introduction for clinical attachment in child health nhs fife
advertisement

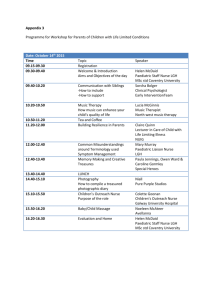
INTRODUCTION FOR CLINICAL ATTACHMENT IN CHILD HEALTH NHS FIFE Welcome to the NHS Fife’s Paediatric & Child Health Department. We hope that you enjoy your time with us. The Paediatric Department in Victoria Hospital delivers acute secondary care to the children of Fife. We have recently moved into our new facilities in phase 3 building of Victoria Hospital. The Department is divided into 3 clinical areas: 1. Children’s ward: The main in-patient bit receiving all Acute Paediatric Medical, Surgical and Orthopaedic admissions. It admits children from 10 days of age up to 16 years of age. It has 26 beds including a 3 bedded High dependency unit. 2. Neonatal intensive care unit: This is a level 2 unit which admits infants from 23 weeks gestational age and has 20 beds including 6 spaces set up for ventilation. 3. Children’s Ambulatory care unit: This area acts like a day bed area were children maybe admitted for minor surgeries including ENT procedures and lengthy endocrinological investigations like glucose tolerance testing. There are 8 beds and also incorporates all outpatient clinics. In addition out-patient clinics are also delivered from Queen Margaret Hospital in Dunfermline. We also work very closely with our colleagues in Community Child Health. The Paediatric Department is staffed by a team of consultants, specialists, specialty trainees, general practice trainees and nurse specialists. Each member of the team will provide valuable teaching opportunities for you. We are also exceptionally lucky to have expert dietetic support from Alison McLoed and her team of Paediatric dieticians as well psychology input from Dr Hillary Maddox and Dr Shona Murphy. As your site Educational Supervisor I will have overall responsibility in coordinating the delivery of the curriculum here. I will meet you on the first day of your block here in Kirkcaldy. As you will normally be attending tutorials in Dundee on the first Monday of your block, this will take place on Tuesday afternoon between 14:00 & 15:30. Normally this will be in the “Meeting room” (otherwise called the green room) on the children’s ward. This will also give you the opportunity to meet with Karen Hogg in the morning and complete formalities. As the Medical Education Services Admin Assistant, Karen (or one of her colleagues in her absence) will be able to sort out your ID cards, accommodation and provide a brief induction to NHS Fife. I can be contacted through the internal DECT phone system on extension 29730 or alternatively by e-mailing kaniruddhan@nhs.net . My secretary Ann Kinnell can be contacted on 28225. TEACHING PROGRAMME The teaching sessions are broadly divided into bedside teaching and tutorials. Besides these you will also be expected to attend scheduled departmental teaching. In general bedside teaching will be delivered by both consultants and medical specialist registrars. This will concentrate on basic medical skills of history taking and examination. In the first week of your child health block you should shadow the Children’s ward and neonatal teams. You will be divided into two groups and allocated to one of these two areas: Children’s ward Neonatal unit Tuesday, Wednesday Group 1 Group 2 Thursday, Friday Group 2 Group 1 You should use these days to observe specialist registrars and consultants taking histories and examining patients. From the second week onwards you will be allocated to one of the following clinical areas: 1. 2. 3. Children’s ward Neonatal unit Out-patient clinics You will spend a full week in each of these areas rotating in turn to next area the following week. Whilst on the children’s ward you will also be expected to undertake long shifts until 21:30 on 2 of the days. Paediatric Student Teaching Timetable, updated April 2013 Time Monday Tuesday 8:30 – 10 am Ward1 8:30 -10 am NNU Paediatric Neonatal AM Grand Round Grand Round Assessment Room 1or2 Wednesday Thursday 8:30 – 9 am 8:30 – 9 am Paediatric teaching by Ward Consultant Paediatric teaching by Ward Registrar Ward Doctors Office Ward Doctors Office Friday 8:30 -9am Neonatal Teaching, NNU Doctors Office Dr Morrice an hour anytime between 12-14 Dr Thanoon Cardiovascular Ex Abdominal Ex 2 MiniCEx 2 MiniCEx (Arlyne 21253) Children’s Ward (Karen 28828) Dr Aniruddhan Dr Ainine Ward teaching 2 Students ppt presentns 2.30-3.30 pm Education Centre Respiratory, 2 MiniCEx 2 – 3:30 pm (Ann 28225) (Arlyne 21253) Dr Humphreys Departmental teaching Education Centre Education Centre, Private study PM 4-5 pm Lecture Theatre (Susan 21733) 3:30 - 5 pm Please confirm with the Teaching Doctors the day before. Or with the secretaries (numbers in (Name xxxxx)) in the morning of your tutorial to see whether the teaching is happening or not (annual, study or sick leave…etc.) Some of these tutorials maybe cancelled or rearranged due to the nominated facilitator being unavailable. Please check with your named tutor or their secretary on the day before if the scheduled teaching will go ahead as planned. Departmental Teaching Timetable: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 08:30-10:00 08:30-10:00 08:30-09:00 08:30-09:00 08:30-09:00 Paediatric Grand Round Neonatal Grand Round Consultant led teaching Registrar led Paediatric teaching Registrar led Neonatal teaching 13:00-14:00 15:00-17:00 Journal club Plenary sessions Educational Supervisor Meetings: As your site Educational Supervisor, I will meet with you for one hour each week. These meetings will take place in the children’s ward between 10:00 and 11:00AM on Fridays. In my absence I shall nominate a replacement to sit in on these meetings. The aim of these meetings is to identify learning objectives and discuss what help you might need to achieve them. At these weekly meetings you will be expected to complete two assessments each of case based discussion (CBD) and clinical skills (mini CEX). In addition I will also advise you of interesting cases and events in the hospital. These will serve as a starting point for discussions on broader scientific, clinical and ethical aspects of any problem and help you to determine what you need to learn. Assessment: Final assessment for this block will be undertaken on the last Thursday of your block between 14:30 & 15:30. You will be required to present a case that you have seen, clerked-in and examined. It should be in the format along the lines of a typical ward round bedside presentation. 10 minutes will be allocated per presentation and over a further 5 minutes you will be required to answer questions on aspects of the case. Use of PowerPoint or other media is not permitted for these presentations. Marking scheme will be: A B C Outstanding/ well above standard expected of a 4 th year Student Achieving standards expected Expected standard not achieved In addition an outcome assessment sheet will also be completed. Whilst completing this I will take into account your overall attendance and performance during this block. This will also reflect the comments and views of other members of the Paediatric team who have seen you in action. Learning objectives: By the end of this attachment, students should be equipped with knowledge about health and disease in children, gain competence in clinical skills in assessing children and applying knowledge and skills to suggest provisional diagnosis and management plans. 1. Key clinical skills a. Recognise the seriously ill child and know how to take immediate action. b. Take a history appropriate to acute and chronic illness c. Elicit normal and abnormal physical signs to reach a provisional diagnosis d. ENT examination e. Have a general knowledge of normal variations in child and adolescent behavior f. Have a good knowledge of normal child development including psychological, social and sexual development g. Formulate a management plan using where appropriate other sources of information, critically appraising evidence from literature. h. Give advice to parents 2. Knowledge base: a. Health promotion i. Schedule of immunisation and provide advice on its benefits ii. Child protection framework iii. Screening principles and application in paediatrics iv. Infant nutrition and feeding 1. Breast feeding 2. Weaning 3. Use of growth charts and interpret its results 4. Obesity b. Neonatal problems: i. Carry out a routine newborn baby examination ii. Recognize common newborn problems 1. Jaundice 2. Respiratory distress 3. Irritability 4. Cyanosis iii. Identifying common congenital abnormalities and discuss the process of informing family of sensitive diagnosis c. Respiratory disease i. Common causes of cough, noisy breathing and breathlessness ii. Diagnosis and management of asthma in school age child iii. Instruct children and parents on use of inhaler devices iv. Recognition of the patterns of presentations of cystic fibrosis d. Cardiovascular disease i. Causes of murmurs in children ii. Recognising congestive heart failure and its causes iii. Recognising cyanotic heart disease iv. Modalities of investigating congenital heart disease in infants e. f. g. h. i. j. k. GI i. Common causes, investigation and management of vomiting ii. Common causes, investigation and management of acute and chronic diarrhea iii. Common causes, investigation and management of constipation iv. Common causes, investigation and management of abdominal pain Renal i. Collecting and interpreting results of urine samples in children ii. Common causes of haematuria (including HSP) iii. Investigating urinary tract infections iv. Enueresis Neurology i. Fits, faints and funny turns: taking history and interpreting information obtained ii. Advising parents on emergency management of seizures iii. Advising parents on prevention and management of febrile convulsions iv. Role of various modalities of investigations: EEG/Imaging v. Recognise the signs of raised intracranial pressure vi. Gait disorders vii. Contribution of different members of a multi-disciplinary team in managing a child with complex needs Haematological conditions i. Anaemia in infancy ii. Bruising & clotting disorders iii. Lymphadenopathy Metabolic disease i. Presentation and diagnosis of Diabetes management ii. Principles of treatment: dietary and insulin iii. Presentations of inborn errors of metabolism Limping child i. Common causes of limping child ii. Initiating and interpreting investigations for child with musculoskeletal pain Infectious diseases i. Meningitis ii. Sepsis iii. Common exanthematous diseases iv. Suspecting immunodeficiency Paediatric team- Medical staff: Name Specialty Sean Ainsworth Neonatologist and clinical lead for paediatrics Ahmad Ainine Diabetes and endocrine, Undergraduate supervisor for University of Edinburgh Krishnan Aniruddhan Respiratory medicine, Undergraduate Supervisor for University of Dundee Aysell Crokett Clinical lead for child protection Norbert Dahlinger Neonatologist Robert Humphreys Orthopaedics Mohammed Khalil Neonatology Evelyn Menzies Renal, constipation John Morrice GI, obesity Louisa Pietersie Allergy Laura Stewart Neonatology Chris Steer Epilepsy, neurology and behavioral disorders Manal Thanoon Neonatology & Cardiology Phone Secretary 29730 28225 28225 Paediatric team- Nursing: Name Speciality Lana Clacher Coordinator for paediatric division Joyce McFarlane Neonatal unit coordinator Jenna Arnott Neonatal unit coordinator Sharon Lappin Children’s ward coordinator Fiona Burt Children’s ward coordinator Anne Mckean Asthma nurse specialist Lyndsey Pert ADHD nurse specialist Sarah Smith CF nurse specialist Angela Toruntay Endocrine nurse specialist Laura Donaldson Epilepsy nurse specialist Kenny McCormack Neonatal nurse practioner Jackie Lees Neonatal nurse practioner Andi Lowe Neonatal nurse practioner Lorna Finlay Neonatal nurse practioner Pamela Cruickshanks Paediatric nurse practioner Liz Melvin Paediatric nurse practioner Jacquie Taylor Paediatric nurse practioner Linda Robertson Diabetes nurse specialist Karen Moir Diabetes nurse specialist Karen Davidson Child protection advisor Cicillie Rainey Child protection advisor