Weak Acid Base Problems (Document) -
advertisement

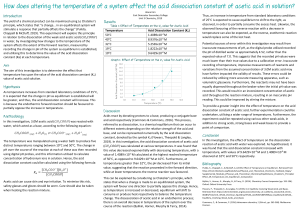
Some Acid Base Stuff For You To Know!! 1) What is % dissociation (also called % ionization) WEAK ACID PROBLEMS 2) What is the pH and percent dissociation of a solution of 0.10 M acetic acid? 3) What is the pH and percent dissociation of a solution of 0.050 M acetic acid? 4a) What do you notice about the pH and the % dissociation of the two acid solutions above? 4b) Why does this seem contradictory at first? 4c) Why does it make sense? 5) Here is a weak acid problem where pH is given and you must get the concentration of the acid. A nitrous acid solution has a pH of 1.80. What is the concentration of the nitrous acid? 6) An unknown weak acid is titrated and it is determined that the concentration of the weak acid is 0.25 M. The pH of the acid is 4.65. What is the Ka of the acid? What is the identity of the acid? WEAK BASE PROBLEMS 7) What is the pH, pOH and % ionization of a 0.20 M solution of ammonia? (How do we calculate % ionization for a base?) 8) An unknown weak base is titrated and it is determined that the concentration of the weak base is 0.35 M. The pH of the base is 9.79. What is the Kb of the base? Identify the base. 9) An unknown weak base has a concentration of 0.10 M and a pH of 10.23. What is the Kb of the base and the Ka of this base’s conjugate acid? Identify the base from the following choices (NaClO, NaBrO, NaIO, NaCN). 10) Something New – A Buffer Problem What is a buffer? A solution containing a _____________________________ and a salt containing the _____________ present in the ____________________________. OR A solution containing a _____________________________and a salt containing the ion formed after the ___________________________ gains a ________________. Buffers are essentially _______________________ and_______________________ mixed together. So why don’t the _______________________ and ________________________ react??? Why are these solutions useful? You create a buffer by adding 4.00 grams of sodium acetate to 100.0 mL of 0.100 M acetic acid. What is the pH of the resulting solution?