warmer ranges
advertisement

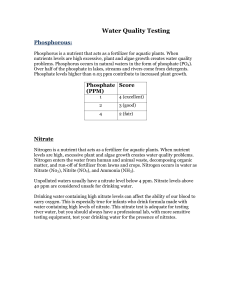
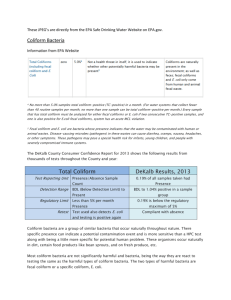
What is dissolved oxygen? Dissolved oxygen is a measure of the amount of gaseous oxygen dissolved in water. Dissolved Oxygen is produced by aquatic plants through photosynthesis. Oxygen also gets into water by diffusion from air and by rapid movements in the water. How does dissolved oxygen affect water quality? Oxygen is used by plants and animals for respiration also by aerobic bacteria which consume oxygen during decomposition. When organic matter such as animal waste or improperly treated wastewater enters a body of water, algae growth increases. This causes the dissolved oxygen levels to decrease as the plant material dies and is decomposed by aerobic bacteria. Decreases in the dissolved oxygen levels can cause changes in the types and numbers of aquatic macro-invertebrates, plants and animals living in an ecosystem. However, dissolved oxygen levels change and vary according to the time of day, the weather and the temperature. A decrease in the dissolved oxygen levels is usually an indication of an entry of some organic pollutant. Dissolved Oxygen Limits for Aquatic Life What is pH? pH is the measure of the acidic or basic nature of a solution. How does pH affect water quality? pH of Common Substances What is water temperature? The degree of hotness of a body of water. How does temperature affect water quality? Since colder water can hold more oxygen than warmer water, the temperature range of a body of water is directly tied to the health of aquatic organisms. Temperature Ranges for Aquatic Life Cold Range Below 13°C Cool Range 13°C - 20°C salmon mayfly stonefly caddisfly mayfly stonefly caddisfly beetle Warm Range 20°C - 25°C Hot Range Above 25 °C dragonfly deadly temperature for aquatic insects What is turbidity? Think of turbidity as the opposite of clarity. It is a measure of how cloudy a water body is. Most people have seen how rivers turn brown after a heavy rain. Soil particles carried by runoff cause this to happen. Why do high levels of turbidity matter? High amounts of soil in the water will block sunlight from reaching the bottom of a river or a lake in shallow water. When the water is turbid, floating particles absorb heat from the sun and cause the water temperature to rise. Higher temperatures cause oxygen levels in the water to fall, limiting the ability of fish and insects to survive there. Another effect is that the floating particles may clog fish gills. When these particles sink, they can smother and kill fish and aquatic insect eggs that lay on the bottom. Turbidity can also limit plant growth. This happens when sunlight cannot reach the plants' leaves. The combination of warmer water, less light and oxygen depletion makes it impossible for some forms of aquatic life to survive. How do turbidity levels rise? Higher turbidity can be caused by human activity like cutting trees and removing vegetation next to a body of water. Trees provide shade to keep the water cooler, and trees and other plants help block mud and soil from washing into the water. When roads and parking lots are constructed without the proper silt fencing, more soil and mud are likely to reach the water. What is fecal coliform bacteria count? How do fecal coliform bacteria get into streams and lakes? Large amounts of fecal coliform are released in the waste of farm animals and can be washed into streams by runoff from rain or irrigation. Urban areas contribute to fecal coliform contamination when wastes from dogs, cats, raccoons, and humans are carried into storm drains, creeks, and lakes during storms. Fecal coliform can also enter streams from illegal or leaky sanitary sewer connections, poorly functioning septic tanks, and wastewater treatment plants that are not functioning properly. These bacteria indicate a possible presence of pathogens, or disease-carrying bacteria, like e coli. These pathogens live in the same environment as fecal coliform. Bacteria and pathogens are mostly a human health concern. However, bacteria can deplete oxygen in the water when it decomposes and act as a fertilizer for algae and other aquatic plants, causing an overgrowth. The EPA has set acceptable limits for fecal coliform in water based upon the use of the water. For example, drinking water cannot contain any fecal coliform but water for swimming may contain up to 400 fecal coliform colonies/ 100 ml. What is nitrogen & its effect? Nitrogen is essential for plant growth. Too much nitrogen can stimulate too much growth, oftentimes resulting in algal blooms in water. A rapid increase in growth ultimately lowers DO for other living organisms: as the algae decays the level of oxygen is depleted. Excess nitrogen may come in the form of nitrates, a compound containing nitrogen. Nitrates are found in sewage from septic systems, fertilizers, manure, and waste from garbage dumps. What about ammonia? Ammonia is a compound that contains nitrogen. It is naturally produced in soil as a by product of decomposition. It is also found in manure, fertilizers, and cleaning products and can be very toxic for fish. The toxicity of ammonia in freshwater depends on the pH, temperature, and DO levels. The higher the temperature and the higher the pH, the more toxic the ammonia is to fish (a smaller amount is necessary to harm fish). Also the lower the DO, the more toxic ammonia is. What are phosphates? Phosphorous is a naturally occurring element and is also essential for all living organisms. It naturally occurs in soil, rocks, sediment, and organic matter. In plants, it is necessary for photosynthesis. Excess phosphorous in streams may come in the form of phosphates, inorganic compounds that contain phosphorous. Common substances that contain phosphates include fertilizer, detergents, pesticides, toothpaste, and oil. Too much phosphorous in freshwater can cause excess algae growth.