Earth Science
advertisement

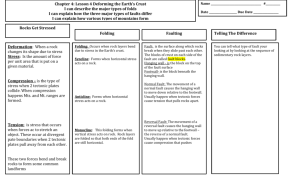
Earth Science Chapter 5 Section 1 A. Stress in the Crust: -An earthquake is the shaking and trembling that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth’s surface. The movement of Earth’s plates create powerful forces that squeeze or pull the rock in the crust. B. Types of Stress: -Three types of stress occur in the crust. - Shearing – stress that pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions . - Tension – pulls on the crust, stretching rock so that it becomes thinner in the middle. Tension occurs where two plates are moving apart. - Compression – squeezes rock until it folds or breaks. Occurs when two plates move toward each other. -A change in the crust is known as deformation. Examples: Bend, stretch, tilt, fold, and slide. C. Kinds of Faults: -A fault is a break in the crust where slabs of crust slip past each other. The rocks on both sides of a fault can move up or down or sideways. -Faults usually occur along plate boundaries, where the forces of plate motion compress, pull or shear the crust. -Three Types of Faults: 1. Strike-slip faults – A fault that occurs as two plates slip past one another in a side to side motion. This fault occurs at a Transform plate boundary. 2. Normal faults – The fault is at an angle, one block of rock is above the fault and the other is below the fault. Form due to tension. Hanging Wall – The half of the fault that lies above the fault. Footwall – The half of the fault that lies below the fault. 3. Reverse fault – This fault has the same structure as the Normal Fault. During compression the hanging wall is forced upward over the footwall. D. Friction Along Faults: Low friction- The rocks on both sides of the fault slide by each other without much sticking. Moderate friction- The sides of the fault jam together, Then jerk free, producing small earthquakes. High friction- The rocks lock together and do not move. Here stress builds up until it overcomes the friction and produces a powerful earthquake. E. Mountain Building: Mountains formed by Faulting: - When normal faults uplift a block of rock, A Fault-block Mountain forms. Mountains formed by Folding: - Folds are bends in rock that form when compression shortens and thickens part of the Earth’s crust. - Plate collisions cause the crust to bend and fold. - Some of the largest mountains in the world are folded mountain ranges. The Himalayas in Asia and the Alps in Europe are examples. F. Anticlines and Synclines: - The upward and downward folds created by compression have been given names by geologists. - Anticlines – An upward fold of rock. - Synclines – A downward fold of rock. G. Plateaus: The forces that raise mountains can raise plateaus. A Plateau is a large area of flat land elevated high above sea level. Some plateaus form when vertical faults push up large flat blocks of rock, such as the Colorado Plateau.