Page: 57
advertisement

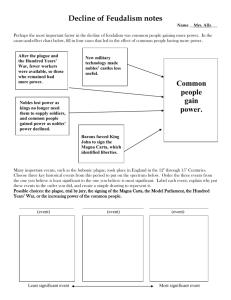
Page: 57 Study Guide for the Middle Ages Quiz Part II Master Copy A Day Quiz on 11-21-2013 B-Day Quiz on 11-22-2013 Timeline of Events Early Middle Ages 476 C.E. – 1000 C.E. High Middle Ages 1000 – 1300 C.E. Late Middle Ages 1300 – 1450 C.E. Year Event Explain The Importance 395 Christianity takes shape and becomes the recognized religion of the Roman Empire Christians are persecuted throughout the Roman Empire prior and must practice their faith in hiding. They risk their belongings and lives to practice their faith. In 312 Constantine the night before the Battle of Milvian Bridge, Constantine has a vision to put the first two letters of Christ’s name (Chi and Rho) on his soldiers’ shields. Constantine wins the battle and sees this as a sign to convert to Christianity. By 395 C.E. Christianity became the recognized religion of the Roman Empire. 1066 Norman Invasion William Duke of Normandy meets Harold Godwinson at the Battle of Hastings. William uses archers to release a flurry of arrows. William fakes a retreat then attacks Harold to win the battle. William defeats Harold and becomes king. Norman Culture changed Saxon tradition. French words blend with Anglo-Saxon language. Established Feudalism in England. Ceremonially crowned King by representatives of the Pope. William keeps the English custom of consulting an advisory council. William creates the Domesday Book. The Domesday book was a census that helped William keep track of all people in England. It also helped settle land disputes among lords Page: 57 1215 Magna Carta At Runnymede England on June 15, 1215 there was a meeting between King John and the English Nobles. The Nobles came dressed in their battle gear to show their displeasure to the king. The Magna Carta limited the power of the King. No longer could he simply throw people in jail. There was no recognition of the “divine right of kings.” Habeas Corpus: Any person accused of a crime needs to know what they are going to jail for. The reason needs to be legitimate. The Magna Carta also created a council of nobles that the king could not ignore. Eventually this led to the idea of democracy. The Magna Carta also establishes the idea of rights and liberties. It limited the kings powers and strengthened the rights of the nobles. It affirmed that monarchs should rule with the advice from the people being governed. 1346 1352 Black Death Deadly plague that was caused by bacteria. It could affect your lungs and your bloodstream. You could also get egg-sized swells. It originated in Mongolia and spread to the Black Sea along the silk road (trade route). It was spread by fleas that lived on black rats. Italian merchant ships brought the rats to Europe along with trade goods. It first appeared in Sicily and eventually spread across Europe. It killed approximately 1/3 of Europeans or 25 million people. People could not figure out the cause. Their remedies varied from using herbs to being a flaggelant. Forced farmers to diversify their crops (think crop rotation). Working class people moved to towns and cities to earn better wages. It reduced the power of feudal lords and led to a decline in feudalism. Page: 57 1338 1453 Hundred Years War There is a dispute over the French throne between the kings of England and France. Charles IV king of France, dies with no sons. His nephew Phillip of Valois gets the throne. King of England was Edward III wanted to become king of France and sent a note to Philip renouncing is allegiance as a vassal and attacks France. First 90 years, English armies are victorious. The English longbow is more effective than the French crossbow because of the longer range. The English army recruits soldiers and pays them to fight instead of the French oaths of loyalty. Joan of Arc, a peasant woman is inspired by God to save France and helped push English armies out of central France. She gets captured and is burned at the stake in 1431 for being a witch. The war contributes to the end of feudalism. People became more patriotic about their monarchs than feudal lords. Monarchs built huge armies with taxes they collected. 1. How did the church use its POWER economically and politically to gain even more power? The Church was the largest landholder in Europe. The Church received gifts from the monarchs and lords. They also added wealth by collecting tithes. People paid the tithes and gave gifts in an attempt to receive eternal salvation. Latin is the common language in the church and Europe. Church officials also kept records for monarchs. Most of the clergy could read but many monarchs could not. 2. Pope Gregory VII made what changes to the Catholic Church that angered King Henry IV? These changes angered King Henry IV resulting in his excommunication temporarily. How does this example display the churches power? Page: 57 Forbidding priests to marry Outlawing the selling of church offices Kings could no longer appoint priests Henry IV thought it was his right to appoint church officials and thought Gregory should no longer be Pope. This led to his excommunication before eventually being reinstated after begging for his reinstatement. 3. The Catholic Churches attempted to tell stories about using stained glass because most people were not ______________________ during the Middle Ages. Stained glass stories were illustrations so anyone could follow the story. This is another example of how little literacy there was in Western Europe. 4. William the Conqueror brought Feudalism to England. Why was this important? Feudalism brings a new way to organize everyone into a society. It brings, safety, stability, and protection. England was being invaded a lot during this period. William the Conqueror provides a way to stabilize the country. He also brought Norman culture which changes Saxon traditions For example, French words blend with the Anglo-Saxon language. 5. Explain the shift in power during the Middle Ages from lords to the merchant class. Why is this important? How did this change happen? (You need to know graphic organizer 55B) New developments such as crop rotation allowed peasants to build a surplus of food. The surplus led to job specialization and a growth in trade at local towns, which were located by rivers. Medieval town life developed away from lords economically, politically, and socially. *****Look at your bubble page, 54B****** A new class of people called merchants began to develop. They were wealthy and powerful. They sat on town councils that governed cities. They also joined guilds that were comprised of a collection of people that were skilled workers in a specific job. Page: 57 Guild members did not need to rely on the manors since they often owned their own business. Since they were part often part of town councils they held political power. The guilds also gained political power. 6. What is the advantage of building a medieval town near a river? It is easier to trade. Being located along a river makes trade easier because it is quicker to move goods on water than it is over land. 7. How did job specialization affect cities? People began to join guilds and become a part of the merchant classes. People produced items such as shoes, leather, clothing, glass , and furniture. These items were distributed from shops, fairs, and trade routes. Also, people joined guilds where other people in the same line of work were members. This empowered all the people within the guild. Making more money towns were able to buy their royal charters which allowed them to govern themselves. 8. What are the events that led to the fall of feudalism? The Black Death The Hundred Years War The Magna Carta The rise of towns in medieval Europe 9. How did the Bubonic Plague reach Europe? How did it continue to spread once it reached Europe? Why were Europeans unable to stop the Bubonic Plague from spreading? The Bubonic plague spread from Mongolia to Europe through the silk road. Fleas on rats on Merchant ships landed in Sicily and began spreading the bubonic plague in Europe. People could not understand the causes of the bubonic plague. Some people believed the disease was related to the alignment of the planets or was God’s wrath aimed at sinful humans. Other people blamed Jews. The remedies were not viable solutions either. Flaggelants (religious fanatics – whipped themselves, massacred Jews). Oranges stuck with cloves; Aged molasses and chopped snake were other remedies. Page: 57 10. The Bubonic Plague killed a large percentage of people able to work. How did the deaths of those workers affect the people that survived? There was a smaller amount of common people to do all the labor (farming, craftsmanship for example) so the people that survived the Bubonic Plague became more valuable. There was a smaller pool so lords had to value the people that were left even more. Prices and wages went up for peasants. Peasants began to move from the countryside to towns for better opportunities. This empowers the peasants and gives them more independence. They revolt and demand more independence. This leads to part of the decline of feudalism as people move into towns and a reduction of the power of the lord. 11. Explain the importance of the Magna Carta. How did the Magna Carta impact common people? The Magna Carta limited the power of the King and established the idea of Habeas Corpus. It created a council of Nobles that the king could not ignore. Eventually these ideas lead to the idea of democracy. People now needed a reason to be thrown in jail that was a reasonable reason. It established the ideas of rights and liberties. It is the precursor to many of the ideas in the U.S. Constitution and British law today. 12. The Bubonic Plague and the Hundred Years War had what effect on Europeans? First explain the importance of each and then the effects of each. The Black Death was a deadly plague caused by bacteria that killed 1/3 of all the population. It forced people to diversify their crops. This reduced the amount of manpower or labor that was able to support the lords. The lords had to give more rights to the working class. Feudal lords lost power. The hundred Years’ war began over a dispute between the kings of England and France. The French king Charles IV did not have any sons causing Edward III to desire to become king of France. He attacks France creating a war that would last over 100 years. Page: 57 The nature of warfare changed. English armies recruited soldiers from common people instead of using the oaths of loyalty to fight. The English also paid soldiers. People became more patriotic and more devoted to their monarch than their feudal lord. Monarhs built huge armies with their taxes they collected which reduced their need to go through the nobles for soliders. That resulted in a reduction of the power of nobles. 13. What events led to William Duke of Normandy becoming the King of England? Edward the Confessor dies without an heir. He promises his thrown to William Duke of Normandy. Harold Godwinson is aware of the promise but takes the thrown after being made king by the Anglo-Saxon Assembly. Harald Hardrada attempts to take the thrown but dies at the battle of Stamford Bridge after being defeated by Harold Godwinson. Harold has to march south (roughly 250 miles) to meet William Duke of Normandy and dies in battle. Legend says that Harold Godwinson had an arrow go through his eye resulting in his death. William Duke of Normandy becomes William the Conqueror and King of England. 14. What is the SIGNIFICANCE or IMPORTANCE of William Duke of Normandy becoming king of England? What changes happened as a result of him becoming king? William becomes King of England. He brings Norman culture and changed Saxon traditions. French words blend with Anglo-Saxon language. He established Feudalism in England. He was ceremonially crowned King by representatives of the Pope. William keeps the English custom of consulting an advisory council. William creates the Domesday Book. A Census that helped William keep track of all people in England. It helps him eventually tax the English people. It also helped settle land disputes among lords. Page: 57 15. What are guilds? What was the purpose of creating guilds? What are the advantages of guilds? A guild is an organization of people in the same craft or trade. Guilds managed the trade and production of goods. Guilds provide protection for members Maintained high standards for work Controlled the hours of work Set fair prices Dealt with complaints from the public Members that cheated their customers were punished. Guilds also helped with funeral services and health care when their members were in a time of need. Guilds helped construct guildhalls, fairs, and festivals so they were contributing to the public good. 16. What are the steps toward membership in a guild? The process of becoming a member of a guild is similar to what process today? 1. Apprentice 2. Journeyman/day worker (need to create a masterpiece) 3. Master As an apprentice you left your house at the age of 12, your apprenticeship lasted 7 years. Rarely were you paid. Your master agreed to house you, feed you, and train you. 2. Journeyman (creating a masterpiece) Apprentices had to prove to the guild that they had mastered their trade. They had to produce a piece of work to show skills 4. Once the guild approved, the apprentice as given the right to set up a business. It was very expensive to open a business. If you were unable to become a master you remained a journeyman. This process is similar to college today. Students go away for at least four years. They are provided housing and food (However, often the student is responsible for paying for this). Students often have internships that are rarely paid. They usually need to produce a project or paper as a culmination of their studies and without that final work often do not graduate.