Whey protein in cosmetology : how to use a by
advertisement

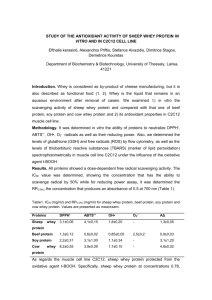
Whey protein in cosmetology : how to use a by- product of milk industry Useful terms to learn and information to read before carrying out the experiments : Whey is the portion of milk left after cheese or casein is made. Whey is about 96% water but contains some valuable protein, much lactose (milk sugar) and various dissolved salts. Years ago, whey was dumped into streams. These streams became polluted as a result; now, whey is processed into a range of dairy products. Whey protein concentrate is made by very fine filtration of whey to concentrate the proteins into a small volume which are then dried to a soluble powder. Milk mineral products are rich in calcium, which is extracted from the whey and then dried. All these products are sold as ingredients to food processing companies who use them to make food products such as custards, confectionery, crab-sticks, sports drinks, baked goods and yoghurts. Whey Protein Concentrate (WPC) Whey Protein Concentrate (WPC) is produced using ultrafiltration. This is also a membrane separation, but it selects on the basis of molecular size and is driven by pressure rather than by applied electric field as in the case of electrodialysis. Ultrafiltration retains (in the liquid product termed retentate) any insoluble material or solutes larger than about 10 000 Da molecular weight. The rest of the whey stream passes through the membrane, driven by the applied pressure and is called permeate The permeate contains most of the lactose, minerals and water from the whey. The retentate, the volume of which is about 1-4% that of the feed whey, is spray dried to a powder containing 35-85% protein as desired. WPCs are made at low to moderate temperatures so that the proteins remain in their native form and the dried product is highly soluble. Glossary lactose the major sugar in milk, not sweet but similar in size to sucrose retentate liquid suspension retained by a membrane permeate liquid solution that permeates through a porous membrane Ultrafiltration: membrane filtration process retaining particles larger than 5000 Da whey :the liquid portion of milk left after cheese or casein manufacture whey protein a group of minor milk proteins soluble at pH 4.6 1 Lesson on Thursday november 15 th STEP 4 Studying the biochemical composition of whey protein Activity 3 Measuring protein level in a retentate after an ultrafiltration in a sample of whey protein using the Biuret method . The pupils today will perform the following tasks: - Reading documents and extracting relevant information - Drawing a diagram of the whole experiment ( organization chart ) - Drawing a chart of the calibration range after the tests - Respecting the protocol of the experiment and carrying out the tests in the laboratory. - Using the correct equipment to perform measuring with a spectrophotometer. - Checking the results of a test - Drawing conclusions and questioning results Document 1, 2 : the principle of ultrafiltration , drawings 1) 2) 2 The aim of the tests is to measure the amount of protein in a fraction of a retentate ( R) , obtained by ultrafiltration of sweet whey , compared with a calibration range .The measuring of proteins will be made using the Biuret assay method.It will therefore be possible to assess the efficiency of the membrane process bearing in mind that the mass concentration of protein in sweet whey is approximately 8 g.L-1 Document 3 Biuret assay Introduction and principle: The Biuret reaction can be used for both qualitative and quantitative analysis of protein. The Biuret method depends on the presence of peptides bonds in proteins. When a solution of proteins is treated with cupric ions (Cu2+ ) in a moderately alkaline medium, a purple colored Cu2+ - peptide complex is formed which can be measured quantitatively by spectrophotometer in the visible region. So, Biuret reagent is an alkaline copper sulfate solution. Cu2+ peptide complex The intensity of the color produced is proportional to the number of peptide bonds that are reacting, and therefore to the number of protein molecules present in the reaction system. The reaction doesn't occur with amino acids because of the absence of peptide bonds, and also that with di-peptide because of the presence of only one peptide bond, but does with tri-, oligo-, and poly-peptides. Biuret reaction needs the presence of at least two peptide bonds in a molecule. The reaction occurs with any compound containing at least two bonds of: HN-CO- , -HN-CH2- , -HN-CSThe staining reagent is Gornall reagent composed of : - Copper sulphate that gives the blue hue to the reactive due to the cupric ions - Sodium hydroyde with a concentration of 0.2 mol/ L , it makes the medium alkaline - Sodium tartrate and potassium that “ chelate “ ( trap ) the cupric ions Cu2+ This avoids them being precipitated in a alkaline medium as insoluble copper hydroxyde (Cu(OH)2) -Potassium iodide to avoid cupric ions reacting before the measuring . -Be careful Gornall reagent is corrosive 3 PRELIMANARY WORK BEFORE CARRYING OUT THE TESTS ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS : Q1 What is the aim of the test you will be carrying out Q2 How does this measuring method work ? Q3 What is the point of using ultrafiltration ? Q4 From what you know about the membrane process, explain the high concentration of protein in the retentate . Q5 Likewise , explain the high concentration of lactose in the permeate . HOW TO OPERATE The assay and the range should be carried out in the exactly the same conditions : 1)Calibration of the spectrophotometer Spectrophotometer cuvettes 0 1 2 3 4 5 BSA Calibration solution 10 g.L-1, (mL) 0 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 Saline (mL) 0,5 0,4 0,3 0,2 0,1 0 Gornall reagent (mL) 2 2 2 2 2 2 BSA: bovine serum albumin Let the colour come out for 30 minutes then read the absorbency at 540 nm (a wavelength ) 2) Diluting the amount of retentate to be measured In a test tube , dilute the whey by half with saline, the final volume should be 2 mL . 3)Measuring the diluted retentate ( two tests) Carry out the measuring using 0.1 mL of the diluted retentate in the same conditions as the calibration range . 4 EQUIPMENT AND REAGENT To carry out this experiment the following products will be available : - BSA Calibration solution with a concentration of 20 g.L-1 - Saline - Gornall reagent - A sample of retentate Equipment : - Fume hood - Spectrophotometer - Automatic pipettes (p1000, p200) PRELIMANARY WORK BEFORE CARRYING OUT THE TESTS Answer the following questions : Q6 What is the crucial point concerning safety rules during this experiment ? Q7 Explain what you will to draw samples of the solutions you use . Q8 What is the dilution ratio for the retentate ? Q9 Draw an organization chart of the whole procedure . Q10 Collect in a chart the data about the preparation of the cuvettes for the calibration and tests ( indicate the number of the cuvette , SAB solution used( mL ),sample of diluted retentate, saline, Gornall reactive . BEFORE ACTUALLY CARRYING OUT THE HANDLING OF THE TESTS CHECK WITH THE TEACHER PRESENTING AND USING THE RESULTS Q11 Collect in a chart the data about the results ( calibration and tests ) : number of the cuvette, amount of protein in mg per cuvette, absorbency ) Q12 Draw the calibration curve A= f ( amount of protein per cuvette ) Q13 Calculate graphically the amount of protein ( mg/cuvette ) in the tests. Q14 Deduce the mass concentration average protein in retentate ( g.L-1). Q15Deduce the average mass concentration average protein in retentate ( g.L-1). reproducibility standard deviation Sr= 2,1 g.L-1 of retentate Combined uncertainty ( deviation )= uc = 3,2 g.L-1 of retentate Q16 Draw conclusions and comment on the results according to your knowledge on the composition of sweet whey. 5