Colonial America: Founding, Purpose, and Characteristics
advertisement

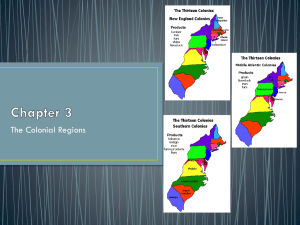
Colony Plymouth, Mass. Founded Region 1620 Founder New William Bradford/pilgrims England 1630 Massachusetts Bay Religion Government Original Purpose Economics Puritan Corporate Puritan Corporate New John Winthrop England Religious freedom for Separatists(Called Mixed Pilgrims & farming Strangers) Mixed farming, Religious freedom fishing, for Puritans shipbuilding 1636 Connecticut New Thomas Hooker England Rhode Island 1636 & Providence Plantations New Roger Williams England Puritan Corporate None Corporate 1630 New Hampshire Corporate, then royal New John Mason England New England Colonies: Long winters Thin rocky soil Subsistence farming Small farms small Puritan Triangular Trade Routes (Middle Passage) Fishing Whaling Notes Mayflower Compact. 18,000 settlers by 1642 – Representative Gov’t through election to General Court Great Migration 15,000 Puritans to Mass. Religious and Mixed economic freedom/expansion farming of trade Leaders of Massachusetts asked Hooker and followers to leave. Fundamental Orders of Connecticut any man owning property can vote limited power of Governor Mixed Religious farming freedom/toleration Williams set up most tolerant colony/ diverse population Escape for those constricted by religious and economic rules 1st place in America where people can worship freely Mixed farming/profit from trade & Puritan harshness led fishing these settlers north and inland. businesses 1626 New York Middle Peter Minuit-Dutch Royal charter from King to brother, Duke of York None Shipbuilding lumber Proprietary, then royal Trade and profits Mixed farming, furs 1638 Delaware Middle Peter Minuit& New Sweden Company Middle Lord Berkeley & Sir George Careret Names after island in England where Careret was born 1660 New Jersey 1682 Pennsylvania Middle William Penn Middle Colonies: “Breadbasket” Cultural Diversity Fertile soil Mild climate Cash crops German immigrants Wheat Mixed farming None Established by Sweden; taken by Dutch, then English. Known as “Lower Counties” Proprietary Trade and profits. None Proprietary None Proprietary Trade and profits Religious & Political freedom Set up as Dutch colony, taken over by English in 1664 New Amsterdam becomes NYC Mixed farming Wheat, mixed Religious freedom farming for Quakers (pacifists); trade and profits Established by Sweden; taken by English in 1664 Few Colonist/Mainly Native Americans " Originally Quaker, this colony became home to many European immigrants “Holy Experiment” diverse population Tobacco 1607 Virginia, Jamestown (1st permanent settlement) Anglican Southern John Smith London Company None (Anglican after 1692) Proprietary Maryland North Carolina 1634 Trade and profits, farming Founded as joint-stock company. House of Burgesses (1619). Only 60 of 1st 900 colonists survived. Establishes self-gov’t under House of Burgesses John Rolfe marries Pocahontas 1609-10 “Starving time” Bacon’s Rebellion – settlers don’t want to be restricted to the coast Tobacco & corn (don’t Religious freedom want to be for Catholics/trade dependent on 1 crop) Slow growing Act of Toleration Religious freedom to all Christians (1649) Royal Southern George Calvert 1653 Rice Southern Group of proprietors Anglican Proprietary 1585 Roanoke, NC 1670 Georgia 1733 Southern Group of proprietors Southern James Oglethorpe Anglican Proprietary Anglican Royal Trade and profits Debtor colony. Military buffer from Spanish Joint business venture Eliza Lucas – Indigo Colonists disappeared without a trace. Virginia Dare – 1st English child corn in New World. Establish English colony in New World Southern Sir Walter Raleigh South Carolina Trade and profits Rice Rice Rice major crop. Originally outlawed slavery and restricted size of land grants to Florida Southern Colonies: Warmer Climate Great rich soil Tobacco Rice Cash crops Slaves/indentured servants Tidewater – along sea coast Back Country – hills & forest climbing up App. Mts. Based on several sources, including The American Journey by Goldfield 500 acres.