tutorial1_answer
advertisement

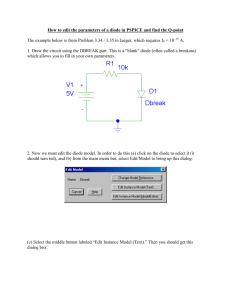
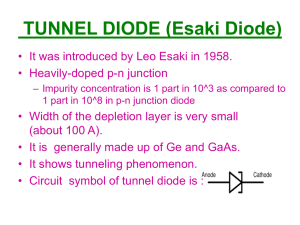
TUTORIAL 1 1.1 Atomic Atom a) What are the three particles that make up the atom? - Proton, neutron, electron b) If the atomic number of a neutral atom is 6, how many electron and proton does the atom have? - Proton: 6, electron : 6 c) What is the maximum number of electron that can exist in the 3rd shell of an atom? - 18 electron 1.2 Insulator, Conductor and Semiconductor a) What is the basic different between conductors and insulators? - Conductors have many free electron and can easy to conduct electron whereas insulator have essentially no free electrons and do not conduct current. b) What is the energy gap? - Energy gap is the difference of energy between valence band and conduction band. c) How many covalent bonds does a single atom form in a silicon crystal? - 4 covalent bonds 1.3 Current in Semiconductor a) What is an electron-hole pair? - Due to the electron that raised to the conduction band by external energy, one hole left in the valence band and it will create electron-hole pair b) Name the two energy bands at which current (electron current and hole current) is produced in silicon. - Electron current at conduction band, hole current at valence band c) Why aren’t electron-hole pairs generated in a semiconductor when its temperature drops to absolute zero? - When temperature drops to zero, there is no thermal energy at this temperature hence there are no energy for the electron to absorb, so they cannot jump to the conduction band and create electron-hole pairs. 1.4 N-type and P-type Semiconductors a) What is doping? - Doping is the process of adding impurities to semiconductor elements to improve their conductivity rating b) What are trivalent and pentavalent elements? - Trivalent is the elements with three valence electron, pentavalent is the elements with five valence electron. c) How is an N-type and P-type semiconductor formed? - N-type is formed by the addition of pentavalent impurity atoms to intrinsic (pure) semiconductor, P-type is formed by the addition of trivalent impurity atoms to intrinsic (pure) semiconductor. 1.5 The diode a) How is the electric field across the pn junction created? - Electric field is obtain form the force between positive charges and negative charges at the depletion region b) What is barrier potential? - The potential difference of the electric field across the depletion region is the amount of voltage required to move electrons through the electric field. c) What is the typical value of the barrier potential for a germanium diode? - 0.3V 1.6 Biasing a Diode a) Describe forward bias of a diode. - During forward bias diode allow to conduct current. Free electron from n region move across the pn junction and combine with holes in the p region after losing energy to overcome the barrier potential. b) Give explanation on how to reverse bias a diode. - The positive source (external bias voltage) is applied to the n region and the negative source to the p region c) Compare the depletion regions in forward bias and reverse bias. - Depletion region in forward bias is narrow compared to reverse bias the depletion region is wider 1.7 Voltage –Current Characteristics of a Diode a) What is the significance of the knee of the characteristics curve in forward bias? - The significance is the knee of the characteristics curve in forward bias is the point which the barrier potential is overcome and current will increase rapidly. b) Draw and label the complete V-I characteristics curve. (refer to the Floyd Book) page 23 c) What happens to the barrier potential when the temperature increase? - barrier potential decreases as the temperature increases. 1.8 Diode Models a) Draw and label for ideal diode model and practical diode model. (refer to the Floyd book) page 26 & 27 b) What are the two conditions under which a diode is operated? - A diode is operated in forward and reverse bias c) Which diode model represent the most accurate approximation? - Complete model diode represent the most accurate approximation. * 2 marks each question * Total 48 marks
![Semiconductor Theory and LEDs []](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005344282_1-002e940341a06a118163153cc1e4e06f-300x300.png)