Physics of Semiconductor Devices Formation of PN
advertisement

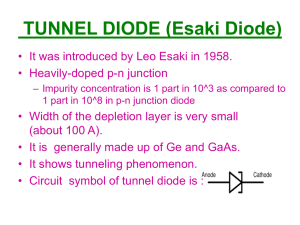
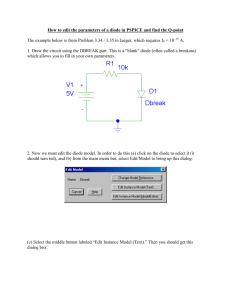
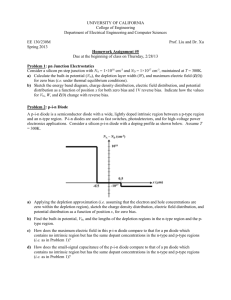
Physics of Semiconductor Devices Formation of PN - Junction When a P-type Semiconductor is joined together with an N-type Semiconductor a PN junction is formed. And it is also known as a Semiconductor Diode. Semiconductor diodes are widely used in Rectifiers which converts input AC signal into DC output signal. Ionized donors Junctio n P - - + + + + N + + + + Space charge region (OR) Depletion region Potential barrier height(V0) Potential barrier width (W) Depletion Region & Space Charge The diffusing majority carriers from the two regions recombine near the junction and disappear. The uncompensated Acceptor and Donor ions set up an Electric field which halts majority carrier Diffusion and causes minority carrier Drift. The two kinds of majority carriers diffusing across the junction meet each other near the junction and undergo recombination's, leaving negative ions on the P-side and positive ions on the N-side of the junction. This distribution of Positive and Negative Charges is called Space charge. Diode Symbol N Cathode _ P Anode + Energy level diagram Depletion region E PN - junction eVB Ec Conduction band Ec EFp EFn Fermi level Ev Valence band Ev eVB P N V - I Characteristics of PN Junction The diode can be operated in two different ways, as Forward and Reverse bias. When positive terminal of the battery is connected to the P-type & negative terminal is to the N-type of the PN-junction diode, known the diode is kept in forward bias. When negative terminal of the battery is connected to the P-type & positive terminal is to the N-type of the PN-junction diode, known the diode is kept in reverse bias. P Open circuit PN -junction - - + + + + N + + + + Space charge region P N - + + + + Forward bias VF P Open circuit PN -junction - - + + + + N + + + + Space charge region P N - - - + + + + Reverse bias VR + + + + + + + + I Current Forward Current Knee Voltage Reverse Bias V Forward Bias Reverse break down current The region between knee voltage & breakdown voltage is known as non-ohmic region. Above the knee & breakdown voltage the current increases. Breakdown voltage is due to thermally broken covalent bonds. Diode is conducting in forward bias & non-conducting in reverse bias. Rectifiers • A Rectifier is a device which converts alternating current to direct or unidirectional current. • Rectifiers are mainly three types… 1.Half wave Rectifiers 2.Full wave Rectifiers 3.Bridge Rectifiers Half – Wave Rectifier A transformer A.C input D .C output B Full Wave Rectifier Center tapped transformer A C A.C input B D .C output Efficiency of a Rectifier The efficiency of a Rectifier is defined as the ratio of D.C. out put power to the A.C. input power supplied to the Rectifier. op(d .c) power efficieny ip(a.c) power Light emitting diodes: • LED’ s are the most visible type of diode, that emits a fairly visible colored light, invisible infrared or laser type light when a forward current is passed through them. Principle: Basically LED are made from a very thin layer of fairly heavily doped semiconductor material. When the diode is forward biased, electrons from conduction band combine with holes from in valence band, releasing sufficient energy to produce photons of light. Semicondu Wave ctor length material Color Vf @ 20mA GaAs 850-940nm Infra-Red 1.2V GaAsP 630-660nm Red 1.8v GaAsP 605-620nm Amber 2.0v GaAsP:N 585-595nm yellow 2.2v GaP 550-570nm Green 3.5v SiC 430-505nm Blue 3.6v GAInN 450nm 4.0v white Anode Cathode + _ Cathode Current I(MA) V Photo diode • A photodiode is a diode optimized to produce an electron current flow in response to irradiation by ultraviolet, visible, or infrared light. • Silicon, Ge & gallium arsenide is most often used to fabricate photodiodes. • Few electron-hole pairs in the N and P–regions, and most in the depletion region contribute to photo current. Photo diode Sun radiation Top metal contact + P-diffusion Depletion region N-type N+ contact region Bottom metal contact Photo diode Symbol Depletion region Heavily doped & very thin Anode N N+ Lightly doped Cathode _ P +