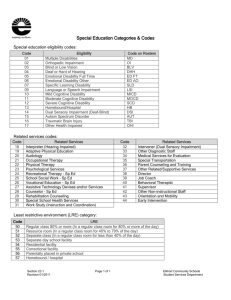
Eligibility Criteria and Determination Templates
advertisement

Effective Evaluation Resource Center USE OF ELIGIBILITY DETERMINATION TEMPLATES The Effective Evaluation Resource Center has developed a template of eligibility forms for each of the 13 eligibility categories specified in Indiana Article 7 (511 IAC 4). These templates include all necessary eligibility components or characteristics that the Case Conference Committee must consider when determining whether a disability exists. Districts or special education cooperatives should determine what evidence, criteria, and data sources are acceptable and necessary to establish eligibility. This information can be added to the provided templates. An example of a completed eligibility checklist, SLD Checklist with Examples 2011, is available on the EERC website. For SLD, the checklist can include signatures which would satisfy the Article 7 requirement (511 IAC 7-40-5(g)(2)(C)) for written certification of the multidisciplinary team members’ opinion regarding the presence of a SLD. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Checklist Autism spectrum disorder is a lifelong developmental disability that includes autistic disorder, Asperger’s syndrome, and other pervasive developmental disorders, as described in the current version of the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Other characteristics often associated include engagement in repetitive activities and stereotyped movements, resistance to environmental change or change in daily routines, and unusual responses to sensory experiences. (511 IAC 7-41-1) 1. Evidence that disability significantly affects verbal, nonverbal, or pragmatic communication Evidence A. B. C. D. No Yes No Yes No Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. 2. Evidence that disability significantly affects social interaction skills Evidence A. B. C. D. Data Sources A. B. C. D. 3. Evidence of disability prior to three years of age Evidence A. B. C. D. Data Sources A. B. C. D. 4. Evidence of adverse effect on academic achievement and/or functional performance and student’s need for specially designed instruction No Evidence A. B. C. D. Data Sources A. B. C. D. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Yes Educational Evaluation findings: ___ Yes, there is sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of an autism spectrum disorder. ___ No, there is not sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of an autism spectrum disorder. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Blind or Low Vision (BLV) Checklist Blind or low vision, which may be referred to as a visual impairment, means a disability that even with best correction affects the student’s ability to use vision for learning. (511 IAC 7-41-2) 1. Evidence of a reduced ability or a complete inability to utilize the visual system to acquire information. No Yes Evidence A. B. C. D. Data Sources A. B. C. D. AND/OR 2. Evidence of reduction in field of vision. No Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. 3. Evidence of adverse effect on academic achievement and/or functional performance and student’s need for specially designed instruction. No Evidence A. B. C. D. Data Sources A. B. C. D. Educational Evaluation findings: ___ Yes, there is sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of blind or low vision. ___ No, there is not sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of blind or low vision. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Yes Cognitive Disability (CD) Checklist A cognitive disability is manifested during the developmental period; is characterized by significant limitations in cognitive functioning; is demonstrated through limitations in adaptive behavior; and adversely affects educational performance. (511 IAC 7-41-3) 1. Evidence of significant limitations in cognitive functioning (two standard deviations below the mean for mild cognitive disability; three standard deviations below the mean for moderate cognitive disability; and four standard deviations below the mean for severe cognitive disability) that is manifested during the developmental period. No Evidence A. B. C. D. Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. 2. Evidence of delays in adaptive behavior across various environments and multiple sources (consistent with a mild, moderate, or severe cognitive disability) No Evidence A. B. C. D. Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. 3. Evidence of adverse effect on academic achievement and/or functional performance and student’s need for specially designed instruction. Evidence A. B. C. D. No Data Sources A. B. C. D. Educational Evaluation findings: ___ Yes, there is sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of a mild/moderate/severe (circle one) cognitive disability. ___ No, there is not sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of a cognitive disability. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Yes Deaf-blind (DB) Checklist Deaf-blind, which may be referred to as dual sensory impaired, are students that are both deaf and blind. (511 7-41-5) 1. Evidence of a concomitant hearing and vision loss or reduction in functional hearing and vision capacity No Yes Evidence Data Sources A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. 2. Evidence of significant communication deficits Evidence No Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. 3. Evidence of significant adaptive behavior deficits Evidence A. B. C. D. No Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. 4. Evidence of adverse effect on academic achievement and/or functional performance and student’s need for specially designed instruction Evidence A. B. C. D. No Data Sources A. B. C. D. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Yes Educational Evaluation findings: ___ Yes, there is sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of deaf-blind. ___ No, there is not sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of deaf-blind. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Developmental Delay (DD) Checklist Developmental delay is a disability category solely for students who are at least three years of age and not more than five years of age, or five years of age but not eligible to enroll in kindergarten. Developmental delay means a delay of either two (2) standard deviations below the mean in one (1) of the following developmental areas or one and one-half (1.5) standard deviations below the mean in any two (2) of the following developmental areas: (1) Gross or fine motor development, (2) Cognitive development, (3)Receptive or expressive language development, (4) Social or emotional development, (5) Self-help or other adaptive development. (511-IAC 7-41-6) 1. Evidence of a delay in gross or fine motor development No Yes Evidence A. B. C. D. Data Sources A. B. C. D. 2. Evidence of a delay in cognitive development Evidence A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. No Yes No Yes A. B. C. D. Data Sources A. B. C. D. 4. Evidence of a delay in social or emotional development Evidence Yes Data Sources 3. Evidence of a delay in receptive or expressive language development Evidence No Data Sources A. B. C. D. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) 5. Evidence of a delay in self-help or other adaptive development Evidence A. B. C. D. No Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. 6. Evidence of a delay of either two standard deviations below the mean in one of the developmental areas or one and one-half standard deviations below the mean in any two of the developmental areas. No Yes Educational Evaluation findings: ___ Yes, there is sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of developmental delay. ___ No, there is not sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of developmental delay. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Deaf or Hard of Hearing (DHH) Checklist Deaf or hard of hearing, which may be referred to as a hearing impairment, means a disability that, with or without amplification, affects the student’s ability to use hearing for learning. Students who are deaf or hard of hearing may use spoken language, sign language, or a combination of both. (511 IAC 7-41-4) 1. Evidence of a reduced ability or a complete inability to use hearing for developing language and learning and/or developmental progress, with or without amplification No Yes Evidence Data Sources A. B. C. D. 2. Evidence that the hearing loss is: A. B. C. D. permanent or Evidence Data Sources A. B. 3. Evidence that the hearing loss is: profound Evidence A. B. mild moderate Evidence A. B. moderately-severe Data Sources A. B. 4. Evidence that the hearing loss is: fluctuating A. B. unilateral or bilateral Data Sources A. B. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) severe 5. Evidence of adverse effect on academic achievement and/or functional performance and student’s need for specially designed instruction. No Yes Evidence A. B. C. D. Data Sources A. B. C. D Educational Evaluation findings: ___ Yes, there is sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of deaf or hard of hearing. ___ No, there is not sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of deaf or hard of hearing. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Emotional Disability (ED) Checklist Emotional disability means an inability to learn or progress that cannot be explained by cognitive, sensory, or health factors. The student exhibits one (1) or more of the following characteristics over a long period of time and to a marked degree that adversely affects educational performance: (1) A tendency to develop physical symptoms or fears associated with personal or school problems. (2) A general pervasive mood of unhappiness or depression. (3) An inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships. (4) Inappropriate behaviors or feelings under normal circumstances. (5) Episodes of psychosis. (511 IAC 7-41-7) 1. Evidence of a tendency to develop physical symptoms or fears associated with personal or school problems, over a long period of time and to a marked degree No Yes Evidence A. B. C. D. Data Sources A. B. C. D. 2. Evidence of a general pervasive mood of unhappiness or depression, over a long period of time and to a marked degree Evidence A. B. C. D. No Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. 3. Evidence of an inability to build or maintain satisfactory interpersonal relationships, over a long period of time and to a marked degree Evidence A. B. C. D. No Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. 4. Evidence of inappropriate behaviors or feelings under normal circumstances, over a long period of time and to a marked degree Evidence A. B. C. D No Data Sources A. B. C. D Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Yes 5. Evidence of episodes of psychosis No Evidence A. B. C. D. Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. 6. Evidence that Exclusionary Factors: cognitive, sensory, or health factors are NOT the primary factor for underachievement Evidence A. B. C. D. No Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. 7. Evidence of adverse effect on academic achievement and/or functional performance and student’s need for specially designed instruction Evidence A. B. C. D. No Data Sources A. B. C. D. Educational Evaluation findings: ___ Yes, there is sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of an emotional disability. ___ No, there is not sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of an emotional disability. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Yes Language or Speech Impairment (LI and/or SI) Checklist Language impairments are characterized by impairments in the comprehension or expression of spoken or written language resulting from organic or nonorganic causes that are nonmaturational in nature. Speech impairments may include fluency, articulation, and voice disorders in the student’s speaking behavior in more than one speaking task that are nonmaturational in nature, including impairments that are the result of deficiency of structure and function of the oral peripheral mechanism. Students who are deaf or hard of hearing or students with specific learning disabilities, who have language deficits or auditory processing difficulties, are not eligible for services designed solely for students with language impairments in lieu of services designed for students who are deaf or hard of hearing or students with specific learning disabilities. (511 IAC 7-41-8) 1. Evidence of a language impairment affecting the student’s primary language systems , in one or more of the following: word retrieval phonology morphology syntax semantics, and or pragmatics, that are nonmaturational in nature. No Evidence Yes Not Applicable Data Sources A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. 2. Evidence of a speech impairment affecting the student’s speaking behavior in more than one speaking task that may include: nonmaturational in nature. fluency articulation, and or voice disorder, that are No Evidence A. B. C. D. Yes Not Applicable Data Sources A. B. C. D. 3. Evidence that English Proficiency is NOT Primary Factor for language or speech delay. (A student who is bilingual or multilingual may be a student with a language or speech impairment only if the impairment is exhibited in all languages spoken by the student.) No Evidence A. B. C. D. Data Sources A. B. C. D. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Yes 4. Evidence of adverse effect on academic achievement and/or functional performance and student’s need for specially designed services. Evidence A. B. C. D. No Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. Educational Evaluation findings: ___ Yes, there is sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of a language impairment. ___ Yes, there is sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of a speech impairment. ___ No, there is not sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of a language and/or speech impairment. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Multiple Disabilities (MD) Checklist Multiple disabilities means coexisting disabilities that are lifelong and interfere with independent functioning, and it is difficult to determine which disability most adversely affects educational performance. The term does not include deaf-blind. (511 IAC 7-41-9) 1. Evidence of a significant cognitive disability Evidence A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. No Yes No Yes A. B. C. D. Data Sources A. B. C. D. 3. Evidence of the disabilities’ impact on independent functioning Evidence Yes Data Sources 2. Evidence of other, co-existing disability(ies) Evidence No Data Sources A. B. C. D. 4. Evidence of adverse effect on academic achievement and/or functional performance and student’s need for specially designed instruction. No Yes Evidence A. B. C. D. Data Sources A. B. C. D. Educational Evaluation findings: ___ Yes, there is sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of multiple disabilities. ___ No, there is not sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of multiple disabilities. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Other Health Impairment (OHI) Checklist Other health impairment means having limited strength, vitality, or alertness, including a heightened alertness to environmental stimuli, that results in limited alertness with respect to the educational environment (511 IAC 7-41-10). 1. Evidence of chronic or acute health problems, such as asthma, attention deficit disorder, or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, diabetes, epilepsy, a heart condition, hemophilia, lead poisoning, leukemia, nephritis, rheumatic fever, sickle cell anemia, and Tourette syndrome. No Evidence A. B. C. D. Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. 2. Evidence of adverse effect on academic achievement and/or functional performance and student’s need for specially designed instruction. Evidence A. B. C. D. No Data Sources A. B. C. D. Educational Evaluation findings: ___ Yes, there is sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination an other health impairment. ___ No, there is not sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of an other health impairment. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Yes Orthopedic Impairment (OI) Checklist An orthopedic impairment is a severe physically disabling condition that adversely affects educational performance (511 IAC 7-41-11). 1. Evidence of a severe physically disabling condition, such as a congenital anomaly; a disease, such as poliomyelitis or bone tuberculosis; or other causes, such as cerebral palsy, amputations, or fractures or burns that cause contractures No Yes Evidence A. B. C. D. Data Sources A. B. C. D. 2. Evidence of adverse effect on academic achievement and/or functional performance and student’s need for specially designed instruction Evidence A. B. C. D. No Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. Educational Evaluation findings: ___ Yes, there is sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination an orthopedic impairment. ___ No, there is not sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of an orthopedic impairment. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Checklist A traumatic brain injury is an acquired injury to the brain caused by an external physical force, resulting in total or partial functional disability or psychosocial impairment, or both, that adversely affects a student’s educational performance. The term does not apply to brain injuries that are: (1) congenital or degenerative; or (2) induced by birth trauma (511 IAC 7-41-13). 1. Evidence of open or closed head injury No Yes Evidence Data Sources A. B. C. D. A. B. C. D. 2. Evidence of functional disability or impairment in one or more of the following areas: cognition language memory attention reasoning abstract thinking judgment problem solving sensory, perceptual, and motor abilities psychosocial behavior physical functions information processing and speech. No Evidence A. B. C. D. Yes Data Sources A. B. C. D. 3. Evidence of adverse effect on academic achievement and/or functional performance and student’s need for specially designed instruction Evidence A. B. C. D. No Data Sources A. B. C. D. Educational Evaluation findings: ___ Yes, there is sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination a traumatic brain injury. ___ No, there is not sufficient evidence of all criteria to support determination of a traumatic brain injury. Effective Evaluation Resource Center, Blumberg Center, Indiana State University. (2012) Yes