Exam 3
advertisement

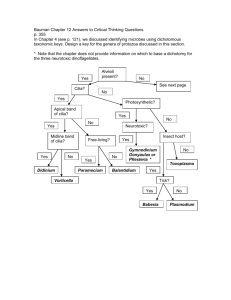
Exam III Review Bio 2010 Lecture Chapter 12 1. What are the major difference between the Eukarya, the Bacteria, and the Archaea? 2. What distinguishes algae from all the other eukaryotic organisms? 3. Why are algae economically important? 4. Explain the classificat ion of algae. 5. Contrast the various habitats for algae, protozoa, and fungi. 6. Explain the structure of algae 7. Contrast the reproduction of algae, protozoa, and fungi. 8. Explain paralytic shellfish poisoning. 9. Contrast the various modes of locomotion in protozoa. 10. Why are protozoa economically important? 11. Explain the classification of protozoa. 12. What are the differences between yeast, mold, and mushroom? 13. What are fungi diseases called? 14. Why are fungi economically important? 15. Explain the symbiotic relationships between fungi and other organisms. 16. Discuss the differences and similarities of slime molds and water molds. 17. Discuss the differences and similarities in the way algae, protozoa, fungi, helminths, and arthropods cause disease in humans. 18. What is a vector? Give two ex amples. Chapter 5 1. Describe the procedure for the selection of an antimicrobial. 2. What is the primary reason that milk is pasteurized? 3. What is the primary reason that wine is pasteurized? 4. What is the most chemically resistant non -spore forming pathogen? 5. Explain how microorganisms and viruses are destroyed using heat. 6. Why are low acid foods processed at higher temperatures than high acid foods? 7. Explain why it takes longer to kill a population of 10 9 cells than it does to kill a population of 10 3 cells. 8. Explain how microorganisms and viruses are destroyed using chemicals. 9. How is an iodophore different from a tincture of iodine? 10. How does microwaving a food product kill bacteria? 11. How is preservation different from pasteurization 12. How are heat-sensitive liquids st erilized? 13. Name two products that are commonly sterilized using ethylene oxide gas. 14. Explain the removal of microorganisms by filtration. 15. Explain how to destroy microorganisms and viruses using radiation. 16. Explain the methods of preserving perishable products. Chapter 21 1. Explain the history and development of antimicrobial drugs. 2. Explain the features of antimicrobial drugs. 3. Explain the mechanisms of actions of antibacterial drugs. 4. Describe the difference between what is implied by the terms antibiotic and an timicrobial. 5. Define therapeutic index and explain the importance. 6. Explain the role of penicillin -binding proteins in drug susceptibility. 7. Explain how to determine the susceptibility of a bacterial strain to an antimicrobial drug. 8. Name three of the first -line drugs used to treat tuberculosis. 9. Explain the mechanisms of antimicrobial drug resistance. 10. Name three antimicrobial medication that target ribosomes. 11. Compare and contrast the method for determining the minimum inhibitory concentration of an antimicrobia l drug by serial dilution with the Kirby Bauer disc diffusion test. 12. Name three targets that can be altered sufficiently via spontaneous mutation to result in resistance to an antimicrobial drug. 13. What is MRSA? Why is it significant? 14. Explain the mechanism of action of antiviral drugs. 15. Why is it difficult to develop antiviral drugs? 16. Explain the mechanisms of action of antifungal drugs. 17. Explain the difference between the mechanism of action of an azole and that of a polyene. 18. Explain the mechanisms of action of antiprotozoan and antihelminthic drugs.