Class 5 - Slimbridge Primary School
advertisement

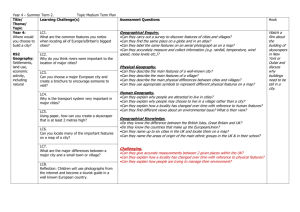
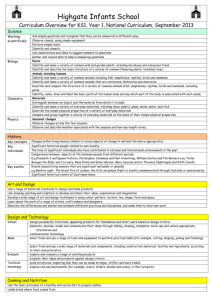
Year 5 & 6 (Cycle A) Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Focus Subject – Geography/History Focus Subject - Science Focus Subject - History Title – The Adventures of Scott Title – Amazing Human Bodies Title – War and Peace Main Objectives - Science Animals, including humans Yr 6 • Identify and name the main parts of the human circulatory system, and describe the functions of the heart, blood vessels and blood • Recognize the impact of diet, exercise, drugs and lifestyle on the way their bodies function • Describe ways in which nutrients and water are transported within animals, including humans Main Objectives – History – a study of an aspect or theme in British history that extends pupils’ chronological knowledge beyond 1066 A significant turning point in British history Main Objectives – A local study • A study of an aspect of history or a site dating from a period beyond 1066 that is significant in the locality. Main Objectives – Science All living things and their habitats Yr 6 • Describe how living things are classified into broad groups according to common observable characteristics and based on similarities and differences, including micro-organisms, plants and animals • Give reasons for classifying plants and animals based on specific characteristics Geography– Location knowledge Locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including Russia) and N & S America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries and major cities. Name and locate countries and cities in the UK, geographical regions and identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), and land-use patterns; and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time. Identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the Prime/Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night Understanding the Water Cycle Science - Evolution and inheritance • Recognise that living things have changed over time and that fossils provide information about living things that inhabit the Earth millions of years ago • Recognise that living things produce offspring of the same kind, but normally offspring vary and are not identical to their parents • Identify how animals and plants are adapted to suit their environment in different ways and that adaptation may lead to evolution Enrichment – WWT (Bird Studies) Enrichment – WWT – Bird Migration Studies Geography - Place knowledge Understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the UK, Europe and N & S America Science – Earth & Space Yr 5 • Describe the movement of the Earth, and other planets, relative to the Sun in the solar system • Describe the Sun, Earth and Moon as approximately spherical bodies • Use the idea of the Earth's rotation to explain day and night and the apparent movement of the sun across the sky Enrichment – Term 5 Term 4 Term 6 Focus Subject – History Focus Area – History/Geography Focus Area - Geography Title - Ancient Civilisations Title – The Ancient Greeks/The Olympics/Brazilian Study Title – Cool Coastlines Main Objectives • The achievements of the earliest civilisation - an overview of where and when the first civilisations appeared and a depth study of the Indus Valley Main Objectives – History • The legacy of Greeks on later periods on later periods in British history, including the present day • A study of Ancient Greek Life and achievements and their influence on the Western World Main Objectives – Geographical skills and fieldwork Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied Use the eight points of a compass, four and six-figure grid references, symbols and key (inc OS maps) to build their knowledge of the UK and the wider world Use fieldwork to observe, measure and record human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs and digital technologies Science – Light • Recognise that light appears to travel in straight lines • Use the idea that light travels in straight lines to explain that objects are seen because they give out or reflect light into the eye • Explain that we see things because light travels from light sources to our eyes or from light sources to objects and then to our eyes • Use the idea that light travels in straight lines to explain why shadows have the same shape as the objects that cast them Geography - Human and Physical Geography Describe and understand the key aspects of: Physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes, and the water cycle. Human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water Geography - Human and Physical Geography Describe and understand the key aspects of: Physical geography: including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes. • Human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water • Understand geographical similarities and differences of a region within South America Science – Electricity Yr 6 • Associate the brightness of a lamp or the volume of a buzzer with the number and voltage of the cells used in a circuit • Compare and give reasons for the variations in how components function, including the brightness of bulbs, the loudness of buzzers and the on/off positions of switches • Use recognized symbols when representing a simple circuit in a diagram Forces Yr 5 Explain that unsupported objects fall towards the Earth because of the force of gravity acting between the Earth and the falling object Identify the effects of air resistance, water resistance and friction, that act between moving surfaces Recognize that some mechanisms, including levers, pulleys and gears, allow a smaller force to have a greater effect History – A non-European society that provides a contrast with British History (Baghdad c AD900) Enrichment – Topic Days Enrichment – Greek Topic Day Enrichment – Drama Activities Year 5 & 6 (Cycle B) Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Focus Subject - History Focus Subject - Science Focus Subject – History/Geography Title – Crime and Punishment Title – Buzzing Electricity Title - Slavery Main Objectives – History – a study of an aspect or theme in British history that extends pupils’ chronological knowledge beyond 1066 A significant turning point in British history Science - All living things and their habitats Yr 6 • Describe how living things are classified into broad groups according to common observable characteristics and based on similarities and differences, including micro-organisms, plants and animals • Give reasons for classifying plants and animals based on specific characteristics History Ancient Greece – a study of Greek Life and achievements and their influence on the western world (Democracy) Enrichment – Houses of Parliament Trip / Gloucestershire Archives Trip Electricity Yr 6 • Associate the brightness of a lamp or the volume of a buzzer with the number and voltage of the cells used in a circuit • Compare and give reasons for the variations in how components function, including the brightness of bulbs, the loudness of buzzers and the on/off positions of switches • Use recognized symbols when representing a simple circuit in a diagram Geography– Location knowledge Locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including Russia) and N & S America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries and major cities. Name and locate countries and cities in the UK, geographical regions and identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), and land-use patterns; and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time. Identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the Prime/Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night) Enrichment – Term 4 Main Objectives – History - A local study • A study overtime tracing how several aspects of national history are reflected in the locality (Bristol) Main Objectives – History – a study of an aspect or theme in British history that extends pupils’ chronological knowledge beyond 1066 A significant turning point in British history A non-European society that provides contrast with British history – Benin (West Africa) c AD900 – 1300 Science – Earth and Space - Yr 5 Describe the movement of the Earth, and other planets, relative to the Sun in the solar system Describe the Sun, Earth and Moon as approximately spherical bodies Use the idea of the Earth's rotation to explain day and night and the apparent movement of the sun across the sky Geographical skills and fieldwork Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied Use the eight points of a compass, four and six-figure grid references, symbols and key (inc OS maps) to build their knowledge of the UK and the wider world Use fieldwork to observe, measure and record human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs and digital technologies Enrichment – Term 5 Term 6 Focus Subject – Geography Focus Area - Science Focus Area – Geography/History Title – Super Structures - Brunel Title – Our Evolving Earth Title - Edward Jenner Main objectives – Geography - Place knowledge Understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the UK, Europe and N & S America Science - Evolution and inheritance Yr 6 • Recognise that living things have changed over time and that fossils provide Main Objectives - human and physical geography information about living things that inhabit the Earth millions of years ago Describe and understand the key aspects of: • Recognise that living things produce offspring of the same kind, but Physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, normally offspring vary and are not identical to their parents rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes, and the water cycle. History – Local study - Brunel • Identify how animals and plants are adapted to suit their environment in Human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic A study over time tracing how several aspects of national history are different ways and that adaptation may lead to evolution activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources reflected in the locality • including energy, food, minerals and water Main objectives – Light Yr 6 a study of an aspect or theme in British history that extends pupils’ • Recognise that light appears to travel in straight lines Science - Animals, including humans Yr 6 chronological knowledge beyond 1066 (Railways/Brunel) • Use the idea that light travels in straight lines to explain that objects are • Identify and name the main parts of the human circulatory system, and seen because they give out or reflect light into the eye describe the functions of the heart, blood vessels and blood Science - Forces Yr 5 • Explain that we see things because light travels from light sources to our • Recognize the impact of diet, exercise, drugs and lifestyle on the way their • Explain that unsupported objects fall towards the Earth because of the force eyes or from light sources to objects and then to our eyes bodies function of gravity acting between the Earth and the falling object • Use the idea that light travels in straight lines to explain why shadows have • Describe ways in which nutrients and water are transported within animals, • Identify the effects of air resistance, water resistance and friction, that act the same shape as the objects that cast them including humans between moving surfaces • Recognize that some mechanisms, including levers, pulleys and gears, allow a smaller force to have a greater effect Enrichment – Bristol SS Great Britain and Suspension Bridge History – The achievements of the earliest civilisations – an overview of where and when the first civilizations appeared and a depth study of the Shang Dynasty of Ancient China Enrichment – Topic Day Enrichment – Jenner Museum