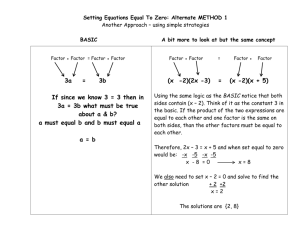
biases
advertisement
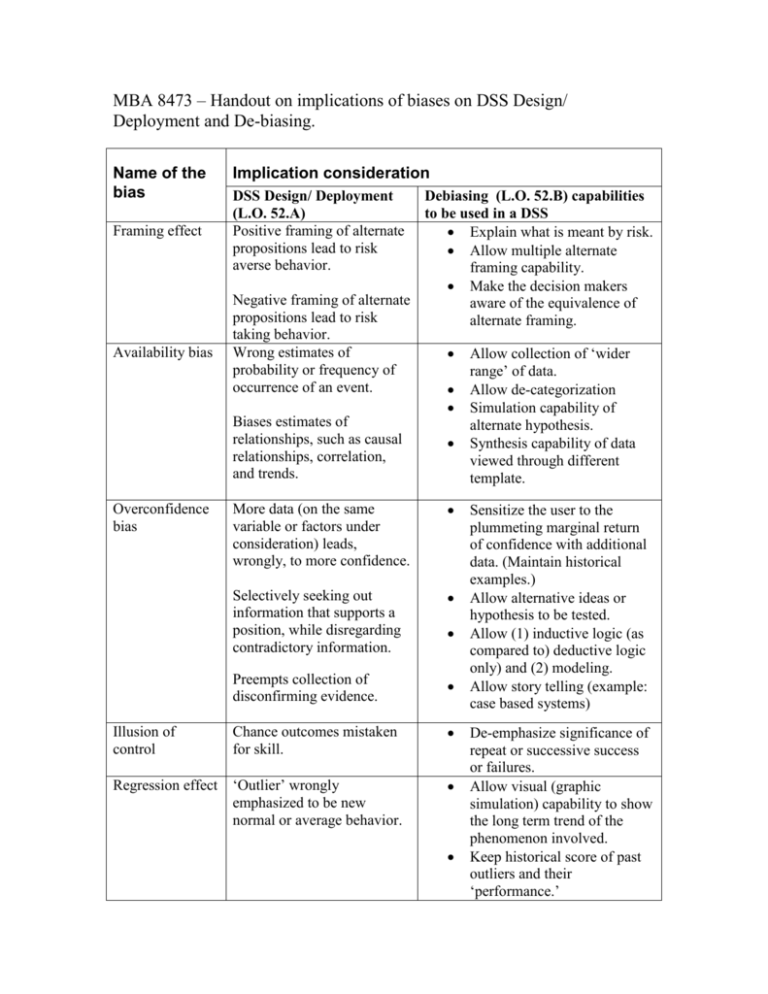
MBA 8473 – Handout on implications of biases on DSS Design/ Deployment and De-biasing. Name of the bias Framing effect Availability bias Overconfidence bias Illusion of control Implication consideration DSS Design/ Deployment (L.O. 52.A) Positive framing of alternate propositions lead to risk averse behavior. Debiasing (L.O. 52.B) capabilities to be used in a DSS Explain what is meant by risk. Allow multiple alternate framing capability. Make the decision makers Negative framing of alternate aware of the equivalence of propositions lead to risk alternate framing. taking behavior. Wrong estimates of Allow collection of ‘wider probability or frequency of range’ of data. occurrence of an event. Allow de-categorization Simulation capability of Biases estimates of alternate hypothesis. relationships, such as causal Synthesis capability of data relationships, correlation, viewed through different and trends. template. More data (on the same variable or factors under consideration) leads, wrongly, to more confidence. Selectively seeking out information that supports a position, while disregarding contradictory information. Preempts collection of disconfirming evidence. Chance outcomes mistaken for skill. Regression effect ‘Outlier’ wrongly emphasized to be new normal or average behavior. Sensitize the user to the plummeting marginal return of confidence with additional data. (Maintain historical examples.) Allow alternative ideas or hypothesis to be tested. Allow (1) inductive logic (as compared to) deductive logic only) and (2) modeling. Allow story telling (example: case based systems) De-emphasize significance of repeat or successive success or failures. Allow visual (graphic simulation) capability to show the long term trend of the phenomenon involved. Keep historical score of past outliers and their ‘performance.’