them will develop extensive rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) b) be killed and therefore he will become ill with flu c) multiply by mitosis when activated d) be activated and multiply by meiosis e) (a) and (c) will occur 4. Cueball grew up in Borneo (not in OK) as part of a wild dog population that was growing exponentially. Parvo (a virus that can kill dogs) was introduced into this population when an infected dog was dropped out of a car in rural Borneo by some young women who were moving to Scotland. You would correctly predict that growth of the wild dog population after the arrival of Parvo would ____________________. a) remain exponential (J-shaped) d) (a) and (c) would occur b) be affected by the introduction of Parvo e) (b) and (c) would occur c) become logistic (S-shaped) 5. Cueball survived infection with Parvo and immigrated to the US with Jake. He was exposed to Parvo again in Stillwater OK as an adult. You would correctly predict that Cueball’s B cells_____ when he was exposed to Parvo in OK. a) rapidly produced antibodies to Parvo d) reproduced rapidly by mitosis b) produced many ribosomes e) all of these (a-d) would occur c) secreted (released) proteins by exocytosis 6. Jake thinks Cueball is handsome because his head is almost spherical and his coat is an unusual yellowish shade of white. The yellowish pigment is produced with the aid of a rare enzyme. A portion of the dominant allele which codes for this enzyme contains the DNA sequence A-T-G-C-T-A. The complementary DNA sequence would be __________. a) A-T-G-C-T-A b) T-A-C-G-A-T c) T-U-C-G-U-T d) U-T-C-G-T-A e) C-G-A-T-G-C 7. The result of transcription of A-T-G-C-T-A would be a strand with the sequence _______. a) C-G-A-T-G-C b) A-T-G-C-T-A c) T-A-C-G-A-T d) T-U-C-G-U-T e) U-A-C-G-A-U 8. What is the correct translation product of the sequence G-U-C-G-C-U-A-G-C-G-A-A? [See table on last page.] a) G-T-C-G-C-T-A-G-C-G-A-A d) Val-Ala-Ser-Glu b) C-A-G-C-G-A-T-C-G-C-T-T e) Val-Ser-Arg-Ala-Leu c) Gln-Arg-Ser-Leu 9. Jake’s friend Bass is so impressed with Cueball that he brings a female survivor of the Borneo Parvo epidemic to Stillwater. Bunny (Bass’s dog) looks just like a female version of Cueball, and Jake and Bass decide to start a Stillwater population of these unusual dogs. Bunny and Cueball’s first litter has 6 yellowish-white pups and 2 pure white pups. You correctly predict that ___________. a) both dogs are homozygous for the pure white allele b) Cueball is homozygous for the pure white allele and Bunny is heterozygous c) both dogs are homozygous for the yellowish white allele d) both dogs are heterozygous e) Bunny is homozygous for the pure white allele and Cueball is heterozygous _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Use the following information for QUESTIONS 10-14. When silk moths (Hyalophora cecropia) are wounded or injected with some types of bacteria, the moths produce small proteins, called cecropins, that kill bacteria. Cecropins act by making holes in bacterial cell membranes, so that they become leaky to molecules and ions. Bacteria function much like mitochondria in eukaryotic (plant and animal) cells. 10. You would correctly predict which one or more of the following lethal effects of cecropins on bacteria. a) Cecropins cause bacteria to mutate so they no longer need membranes. b) Bacterial mitochondria would be unable to conduct photosynthesis. c) Leaky membranes would prevent bacteria from getting oxygen (O 2) for respiration. d) Bacteria would be unable to make ATP by chemiosmosis. e) All of these (a-d). 11. Some other species of insects besides silk moths also produce proteins similar (but not identical) to cecropins. This is best explained by ____________. a) founder effect b) mitosis c) mutations d) crossing over e) both (a) and (b) 12. Suppose that silk moths have the potential to produce two types of cecropins, called cecropin-R and cecropin-S, both coded by the same gene. When a homozygous cecropin-R male moth is mated with a homozygous cecropin-S female, all 70 of the offspring produce both types of cecropins when wounded. This genetic situation is an example of ________. a) natural selection b) complete dominance c) sex linkage d) mitosis e) codominance 13. One of the female offspring in the previous question that can produce both cecropin-R and cecropin-S is mated with a male moth of unknown cecropin type. Their offspring are as follows: 23 moths that produce only cecropin-R and 25 moths that produce both cecropin-R and cecropin-S. None of the offspring produces cecropin-S only. The unknown male parent moth must produce ___________. a) cecropin-S only b) cecropin-R only c) neither cecropin-R nor cecropin-S d) cecropin-R and cecropin-S 14. In natural populations of silk moths, some individual moths can only produce cecropin-R, whereas other individuals can only produce cecropin-S, and still others produce both types of cecropins when wounded. This situation is best explained by which one or more of the following? a) Two alleles of the cecropin gene are present in the population. b) Individual moths are infected by different types of bacteria. c) Silk moths are diploid. d) Some moths are smarter than others. e) Both (a) and (c). _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 15. As a child, Mortimer had the mumps. Mortimer is now 50 years old and is immune to this disease. Which one of the following is the best hypothesis to explain this observation? a) The mumps pathogen can no longer invade his body. b) Mortimer possesses memory cells specific to the mumps due to his previous infection. c) Mortimer produces more macrophages at age 50 than he did as a child. d) Mortimer's DNA mutated due to his previous infection. 16. The evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria is due to which one or more of the following? a) The antibiotic causes mutations in the bacteria. b) Natural selection works on the bacteria population. c) Chance mutations occur in the DNA of the bacteria. d) Natural selection causes mutations in the bacteria. e) Both (b) and (c). 17. Streptomycin is a commonly used antibiotic that inhibits protein synthesis in bacteria. You would correctly hypothesize that the antibiotic targets which one of the following organelles? a) ribosomes b) smooth endoplasmic reticulum c) chloroplast d) mitochondria e) Golgi body _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Use this information to answer QUESTIONS 18-21. Elvis was bored and wanted something to liven up his Graceland Mansion. He went to the local pet store and bought an aquarium with all the appropriate accessories. He also purchased 12 female Neon tetras (a type of fish) and 8 male Neon tetras. Because money was no object and he wanted the fish to have lots of space he bought a 4 cubic foot aquarium. After one year Elvis counted all the fish in his tank and found that there were 160 Neon tetras in the tank. 18. Neon tetra population density in Elvis' aquarium at the end of one year was _________. a) 160 neons/cubic foot b) 40 neons/cubic foot c) 40 neons/ 4 cubic feet d) 40 neons e) 80 neons/cubic foot 19. The population growth rate (r) of the fish population for the year was _______. a) 7 neons b) 140 neons/neon/year c) 160 neons d) 160 neons/neon/year e) 7 neons/neon/year 20. The population growth increment (G) of the fish population for the year was ________. a) 160 neons b) 160 neons/neon/year c) 140 neons d) 140 neons/neon/year e) 70 neons/neon/year 21. During the next year, Elvis noticed that 200 neons were born and 40 died. The neon population size (N) at the end of the 2nd year was ______. a) 160 neons/neon/year b) 160 neons c) 180 neons d) 280 neons e) 320 neons _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Use this information for QUESTIONS 22-23. A scientist discovers a flask with unknown contents in her lab. After some intitial tests, she discovers it contains sugar (deoxyribose), phosphate, and nitrogen-containing bases. Further testing reveals that the following nitrogen-containing bases are present: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). Adenine makes up 22% of the bases found in the flask. 22. The scientist correctly hypothesizes that the flask contains ____________. a) ribosomes b) RNA c) DNA d) amino acids only e) protein only 23. Knowing the adenine content, the scientist correctly predicts which one or more of the following proportions of the other nitrogen-containing bases? a) guanine 22% b) thymine 22% c) cytosine 28% d) thymine 78% e) both (b) and (c) are correct predictions _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 24. If a human red blood cell is placed in a solution that contains more salt than found inside the red blood cell, what would happen to the cell? a) Water moves out of the cell by osmosis, the cell swells. b) Water moves into the cell by osmosis, and the cell shrinks. c) Water moves out of the cell by osmosis, and the cell shrinks. d) Water moves into the cell by osmosis, and the cell swells. e) Water moves in and out of the cell at the same rate, and the cell stays the same size, but it smells like a pickle. 25. Which one or more of the following is/are product(s) of the light independent reactions of photosynthesis (the Calvin cycle)? a) glucose b) carbon dioxide c) NADPH d) oxygen e) all of these (a-d) 26. In the mid 1850s a small number of rabbits were introduced into Australia. For at least 10 generations, the rabbits had virtually no predators, parasites, or competition for food and space. There were abundant food sources for rabbits in this part of Australia. You would correctly predict, given these circumstances, that during the first 11 generations after their introduction the rabbit population would most closely resemble which one of the following? 600 6000 a b 500 Population size Population size 5000 4000 3000 2000 400 300 200 100 1000 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 10 11 2 3 4 Generation 600 6 7 8 9 10 11 8 9 10 11 120 d c 100 Population size 500 Population size 5 Generation 400 300 200 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Generation 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Generation 300 e Population size 250 200 150 100 50 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Generation 27. You are doing a 4-year study of field mice on a two-acre field adjacent to Uncle Sneed’s moonshine factory. During year 4 of the study, a hawk begins to feed upon the mice in your study area and the growth rate of the mouse population declines and stabilizes. You would correctly describe this type of population control as __________. a) herbivory b) carnal c) density supplemental d) density independent e) density dependent 28. A year later, you visit Uncle Sneed and discover that his moonshine factory had exploded, setting fire and devastating the adjacent field you had used as a study site. Uncle Sneed said that there were only about half the mice in the field as there used to be and you correctly explain to him that the fire was a kind of ________________ population control. a) anti-climatic b) climatic c) density independent d) density dependent e) density supplemental 29. In somes cases, if you know the phenotype of an organism, you also know the genotype. In which one or more of the following situations would that be true? a) A person without cystic fibrosis. d) A person with type A blood. b) A person with type AB blood. e) In both (b) and (c) phenotype would predict the genotype. c) A person with cystic fibrosis. 30. In prokaryotes (bacteria), transcription takes place in the __________ and translation takes place in the ___________. a) nucleus, nucleus d) nucleus, Golgi bodies b) cytoplasm, cytoplasm e) ribosome, nucleus c) nucleus, cytoplasm 31. Eukaryotic cells are on average, much larger than prokaryotic cells. Which, on average, has the greater surface area to volume (SA/V) ratio? a) prokaryotic cells b) eukaryotic cells c) They have the same SA/V, which has nothing to do with size. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Use this information for QUESTIONS 32-36. The potato is a very important plant that provides us with carbohydrates in the form of starch (starch is a long molecule made up of subunits of the sugar glucose that is formed in photosynthesis). The starch accumulates in a storage organ called a tuber (a spud). Each plant develops many large tubers underground from a stem and there are many buds on each tuber. The potato crop is propagated (reproduced) asexually. One tuber is cut into many small pieces that are put in the soil. Each piece grows into a new plant that later will develop many large tubers. The potato plant is native to South America and it was introduced to Ireland. By 1840 the nutrition of the Irish population was completely dependent on potatoes. From 1843-1848, all the Irish potato crop was destroyed by a disease caused by a fungus. The famine forced many Irish people to emigrate and many of them came to the USA. 32. As a potato plant develops new leaves, stems and roots, new growth is added as cells ____________. a) divide by meiosis d) divide alternately by meiosis followed by mitosis b) divide by mitosis e) (a), (b) and (d) contribute equally to the new growth. c) gain weight (but do not divide) 33. On a cool cloudy day, _______ starch will accumulate in the tuber because ___________ on a warm sunny day. a) less, respiration rate is faster than d) less, photosynthesis rate is slower than b) more, respiration rate is faster than e) less, respiration rate does not occur c) more, respiration does not occur 34. The origin of the carbon in the starch in the tuber is_____________ and the source of carbon in CO 2 released by the plant cells is_____________. a) atmospheric CO2 fixed in respiration, starch converted to glucose and used in photosynthesis b) atmospheric CO2 produced in photosynthesis, breakdown of ATP in respiration c) atmospheric CO2 fixed in photosynthesis, starch converted to glucose and used in respiration d) atmospheric CO2 fixed in respiration, breakdown of ATP in photosynthesis e) (b) in the day (light) and (d) in the dark (night) 35. Why was the entire potato crop so vulnerable to the fungal disease? a) The fungus was more efficient than the plant at using CO2 in photosynthesis. b) The fungus was more efficient than the plant at using CO2 in respiration. c) The crop was genetically very diverse because it was propagated asexually. d) The crop was genetically uniform because it was propagated asexually. e) The Irish farmers had very little experience in cultivation of potato plants. 36. When a potato plant is propagated asexually, _______________. a) all the daughter plants are genetically identical to the parent plant. b) half of the daughter plants are genetically identical to the parent plant and half of them have a new genetic make up. c) three quarters of the daughter plants are genetically identical to the parent plant and one quarter of them have a new genetic make up. d) none of the daughter plants is genetically identical to the parent plant. e) all the daughter plants are genetically identical to the parent plant but they have half of the chromosome number as compare to the parent plant. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Use this information for QUESTIONS 37-38. A man and his wife both have normal skin pigmentation. But both had one parent who was an albino. Albinism is autosomal recessive and results in complete lack of skin pigmentation. 37. If they have two children with normal pigmentation, what is the chance that their third child will be an albino? a) 0% b) 25% c) 50% d) 75% e) 100% 38. What is the probability that their fourth child will have a homozygous genotype? a) 100% b) 75% c) 50% d) 25% e) 0% _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 39. Ichthyosis is an X-linked recessive trait. Which one of the following is a correct prediction concerning a cross between a normal male and a female that is homozygous for the ichthyosis allele? a) Both sons and daughters will have the disease in equal proportions. b) All daughters will have the disease. c) All sons will have the disease. d) Both sons and daughters will have the disease, but the disease will occur in a higher percentage of sons than daughters. e) All offspring will be normal. 40. Given: a mother with type AB blood and her child with type AB blood. Which of the following blood types would a man need to have to EXCLUDE him as a possible father of this child? a) type B b) type A c) type O d) type AB _____________________________________________________________________________________________