Forms of Energy (Stored energy and the energy of position.) (Motion
advertisement
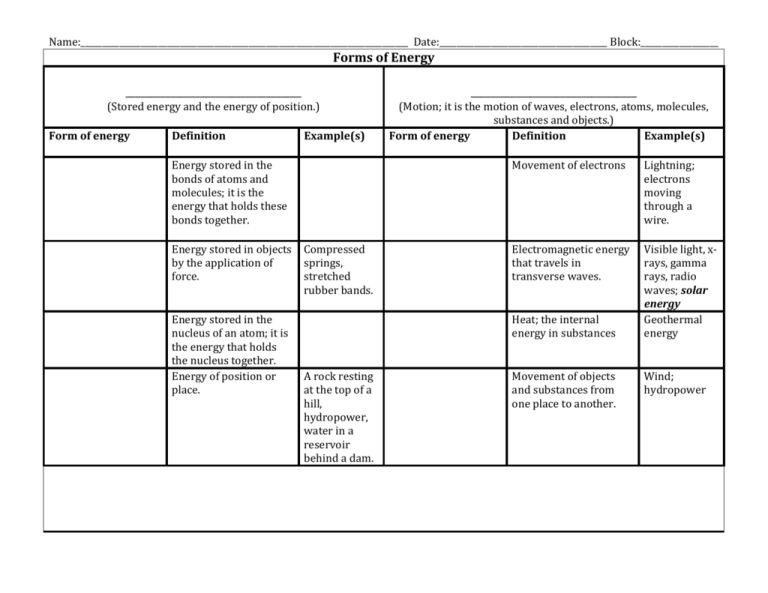
Name:____________________________________________________________________________ Date:_______________________________________ Block:__________________ Forms of Energy ___________________________________ _________________________________ (Stored energy and the energy of position.) Form of energy Definition Example(s) Energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules; it is the energy that holds these bonds together. Energy stored in objects by the application of force. Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom; it is the energy that holds the nucleus together. Energy of position or place. Compressed springs, stretched rubber bands. (Motion; it is the motion of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules, substances and objects.) Form of energy Definition Example(s) Movement of electrons Lightning; electrons moving through a wire. Electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse waves. Visible light, xrays, gamma rays, radio waves; solar energy Geothermal energy Heat; the internal energy in substances A rock resting at the top of a hill, hydropower, water in a reservoir behind a dam. Movement of objects and substances from one place to another. Wind; hydropower Sources of Energy ___________________________________ __________________________________ (Energy sources that cannot be replenished in a short time; Supplies are limited.) (Energy sources that can be replenished in a short time.) Source of energy Definition A liquid fossil fuel formed from the remains of plants that lived and died millions of years ago. Also known as crude oil or oil. A fossil fuel formed from the remains of ancient sea plants and animals; Mostly consists of methane gas. Form of Energy Source of energy Definition Any organic matter that can be used as an energy source. Examples are wood, crops, and yard and animal waste. Energy that comes from the force of moving water. A solid fossil fuel formed from the remains of plants that lived and died millions of years ago. Energy that comes from moving air. A common metal found in rocks all over the world whose atoms are easily split apart. Heat from within the earth, generated in the earth’s core. A fossil fuel related to petroleum and natural gas. Also called Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG) in the U.S. Energy from the Sun Form of energy Forms of Energy Potential Energy Kinetic Energy (Stored energy and the energy of position.) (Motion; it is the motion of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules, substances and objects.) Form of energy Definition Example(s) Form of energy Definition Example(s) Chemical energy Energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules; it is the energy that holds these bonds together. Biomass, petroleum, natural gas, propane Electrical Energy Movement of electrons Lightning; electrons moving through a wire. Stored mechanical energy Energy stored in objects by the application of force. Compressed springs, stretched rubber bands. Radiant energy Electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse waves. Nuclear energy Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom; it is the energy that holds the nucleus together. Nuclear fission Thermal energy in nuclear reactors, nuclear fusion in the Sun. Heat; the internal energy in substances Visible light, xrays, gamma rays, radio waves; solar energy Geothermal energy Gravitational energy Energy of position or place. A rock resting at the top of a hill, hydropower, water in a reservoir behind a dam. Movement of objects and substances from one place to another. Motion energy Wind; hydropower Sources of Energy Nonrenewable Energy Renewable Energy (Energy sources that cannot be replenished in a short time; Supplies are limited.) (Energy sources that can be replenished in a short time.) Source of energy Definition Form of Energy Source of energy Definition Form of energy Petroleum A liquid fossil fuel formed from the remains of plants that lived and died millions of years ago. Also known as crude oil or oil. Potential, chemical Biomass Potential, chemical Natural Gas A fossil fuel formed from Potential, the remains of ancient sea chemical plants and animals; Mostly consists of methane gas. Hydropower Any organic matter that can be used as an energy source. Examples are wood, crops, and yard and animal waste. Energy that comes from the force of moving water. Coal A solid fossil fuel formed from the remains of plants that lived and died millions of years ago. Potential, chemical Wind Energy that comes from moving air. Kinetic, motion. Uranium A common metal found in rocks all over the world whose atoms are easily split apart. Potential, nuclear Geothermal Heat from within the earth, generated in the earth’s core. Kinetic, thermal. Propane A fossil fuel related to petroleum and natural gas. Also called Liquified Petroleum Gas (LPG) in the U.S. Potential, chemical Solar Energy from the Sun Kinetic, radiant Kinetic, motion.







