Intensive Care Unit Survival
advertisement

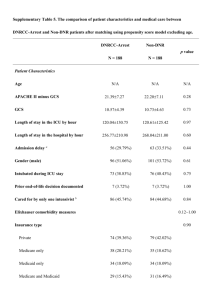
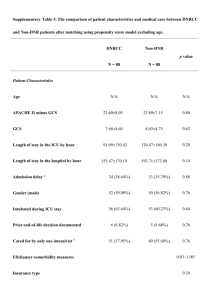
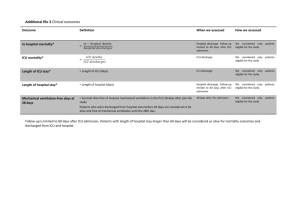
DATA: ICU OBSERVATIONS: 200 VARIABLES: 21 VARIABLE DESCRIPTION: ID ID number of the patient STA Vital status 0 = Lived 1 = Died AGE Patient's age in years SEX Patient's sex 0 = Male 1 = Female RACE Patient's race 1 = White 2 = Black 3 = Other SER Service at ICU admission 0 = Medical 1 = Surgical CAN Is cancer part of the present problem? 0 = No 1 = Yes CRN History of chronic renal failure 0 = No 1 = Yes INF Infection probable at ICU admission 0 = No 1 = Yes CPR CPR prior to ICU admission 0 = No 1 = Yes SYS Systolic blood pressure at ICU admission (in mm Hg) HRA Heart rate at ICU admission (beats/min) PRE: Previous admission to an ICU within 6 months 0 = No 1 = Yes TYP Type of admission 0 = Elective 1 = Emergency FRA Long bone, multiple, neck, single area, or hip fracture 0 = No 1 = Yes PO2 PO2 from initial blood gases 0 = PO2 > 60 1 = PO2 60 PH PH from initial blood gases 0 = PH 7.25 1 = PH < 7.25 PCO PCO2 from initial blood gases 0 = PCO2 45 1 = PCO2 > 45 BIC Bicarbonate from initial blood gases 0 = Bicarb 18 1 = Bicarb < 18 CRE Creatinine from initial blood gases 0 = Creatin 2.0 1 = Creatin > 2.0 LOC Level of consciousness at admission 0 = no coma or stupor 1 = deep stupor 2 = coma DESCRIPTIVE ABSTRACT: The ICU data set consists of a sample of 200 subjects who were part of a much larger study on survival of patients following admission to an adult intensive care unit (ICU). The major goal of this study was to develop a logistic regression model to predict the probability of survival to hospital discharge of these patients and to study the risk factors associated with ICU mortality (Vital status variable). SOURCES: Data were collected at Baystate Medical Center in Springfield, Massachusetts. REFERENCES: 1. Hosmer and Lemeshow, Applied Logistic Regression, Wiley, (1989), Appendix 2. 2. Lemeshow, S., Teres, D., Avrunin, J. S., Pastides, H. (1988). Predicting the Outcome of Intensive Care Unit Patients. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 83, 348-356. WEBSITE: http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/DASL/