File
advertisement

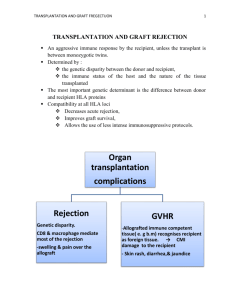
Running head: RESEARCH ON EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX Further research on Extracellular matrix’s side effects and solutions by literature review Junchen Liu ENGL 106i Purdue University Author Note Junchen Liu, Department of Engineering, Purdue University. Junchen Liu is now at Department of Engineering, Purdue University. Correspondence concerning this article should be addressed to Junchen Liu, Department of Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, 47906. Contact:liu1320@purdue.edu 1 REPORT OF THE EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX 2 Abstract This thesis is a synthesis paper targeting at the transplant rejection caused by the extracellular matrix and the possible treatment for the rejection. Coito and Kupiec-Weglinski found out the relationship between the extracellular matrix and the transplantation rejection while Dr. Kirk and his team found out an effective suppressor for the acute transplant rejection and the Dr. Libby and Dr. Pober stated that the chronicle transplant rejection, which is transformed from the acute transplant rejection, have no antidote. This paper shows to what extent the side effect of the extracellular matrix, the transplant rejection can be cured. In all, the in the acute rejection phase, the symptom is still curable, but once the acute rejection transformed to the chronicle rejection phase, the side effect can’t be cured. Keyword: Extracellular matrix, the acute transplant rejection, the chronicle transplant rejection REPORT OF THE EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX 3 Further research on Extracellular matrix’s side effects and solutions People get wounded all the time, so in order to minimize the loss caused by the wound, I started doing research on extracellular matrix. I am trying to explore the side effects of the extracellular matrix because even the social media started to claim its great potential (Andrews, 2008). But I recon it as an unknown matter and I am trying to find out why experts are so confident about extracellular matrix. To get some basic insights, I’ve been interviewing with Yumin Gao. He indicated me with three side effects that could occur by this technology: malnutrition, muscle loss and the transplant rejection. Yumin Gao gave me the solutions to the first to side effects and he said those two problems, with proper treatment will be cured and he didn’t consider there two as serious problems. However, he didn’t have any idea on the last side effect and he proposed me to do more research (Gao, Y. personal communication, March 1st, 2015). First, I researched the mechanism and the reason of the transplant rejection caused by extracellular matrix. Then in the other two paragraphs, I researched the solutions for two different kind of the transplant rejection. Dr. Coito and Dr. Kupiec-Weglinski from Harvard University studied the components of extracellular matrix by using different combination of the components and implemented them on rats with the transplanted organs. They added the fibronectin and the laminin, both of them are one of the components is extracellular matrix. They observe the acute rejection, which is the rejection that will be developed as early as one week after the transplantation. They also found out the newly synthesized fibronectin, but not the laminin, from the transplantation will increase the likelihood of the acute and late rejection. Dr. Coito (2000) finally concluded that REPORT OF THE EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX 4 the fibronectin, a protein in the extracellular matrix “are active participants in the immune cascade leading to graft rejection.” (p.2467), which means it may lead to the rejection of the transplantation. Dr. Coito have found out that patient will take the risk to have transplant rejection partly because of extracellular matrix (Coito, 2000). The reason why social media still claim extracellular matrix can be used to grow organs for transplanting (Andrews, 2008) is because Dr. Kirk have found a possible solution to deal with the acute rejection (Kirk et al., 1999) Dr. Kirk and his team experimented with CD154, a specific protein that will activate the immune system and claimed (1999) that the CD154 is “a promising agent for clinical use in human allotransplantation” (p.686), a transplantation from the same species. Firstly they deducted that the CD40 is an essential component in our body to mediate the immune and inflammatory system, and CD154, the suggested antidote, works as a pair to suppress the CD40 to activate unnecessary immune reaction. When there are significant amount of the foreign matter attack the body, CD40 will be concentrated and overwhelm the effect of CD154, which will cause the immune system to reject the foreign matters, so the researchers will inject CD154 to suppress the excessive amount of the CD40 to soothe the rejection system. They used monkey to do the renal (kidney) transplantation and inject with CD154. The acute rejection was suppressed after the injection. They then observed the monkey and concluded that the CD154 can suppress the acute rejection for a time as long as 10 months. And more surprisingly, they found out that there is no additional need to do more treatment to prevent the graft loss, as known as the transplanted organ lost. Also, research has found out REPORT OF THE EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX 5 that the existence of CD154 after the treatment is not required by using antibody to eliminate the CD154. The advantages of this treatment is that it doesn’t need to suppress the immune system all around the body. So this is an effective antidote to confront the acute rejection (Kirk et al., 1999). Even though Dr. Kirk and his team have CD154 at stake to soothe the acute rejection (Kirk et al., 1999). , the specialists in the medical area are not very optimistic to find out the suppressor that could totally prevent the acute rejection from changing to chronicle effects. Even worse, till now the chronicle rejection is irreversible, according to Dr. Libby (Libby & Pober, 2001). Dr. Libby and Dr. Pober stated that the chronicle rejection will result in the loss of the transplanted organs, so that eventually the patients will lose the organs which are consumed by the immune system. The cause of the chronicle rejection can be resulted from the failure to suppress the acute rejection. The researchers stated that the 5% of the acute rejection will fail and develop into chronicle rejection. The researchers suggested that the patient take the therapy for the acute rejection continuously even though the affect would be petite. They also pointed out that the suppressor of the acute rejection may be the cause of the chronicle rejection because it may target at wrong mechanism. Till now, there is no possible antidote to defeat the chronicle rejection (Libby & Pober, 2001). REPORT OF THE EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX 6 Conclusion In this paper, we explore the existence and the mechanism of the extracellular matrix. With this knowledge, we then examines two paper regarding the antidote for this side effect. We know that in an early stage, the symptom can be controlled with a failure of 5%, but after developing in to the late stage, the side effect could be vital. Even though the technology is so advanced these days, there are still copious phenomenon that people can’t solved or explain. But in the future, once people know how to control the side effect of the extracellular matrix thoroughly, we can enjoy a life without any missing of the body part. REPORT OF THE EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX 7 References Andrews, W. (2008, February 7). A "Holy Grail" Of Healing. , from http://www.cbsnews.com/news/a-holy-grail-of-healing/ Coito, A. J., & Kupiec-Weglinski, J. W. (2000). EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX PROTEINS IN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION1. Transplantation, 69(12), 2465-2473. Kirk, A. D., Burkly, L. C., Batty, D. S., Baumgartner, R. E., Berning, J. D., Buchanan, K., ... & Harlan, D. M. (1999). Treatment with humanized monoclonal antibody against CD154 prevents acute renal allograft rejection in nonhuman primates. Nature medicine, 5(6), 686-693. Libby, P., & Pober, J. S. (2001). Chronic rejection. Immunity, 14(4), 387-397.






![Immune Sys Quiz[1] - kyoussef-mci](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006621981_1-02033c62cab9330a6e1312a8f53a74c4-300x300.png)