Biology
advertisement

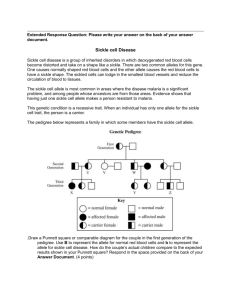
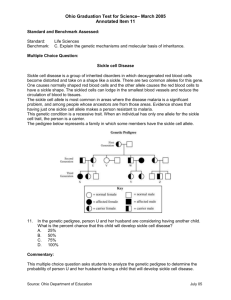
Name ________________________ Date ______________ Period _______ # _____ Advanced Biology Semester 1 Exam Review 1. Be able to construct a graph with data from an experiment. The elements for a proper graph include an appropriate title, labeled axes, appropriate scales, correctly plotted points, and a key if needed. (See labs.) 2. Be able to identify the steps to the scientific method. Know the features of a welldesigned, controlled experiment. Be able to identify the control group, experimental group, independent (manipulated) variable, dependent (responding) variable, and the controlled variables of an experiment. (Ch. 1 Quiz & Study Guide) 3. Formulate a conclusion from experimental data (use a graph or data table) to support or reject an experiment’s hypothesis. (See labs.) 4. What are the seven characteristics that all living things share? (Remember the sewer lice.) 5. Know which organisms in the 6 kingdom classification are prokaryotic and which are eukaryotic. (Ch. 1) What does it mean to have prokaryotic cells or eukaryotic cells? (Ch. 4-5) 6. Give the monomer units for the following organic compounds: proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. (Ch. 3 Biochemistry- Molecules of Life Concept Map) 7. What elements on the periodic table are important to living things? (science journal) 8. Compare and contrast DNA to RNA. (Ch. 3 C Map) 9. What type of protein is responsible for speeding up the rate at which a chemical reaction occurs? (Enzyme Activity) 10. What types of changes can occur in the human body that could denature/destroy enzymes? (Enzyme Activity & Enzyme Lab) 11. List the properties of water that make it so important to living things. (science journal) 12.Compare and contrast the structural differences between plant and animal eukaryotic cells. Remember the Venn diagram you constructed in the cell city assessment #3 b. (Ch. 4-5) 13. What happens to an animal cell when it is placed in a hypotonic solution? (Ch. 5) 14. What happens to an animal cell when it is placed in a hypertonic solution? (Ch. 5) 15. What happens to an animal cell when it is placed in an isotonic solution? (Ch. 5) Name ________________________ Date ______________ Period _______ # _____ 16. Compare and contrast osmosis and diffusion. (Hint: For the comparison, discuss the type of transport- active or passive.) (Ch. 5) 17. Be able to identify and give the function of the following cell structures/organelles: ribosome, cell membrane, cell wall, chloroplast, centrioles, mitochondria, cytoplasm, RER, SER, and Golgi apparatus. (Ch. 4) 18. Know what is needed for photosynthesis and cellular respiration to occur. What are the products of each of these processes? How do they depend on one another? (Ch. 6-7) 19. Know the major differences between mitosis and meiosis. You should also be able to identify the stages of each. (Ch. 8) 20. Be familiar with the following genetics vocabulary: genotype, phenotype, hybrid, pure bred, heredity, Punnett square, allele, gene, dominant, recessive, trait, clone, and human genome project. (Ch. 9) 21. Be able to construct and analyze a Punnett square with specific information. (Sponge Bob genetics or Punnett Square problems) Two parents who are both heterozygous dominant for eye color want to know the probability of having a blue-eyed child. B is brown and b is blue. Make a Punnett Square that shows the probability. What is the probability of having a brown eyed child? What is the probability of having a blue eyed child? (4 points) The probability of having a brown-eyed child is _______% and the probability of having a blue-eyed child is ________%. 22. Be able to understand a pedigree and answer questions relating to the information included in it. Sickle cell Disease Sickle cell disease is a group of inherited disorders in which deoxygenated red blood cells become distorted and take on a shape like a sickle. There are two common alleles for this gene. One causes normally shaped red blood cells and the other allele causes the red blood cells to have a sickle shape. The sickle-shaped cells can lodge in the smallest blood vessels and reduce the circulation of blood to tissues. The sickle cell allele is most common in areas where the disease malaria is a significant problem, and among people whose ancestors are from those areas. Evidence shows that having just one sickle cell allele makes a person resistant to malaria. This genetic condition is a recessive trait. When an individual has only one allele for the sickle cell trait, the person is a carrier. The pedigree below represents a family in which some members have the sickle cell allele. Name ________________________ Date ______________ Period _______ # _____ In the genetic pedigree, person U (heterozygous) and her husband (heterozygous) are considering having another child. Use A to represent the allele for normal red blood cells and S to represent the allele for sickle cell disease. What is the percent chance that this child will develop sickle cell disease? (Remember that AA is normal, AS is a carrier of sickle cell but does not have it, and SS has sickle cell disease.) A. 25% B. 50% C. 75% D. 100% 23. Determine the macromolecules of an unknown food substance, which yielded the following results. The possible answer choices include lipid, protein, simple sugar (monosaccharide), or starch (polysaccharide). (2 points) Chemical Test Result Biuret’s solution (cobalt blue solution) No reaction Benedict’s solution (light blue solution) Turned dark orange Iodine (dark orange solution) Turned blue-black color Brown Paper Bag Did not leave a greasy spot The unknown food substance contained __________________________ and _________________________. 24. If you are stranded on a deserted island, why is it important NOT to drink seawater even if it is the only water source available to you? Name ________________________ Date ______________ Period _______ # _____ 25. Explain how organisms that perform either photosynthesis or cellular respiration depend on one another. 26. Give one compelling reasons (for or against) the use of induced pluripotent stem cells in the United States. 27. Carefully explain how cancer occurs. In your explanation, describe how and when it becomes so deadly.