Weak Acid/Base Calculations with Percent Dissociation and
advertisement

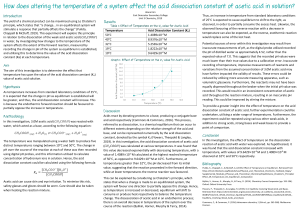
Acetic Acid (HC2H3O2) has 0.767% dissociation in a 0.300M solution at 25°C. Find the Ka for acetic acid at 25°C and the solution’s pH Acids that can give up MORE than one H+ ion Diprotic—2 H+ ions capable of ionizing Triprotic—3 H+ ions capable of ionizing **Each H+ dissociates separately and in a separate step--• Specific Ka value for each step. Ka1 >>> Ka2 generally for these acids Most of the H+ dissociates in the 1st dissociation. **Use Ka from the 1st dissociation to calculate [H+] and pH 2H2CO3 HCO3- H+ + HCO3- (Ka1=4.3x10-7) H+ + CO32- (Ka2=4.7x10-11) Calculate the pH of a 0.125M maleic acid solution. HOOCCH=CHCOOH + H2O H3O+ + HOOCCH=CHCOO- (Ka = 1.2 x 10 -2) HOOCCH=CHCOO- + H2O H3O+ + -OOCCH=CHCOO- (Ka = 4.7 x 10 -7) Finish Weak Read Acid/Base Problems—Friday over lab procedure