Dynamic Planet
advertisement

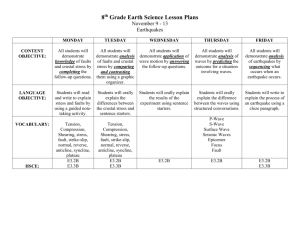
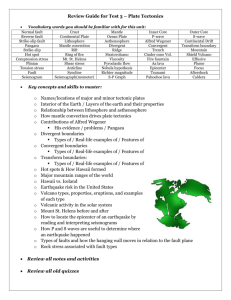
Dynamic Planet Multiple Choice Quiz 1 1 The zone of the earth that is divided into rigid plates is the ____________. A) atmosphere B) lithosphere C) tectosphere D) biosphere E) asthenosphere F) hydrosphere 2 The collision zones between two continental masses are typically marked by ___________________. A) volcanoes B) mountain belts and thrust faults C) earthquakes with small, nondestructive earthquakes D) rift valleys E) transform faults 3 You have just heard a report on the radio of a series of very destructive earthquakes that occurred from 5 to 150 kilometers below the surface of the Earth and affected an area 1000 kilometers long and several hundred kilometers wide. At what type of tectonic boundary did these earthquakes most likely occur? A) transform boundary B) subduction zone C) spreading zone D) triple junction E) continent-continent collision 4 Subduction zones are commonly marked by ________________. A) chains of volcanoes B) an inclined plane, extending hundreds of kilometers into the Earth, of earthquake locations C) a deep ocean trench D) answers A and B E) answers A, B, and C 5 Uniformitarianism is A) B) C) D) the idea that the layers of the Earth are exactly the same thickness everywhere on Earth. the idea that the earth has changed through small gradual processes occurring over very long times. the idea that the same processes occur on the Earth's surface as on every other planet. the idea that the earth is exactly the same as it was when it was first formed. 6 A geologist in the 1997 movie Volcano states that, "continents sit on tectonic plates, great big rafts floating over an ocean of molten rock." What is wrong with this statement? A) The mantle beneath the plates is solid rock except for the weaker, partially melted asthenosphere. B) The mantle everywhere beneath the plates is strong, rigid rock. C) The entire mantle beneath the plates is weak and "plastic-like" due to partial melting. D) The mantle beneath the plates is made of large pockets of solid, rigid rock and molten magma. E) The mantle beneath the plates contains magma and large pockets of water enclosed in solid rock. 7 In the concept of plate tectonics the term "plates" refers to the ________________. A) continental crust B) crust and the entire mantle C) rigid Earth above the asthenosphere D) oceanic crust E) Earth from the surface to the base of the asthenosphere 8 The theory of plate tectonics states that rigid "plates" are driven by forces within the Earth and interact by ___________________. A) colliding with each other B) pulling apart from each other C) sliding past each other D) A and B E) answers A, B, and C 9 When two tectonic plates diverge (pull apart) the Earth is thinned. In this scenario, considering the concept of isostasy, we can predict that the asthenosphere will ________________. A) rise B) sink C) rise then sink D) sink then rise E) undergo no change 10 Evidence that supports the concept of sea-floor spreading includes _______________. A) the chains of volcanoes at zones of spreading B) magnetic polarity reversal patterns C) the fit of continental margins D) the ages of volcanic rocks in ocean basins E) all of the above 11 Most of the earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain belts of the Earth occur _______________. A) within tectonic plates far from their edges B) in ocean basins C) at the edges of tectonic plates D) at zones where tectonic plates slide horizontally past each other E) above hot spots 12 If you were interested in studying the record of sediments and fossils in the ocean over the greatest period of time the most complete record would be found _________________. A) at the mid-ocean ridge B) at the margins of oceans C) between the ocean ridges and margins of the oceans D) at hot spots E) at any point on the ocean floor 13 The mechanisms that drive plate tectonic motion are ________________. A) gravitational push on oceanic crust from the topographically high mid-ocean ridges B) convective flow of heat in the mantle C) gravitational pull of oceanic crust in subduction zones D) all of the above 14 If there are no subduction zones at the margins of an ocean basin then the basin will most likely _____________. A) stay the same size B) become smaller C) become larger D) become larger and then smaller E) become smaller and then larger 15 Los Angeles is located on the Pacific Plate. San Francisco lies on the North American Plate and is about 600 kilometers north of Los Angeles. The Pacific Plate is moving north relative to the North American Plate along the San Andreas fault zone. If it takes 10.7 million years before Los Angeles and San Francisco become neighbors what is the rate of tectonic movement along the San Andreas? A) 560 millimeters per year B) 5.6 millimeters per year C) 5.6 kilometers per year D) 56 kilometers per million years E) 56 meters per year 16 The lithosphere is broken into rigid plates that move from, past, and into other rigid plates. The numerous cracks in the Earth that are common along the boundaries of plates are known as ______________. A) faults B) transform zones C) collision zones D) breaks E) slices 17 The Lisbon earthquake of 1755 caused damage to the city by _____________. A) volcanic eruptions B) collapse of buildings C) fires D) quake-related sea waves E) all of the above except answer A Part 2 1 Which of the following disasters would you most likely experience in San Francisco? A) earthquakes due to movement along faults B) meteorite impact C) nuclear explosion D) undersea landslides E) volcanic activity 2 Earthquakes that occur along faults are created when __________________. A) melted rock is erupted along the fault zone B) water is squeezed out of rock and released along the fault C) stress builds up until rocks break D) the earth shifts and moves along fractures E) answers C and D 3 The type of energy that shakes the Earth during an earthquake is produced by __________________. A) gravitational attraction B) density variations C) shock waves D) heat E) solar energy 4 Which of the following might provide evidence that a fault zone exists in an area? A) Lines or lineaments on the surface of the Earth as seen from above the zone. B) Streams that are offset or end abruptly. C) Tilted layers of rock that were originally horizontal. D) Offset rock layers. E) all of the above 5 A fault is a fracture plane that extends into the Earth. If the footwall of an inclined fault moves down relative to the hangingwall then the fault type is a ___________________. A) strike-slip fault B) normal fault C) reverse fault D) abnormal fault E) transform fault 6 If the hangingwall of an inclined fault moves down relative to the footwall then the fault type is a ________________. A) strike-slip fault B) normal fault C) reverse fault D) abnormal fault E) transform fault 7 You are hiking east across a sequence of rock layers that are tilted 45° to the east. At some point you cross a small linear depression and notice that there is a repetition of the layers that you just walked over. This repetition of rock layers provides evidence that you have crossed a ________________. A) strike-slip fault B) normal fault C) reverse fault D) abnormal fault E) transform fault 8 The most common types of faults in an area being pulled apart between two tectonic plates are ___________________. A) left-lateral strike-slip faults B) right-lateral strike slip faults C) reverse faults D) normal faults E) horsetail faults 9 The most common types of faults in an area being pushed together between two tectonic plates are _____________________. A) left-lateral strike-slip faults B) right-lateral strike slip faults C) reverse faults D) normal fault E) horsetail faults 10 There is a common misconception that someday part of California will sink into the ocean and disappear. With your knowledge of the San Andreas fault zone and plate tectonics you can argue that this will not occur because ___________________. A) the dominant movement on the San Andreas is reverse and part of California will move further inland B) the dominant movement on the San Andreas is left-lateral strike slip and the part of California west of the fault zone will move further south towards Mexico C) the San Andreas is a normal fault that dips to the east so all of the land east of fault zone will move down D) the dominant movement on the San Andreas is right-lateral strike slip but movement on the fault has ceased E) the dominant movement on the San Andreas is right-lateral strike slip and the part of California west of the fault zone will move further north, but it can not sink. 11 The point at which a fault first ruptures in the Earth is called the ______________. A) hypocenter B) hypicenter C) hypercenter D) epicenter E) typocenter 12 Which of the following is not true for P waves? A) They have a push-pull or compression-extension motion. B) They have the greatest velocity of all seismic waves. C) They can move through solids, liquids, and gases. D) They are called primary waves. E) Their velocity depends only on the density and resistance to shearing of materials. 13 If body waves pass from a less dense material into a more dense material the velocity of the waves will _____________________. A) remain the same B) decrease C) decrease and then increase D) increase and then decrease E) increase 14 Which of the following is true for S waves? A) They move by shaking the earth at right angles to the direction of advance. B) They arrive at seismic stations later than P waves. C) They can move only through solids. D) They are called secondary waves. E) all of the above 15 Evidence that supports the hypothesis that the asthenosphere is a weak zone due to small amounts of melting is that the velocity of S waves ____________ as they travel through this zone in the mantle. A) remains the same B) decreases C) decreases to zero D) decreases and then increases E) increases 16 Which of the following is not true for Rayleigh waves? A) They advance in backward-rotating elliptical motion. B) They only have a horizontal movement. C) They would make you feel as if you were riding a wave as they pass. D) They generally have lower velocities relative to body waves. E) They can pass through both ground and water. 17 The Mercalli intensity is useful because A) it is the only method of assessing the energy of an earthquake. B) it allows us to assess the magnitude of historical earthquakes for which there are no instrumented records, and thus estimate recurrence intervals for major earthquakes. C) it helps determine the magnitude of small or distant earthquakes for which the Richter scale is inadequate D) it predicts the next major earthquake.