1. Framework Themes - California State University, Bakersfield

SCHOOL OF BUSINESS and PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION
California State University, Bakersfield
CRITICAL THINKING THEMES
Developing the Framework
by Dr. Donavan Ropp
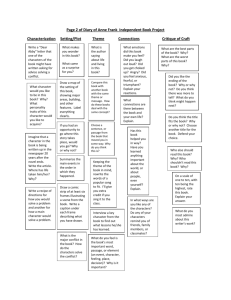
Theme One: Critical Thinking: A Comprehensive Approach
1. Dynamic
2. Reflective
3. Systems Approach (all things make sense in a system)
4. Flexible
5. Autonomous/independent (self-guided/self-disciplined)
6. Integrative/Interconnected/Interdependent
7. Interactive
8. Continuous Improvement
Theme Two: The Dynamic Process
1. Analyze: Take your thinking apart; to break up the whole into its parts.
2. Investigate/Evaluate/Improve: Judge or determine the worth or quality of the various parts.
3. Synthesize;
creatively reconstruct your thinking from the analysis to make it better; the combining of separate elements or substances to form an improved coherent whole.
4. Assessment/Improvement
5. Problem Solving/Decision Making/Resolving Issues/Answering
Questions/Monitoring/Improving
Theme Three: Interconnectedness
1. Everything is different from everything else.
2. Everything is connected to everything else.
3. Everything matters.
Theme Four: Trends of Momentum
1. Accelerating Change: New Game; New Rules
2. Intensified Complexity (free from illusion of simplicity?)
3. Increasing Interdependence
1
4. Never go back to static, simplistic, and fragmented world
Theme Five: The Pluralistic Universe
1. No fixed WORLD
2. Continuous Quest for Workable Solutions to Difficulties
3. Evolutionary Quality of Growth
4. Development to meet new situations and new needs.
5. Work in Progress.
Theme Six: Attitude and Approach
1. Adding Value (creating/managing/measuring)
2. Developing Skills
3. Proactiveness
4. Continuous Improvement
Theme Seven: The (so-called) “Operating Environment”
1. Internal
2. Economic/Business/Commercial
3. Social/Cultural
4. Government/Politics
5. Technological/Engineering/Science/Natural
6. Legal
Theme Eight: Stakeholders – Benefited or Burdened
1. Person(s); Group(s); Organization(s); General Public
2. Internal and External
3. Primary and Secondary
Theme Nine: Addressing Right vs. Wrong
1. Character (beliefs/attitudes)
2. Values
3. Morality/Mores/Taboos/Social Conventions/Culture
4. Ethics
5. Law
Theme Ten: Philosophy
1. Idealistic
2. Realistic
3. Relative
4. Pragmatic
2
Theme Eleven: Where Do We Live?
1. As humans we live inside our minds
2. Everyone thinks – We do it continuously
3. It is our nature to do so ( homo sapiens – species that thinks)
4. We become (and are) what and how we “think” inside our mind
5. Quantity does not count – Quality does
6. “Thinking” is also the source of disaster, trouble, problems, cruelty, injustice [Shoddy thinking: costly (money and quality of life)]
7. The question: Have you taken ownership of your “thinking” – or has your
“thinking” taken control of you?
Theme Twelve: The Logic of Reasoning (Things)
1. All we know are ideas
2. No idea stands alone – They are connected (reciprocal relationships)
3. All ideas exist and work in systems
4. Identify principles connecting/Elements of the system (why it works together)
5. Criteria and standards to assess and judge
6. Everything is Logical
7. Anything we know is interconnected with everything else we know
(expands scope of total understanding)
Theme Thirteen: The Logic of Content (Things)
1. System of logical relationships (between ideas or realities)
2. Reality is logic
3. All things make since in a system
4. There is balance and equilibrium everywhere
5. There are elements and connecting principles everywhere
Theme Fourteen: Basic Functions of the Human Mind:
There is an intimate, dynamic interrelationship among (1) thinking, (2) feeling and (3) wanting. Each is continually influencing the other.
Thoughts, feeling, and desires play equally important roles in the mind, continually influencing and being influenced by one another.
1. Thinking: [cognitive – what is going on in life?] judging, perceiving, analyzing, clarifying, determining, synthesizing, comparing
Thinking is the part of the mind that figures things out and makes sense of life’s events (what is going on – what is happening – Notice this and that, etc.)
Thinking is the key to commanding feelings and desires
3
To change feelings is to change the thinking that leads to the feeling
To change a desire is to change the thinking that underlies the desire
2. Feeling/Emotions: [Feelings (positive or negative) about those events] happy, sad, depressed, anxious, stressed, calm, worried, excited
Feelings are created by thinking, evaluating whether the events of our lives are positive or negative
3. Wanting/desiring: [motivation factor] goals, purposes, agendas, values, motives
Desires allocate energy/motivation to action as to what is desirable and possible
4. Action/Doing/Performance/Behavior: [a product of the mind’s function]
Results of the interaction of the above that continually shape behavior
Theme Fifteen: Defense Mechanisms of the Mind
1. Denial – Identification – Projection – Repression – Rationalization –
Stereotyping – Scapegoating – Sublimation – Wishful Thinking –
2. Defense Mechanisms are used by our native egocentricity
(sociocentric/ethnocentric), leading to self deception so we can see the world as we wish in order to get what we want and/or protect our belief system.
Theme Sixteen: Thinking Left to Itself
1.
Vague – Muddled – Inconsistent – Inaccurate – Illogical – Superficial
– self-deception
2.
Biased – Distorted – Partial – Uninformed – Prejudiced – Ill-founded
3.
Ego – myopic – righteousness – hypocrisy – oversimplification – blindness – absurdity
4.
Essential Duality – Capacity for egocentric tendencies v. capacity for rationality/reasonability [both appear to the mind as rational]
5.
Egocentric – Strives to gain its selfish interests and to self-validate its current way of thinking [being trapped by self-delusion, myth, and illusion]
Theme Seventeen: Egocentric Thinking Tendencies (be aware) vs.
Rational Capacities
1. Strives to gain its selfish interests
2. Strives to validate its current way of thinking.
3. Exists in two forms: Skilled & Unskilled
It’s true because I believe it (Innate Egocentrism)
It’s true because we believe it. (Innate Sociocentrism)
It’s true because I want to believe it.
(Innate Wish Fulfillment)
4
It’s true because I have always believed it.
(Innate Self-validation)
It’s true because it is in my selfish interest to believe it.
(Innate Selfishness)
Theme Eighteen: Reasoning: The Process of Figuring Something Out
1. Elements of Reason
2. Standards of Reasoning
3. Traits of Reasoning
4. Reasoning Abilities
Theme Nineteen: An Approach
1. Identify problem or opportunity
2. Define goal(s) [purpose]
3. Explore possible strategies [concepts – assumptions – inferences]
4. Anticipate outcomes [implications]
5. Look and learn
Theme Twenty: Life Long Learning and Continuous Improvement
5