Year at a Glance
advertisement

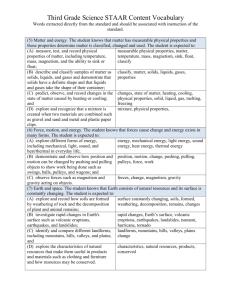
GRADE 2 SCOPE AND SEQUENCE REVISED MAY 2007 TEKS 2.1-2.4 are continuing threads and should be embedded in each unit of study Units of Study Force & Motion Systems Properties and Patterns of Objects and Events Changes in Motion o Position and Movement o Forces – push or pull o Size o Mass Changes in Sound Patterns of Changes in Weather & the Natural World Systems Properties and Patterns of Objects and Events Changes Weather o Movement o Heat o Temperature Night Sky o Position o Size o Quantity Seasons o Color o Temperature Water Cycle Natural Resources Properties of Objects Rocks, Soil, Water, Gases of the Atmosphere Uses of these Natural Resources Timeline 4½ Weeks 9 Weeks 4½ Weeks TEKS – 1ST Semester 2.5 The student knows that organisms, objects, and events have properties and patterns. A Classify and sequence organisms, objects, and events based on properties and patterns. 2.6 The student knows that systems have parts and are composed of organisms and objects. A Manipulate, predict, and identify parts that, when separated from the whole, may result in the part or the whole not working, such as flashlights without batteries and plants without leaves. B Manipulate, predict, and identify parts that, when put together, can do things they cannot do by themselves, such as a guitar and guitar strings. 2.7 The student knows that many types of change occur. A Observe, measure, record, analyze, predict, and illustrate changes in size, mass, temperature, color, position, quantity, sound, and movement C Demonstrate a change in the motion of an object by giving the object a push or pull. 2.5 The student knows that organisms, objects, and events have properties and patterns. The student is expected to: A Classify and sequence organisms, objects, and events based on properties and patterns. B Identify, predict, replicate, and create patterns including those seen in charts, graphs, and numbers. 2.6 The student knows that systems have parts and are composed of organisms and objects. The student is expected to: A Manipulate, predict, and identify parts that, when separated from the whole, may result in the part or the whole not working, such as flashlights without batteries and plants without leaves. 2.7 The student knows that many types of change occur. The student is expected to: A Observe, measure, record, analyze, predict, and illustrate changes in size, mass, temperature, color, position, quantity, sound, and movement. B Identify, predict, and test uses of heat to cause change such as melting and evaporation. D Observe, measure, and record changes in weather, the night sky, and seasons. 2.10 The student knows that the natural world includes rocks, soil, water, and gases of the atmosphere. A Describe and illustrate the water cycle. 2.5 The student knows that organisms, objects, and events have properties and patterns. The student is expected to: A Classify and sequence organisms, objects, and events based on properties and patterns. 2.8 The student distinguishes between living and nonliving objects. A Identify characteristics of nonliving objects 2.10 The student knows that the natural world includes rocks, soil, water, and gases of the atmosphere. A Describe and illustrate the water cycle. B Identify uses of natural resources. * Student expectations tested on the Elementary TAKS. Including is used when the examples that follow it must be taught. Such as is used when the examples that follow it are suggested examples. Verbs are highlighted. Strikethrough is used when this portion of the student expectation is not included in this unit. GRADE 2 SCOPE AND SEQUENCE REVISED MAY 2007 TEKS 2.1 through 2.4 are continuing threads and should be embedded in each unit of study. Units of Study Animals Systems Properties and Patterns of Animals Changes: o Size, Mass, Color, Quantity, Sound, and Movement External Characteristics of Animals Function of Animal Parts Animals’ Dependency on the Environment o Temperature Timeline 9 Weeks Plants Systems Properties and Patterns of Plants Changes: o Size, Mass, Color, Position, and Quantity External Characteristics of Plants Function of Plant Parts Plants’ Dependency on the Environment o Temperature 9 Weeks TEKS – 2nd Semester 2.5 The student knows that organisms, objects, and events have properties and patterns. The student is expected to: A Classify and sequence organisms, objects, and events based on properties and patterns. 2.6 The student knows that systems have parts and are composed of organisms and objects. The student is expected to: A Manipulate, predict, and identify parts that, when separated from the whole, may result in the part or the whole not working, such as flashlights without batteries and plants without leaves. B Manipulate, predict, and identify parts that, when put together, can do things they cannot do by themselves, such as a guitar and guitar strings. D Observe and record the functions of animals parts. 2.7 The student knows that many types of change occur. A Observe, measure, record, analyze, predict, and illustrate changes in size, mass, temperature, color, position, quantity, sound, and movement. 2.8 The student distinguishes between living and nonliving objects. The student is expected to: A Identify characteristics of living organisms. 2.9 The student knows that living organisms have basic needs. A * Identify the external characteristics of different kinds of plants and animals that allow for their basic needs to be met. B* Compare and give examples of the ways living organisms depend on each other and on their environment. 2.5 The student knows that organisms, objects, and events have properties and patterns. The student is expected to: A Classify and sequence organisms, objects, and events based on properties and patterns. 2.6 The student knows that systems have parts and are composed of organisms and objects. The student is expected to: A Manipulate, predict, and identify parts that, when separated from the whole, may result in the part or the whole not working, such as flashlights without batteries and plants without leaves. B Manipulate, predict, and identify parts that, when put together, can do things they cannot do by themselves, such as a guitar and guitar strings. C Observe and record the functions of plant parts. 2.7 The student knows that many types of change occur. A Observe, measure, record, analyze, predict, and illustrate changes in size, mass, temperature, color, position, quantity, sound, and movement. 2.8 The student distinguishes between living and nonliving objects. The student is expected to: A Identify characteristics of living organisms. 2.9 The student knows that living organisms have basic needs. A* Identify the external characteristics of different kinds of plants and animals that allow for their basic needs to be met. B* Compare and give examples of the ways living organisms depend on each other and on their environment. * Student expectations tested on the Elementary TAKS. Including is used when the examples that follow it must be taught. Such as is used when the examples that follow it are suggested examples. Verbs are highlighted. Strikethrough is used when this portion of the student expectation is not included in this unit.