LATIN AMERICA: Humans and the Physical Environment Chapt 9
advertisement
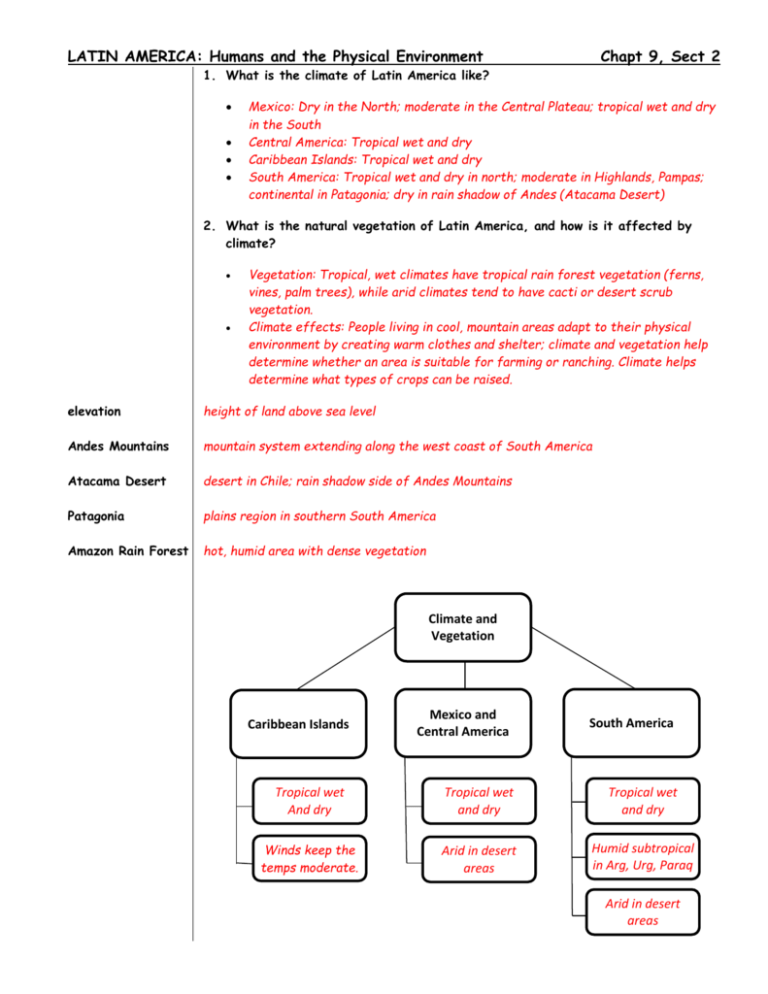
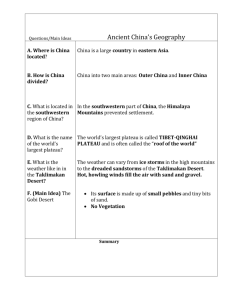
LATIN AMERICA: Humans and the Physical Environment Chapt 9, Sect 2 1. What is the climate of Latin America like? Mexico: Dry in the North; moderate in the Central Plateau; tropical wet and dry in the South Central America: Tropical wet and dry Caribbean Islands: Tropical wet and dry South America: Tropical wet and dry in north; moderate in Highlands, Pampas; continental in Patagonia; dry in rain shadow of Andes (Atacama Desert) 2. What is the natural vegetation of Latin America, and how is it affected by climate? Vegetation: Tropical, wet climates have tropical rain forest vegetation (ferns, vines, palm trees), while arid climates tend to have cacti or desert scrub vegetation. Climate effects: People living in cool, mountain areas adapt to their physical environment by creating warm clothes and shelter; climate and vegetation help determine whether an area is suitable for farming or ranching. Climate helps determine what types of crops can be raised. elevation height of land above sea level Andes Mountains mountain system extending along the west coast of South America Atacama Desert desert in Chile; rain shadow side of Andes Mountains Patagonia plains region in southern South America Amazon Rain Forest hot, humid area with dense vegetation Climate and Vegetation Caribbean Islands Mexico and Central America South America Tropical wet And dry Tropical wet and dry Tropical wet and dry Winds keep the temps moderate. Arid in desert areas Humid subtropical in Arg, Urg, Paraq Arid in desert areas LATIN AMERICA: Humans and the Physical Environment Chapt 9, Sect 2 Nuggets: Hurricane season is June to November. Hurricanes in the Caribbean can blow as much as 180 miles per hour. Temperature can vary by elevation. Wind can affect the climate. o Cool, dry winds from the Polar regions blow toward the Equator. o Warm, wet winds from the Equator blow toward Polar regions. Amazon rain forest is so dense with vegetation, that almost no sunlight reaches the ground. There are thousands of species of trees, plants, and insects in the Amazon Rain Forest. On the coast of Chile the Andes Mountains shield this area from rain – the Atacoma Desert. (Winds in the Southern Hemisphere blow from the East to the West; in the Northern Hemisphere, winds blow from the West to the East.) Elevation not only affects temperature (and therefore climate), but it also affects the type of vegetation that will grow – depending on the elevation of the land. ___________________________________________________________________________________ SUMMARY: Latin America’s physical environment, such as its climate and vegetation, varies greatly even within each country and affects how the people there live.