AP Biology Final Review
advertisement

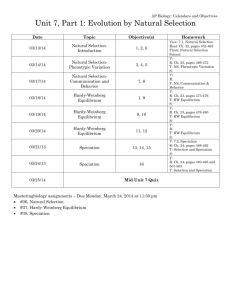
AP Biology Final Review Fall 2010 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. The peppered moth example is an illustration of natural selection (specifically directional selection) at work. The mane of a lion, the tail feathers of a male peacock, and indeed any sexually dimorphic features are examples of sexual selection. The stage of meiosis that accounts for the greatest amount of variation is Prophase I, when chiasmata and crossing over occurs. Halophiles, acidophiles, and thermophiles belong to Kingdom Archaebacteria. They are considered extremophiles because of the extreme environments in which they live… environments that would kill most other organisms. The evolution of warning coloration (aka aposematism) would be very beneficial if the predators learned what to eat and what not to eat through trial and error. Know Invertebrate and Vertebrate characteristics: Annelid: segmented worms; mollusks: clams and snails; arthropods: spiders, crustaceans, insects; Fish: simplest vertebrate; Mammals: most sophisticated vertebrate Fossil evidence shows that amphibians were the first vertebrate group to inhabit the land. Know the differences between fungi and plants. Fungi can be both uni-and multi-cellular. Plants are only multicellular. Fungi are heterotrophs, plants are autotrophs Golgi bodies/apparatus/complex, package and sort proteins and lipids for transport within the cell. Know that punctuated equilibrium and gradualism are related as evolutionary patterns. In punctuated equilibrium, speciation occurs when rapid changes in environments cause speciation to occur quickly, followed by long periods of stability in between. This may occur as a result of cataclysmic happenings, such as meteorite collisions or massive volcanic activity. Gradualism is the evolutionary pattern that occurs when speciation progresses slowly and “gradually over time”. This is said to be the pattern when there are long periods of stability in Earth’s geologic time. Nothing to “rock the boat” so to speak. Remember, there are many constituent particles found within the plasma membrane, some of which include phospholipids, oligosaccharides, proteins, and cholesterol. The cell wall of plants contains cellulose. Lysosomes are responsible for breaking down macromolecules that are no longer needed by the cell. They contain a digestive enzyme. Review Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium: in order for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the following MUST be true: No mutations are occurring No gene flow is occurring No genetic drift is occurring There is only nonrandom mating occurring No natural selection is occurring Since none of these will ever likely occur independently, much less all at the same time, HardyWeinberg Equilibrium is impossible to achieve, and is a theoretical number that we compare actual population calculations to in order to show that evolution is occurring. Know how to calculate Hardy Weinberg frequency. If a population consists of 9% white eyed flies and 91% red-eyed flies, what is the frequency of the red-eyed allele, if it is dominant? .7 (come in if you need a refresher…and don’t wait until the morning of the final, either!) Natural Selection generates individuals who are better able to survive in a new habitat over time. The Urey-Miller experiment of the 1950s attempted to show how life could have begun on Earth. Their experiment had many gases that are present only in trace amounts in our atmosphere today. The one gas that is plentiful, that was not present then, is Oxygen (O 2) Water moves across a membrane (osmosis) in the direction of the higher concentration of solute, in an effort to reach dynamic equilibrium. Water always moves from a region of less negative osmotic potential to a more negative osmotic potential. The higher the concentration, the greater the negativity of osmotic potential. Active transport requires the input of energy; plasmolysis occurs when plant cells’ plasma membranes pull away from the cell wall when placed in a hypertonic solution. Facilitated diffusion occurs when embedded proteins aid in the diffusion of substances over the membrane. 17. Mitochondria store energy for use by the cell, and are therefore more prevalent in cells which require more energy! (perhaps to do work, such as cardiac cells) 18. A mutation is a completely random change in DNA or chromosomes that may or may not influence natural selection. A B C 19. Know and understand how to interpret the above types of natural selection. Which of the graphs above correctly depicts directional selection? (B) Stabilizing Selection (A), and Disruptive Selection (C) 20. Review the following terms, and understand their application in the study of evolution: Bottleneck: Occurs when a large portion of the population is killed (due to any circumstance), or otherwise prevented from reproducing. Adaptive Radiation: A means of speciation (such as divergent evolution) when one species becomes many. (Radiating outward like a fan) Sexual Reproduction: Process which allows new individuals to vary from parents due to genetic recombination of alleles 20. The parts of the Cell Theory are as follows: All cells come from previously existing cells All living things are made up of cells The cell is the most basic unit of structure of living things 21. The original source of energy for all organisms on Earth is the SUN SUN SUN!!! 22. Understand the following terms from our Animal Behavior unit: Habituation: When animals lose instinct due to habit (such as pigeons losing their fear of humans in the city. Trial and Error: When an animal comes to associate particular behaviors with the consequences they produce. (mouse in a maze with cheese at the end) Imprinting: When learning is time-sensitive (such as hatchlings with a parent bird) Insight: Learning of problem solving skills due to exposure to similar circumstances (such as the chimp and the banana on a string) 23. Understand the following stages of meiosis in terms of what is happening or might happen (ie crossing over; chiasmata; nondisjunction…etc.) , and chromosome number: Interphase; Prophase I; Metaphase I; Anaphase I; Telophase I; Prophase II; Metaphase II; Anaphase II; Telophase II; Cytokinesis 24. Understand that genetic variability is due largely to the processes at work in meiosis, and that mitosis pretty much has to do with growth of tissue or repair. For the free response essay, you will have a choice of two: Focus on the concepts of genetic drift, geographic isolation, reproductive isolation and how speciation occurs due to isolation. Focus on the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, understand how to calculate and determine each genotypic and phenotypic possibility; understand the conditions which must be met in order for a population to be in H-W equilibrium; how H-W is evidence of evolution; how allelic frequencies change in populations due to lethal allelic conditions.