Essay Cell Walls
advertisement
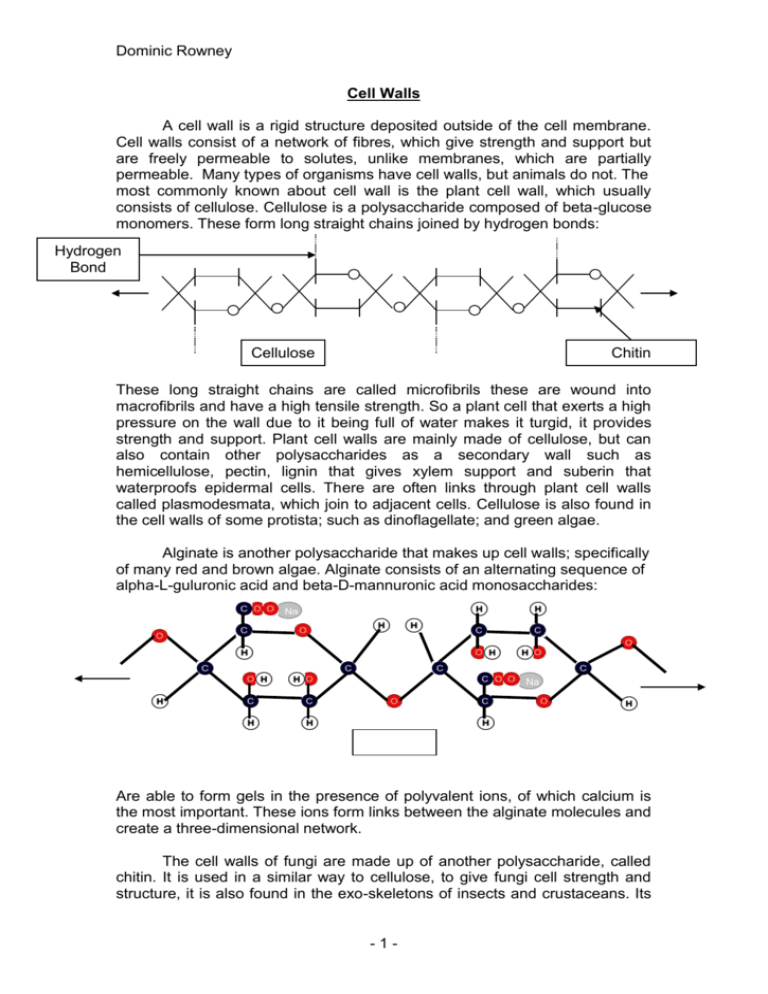
Dominic Rowney Cell Walls A cell wall is a rigid structure deposited outside of the cell membrane. Cell walls consist of a network of fibres, which give strength and support but are freely permeable to solutes, unlike membranes, which are partially permeable. Many types of organisms have cell walls, but animals do not. The most commonly known about cell wall is the plant cell wall, which usually consists of cellulose. Cellulose is a polysaccharide composed of beta-glucose monomers. These form long straight chains joined by hydrogen bonds: Hydrogen Bond Cellulose Chitin These long straight chains are called microfibrils these are wound into macrofibrils and have a high tensile strength. So a plant cell that exerts a high pressure on the wall due to it being full of water makes it turgid, it provides strength and support. Plant cell walls are mainly made of cellulose, but can also contain other polysaccharides as a secondary wall such as hemicellulose, pectin, lignin that gives xylem support and suberin that waterproofs epidermal cells. There are often links through plant cell walls called plasmodesmata, which join to adjacent cells. Cellulose is also found in the cell walls of some protista; such as dinoflagellate; and green algae. Alginate is another polysaccharide that makes up cell walls; specifically of many red and brown algae. Alginate consists of an alternating sequence of alpha-L-guluronic acid and beta-D-mannuronic acid monosaccharides: Na Na Are able to form gels in the presence of polyvalent ions, of which calcium is the most important. These ions form links between the alginate molecules and create a three-dimensional network. The cell walls of fungi are made up of another polysaccharide, called chitin. It is used in a similar way to cellulose, to give fungi cell strength and structure, it is also found in the exo-skeletons of insects and crustaceans. Its -1- Dominic Rowney monomer; N-acetyl glucosamine; has a similar structure to glucose except that it replaces hydroxyl group on carbon 2 with an acetylamino group. Chitin makes a good cell wall because of its tightly bonded structure it is highly N-Acetyl crystalline, insoluble and unreactive, Glucosamine making it a suitable material for cell walls. Acetylamino Groups Bacterial cell walls come in two types gram positive and gram negative. Any bacteria’s cell wall is made of murien, which is a polysaccharide cross-linked with polypeptide chains or a glycoprotein as it is known. An example of this is peptidoglycan which is found in the cell walls of gram positive bacteria, gram positive have a thick cell wall with additional protein and carbohydrate deposits. A gram negative bacterial cell wall has a thin wall with a lipid coating that can provide the cell with protection. The rigidity of the cell wall confers the shape of the cell it can be: Coccus (Spherical) Bacillus (Rod) -2- Spirilium (Helical)











