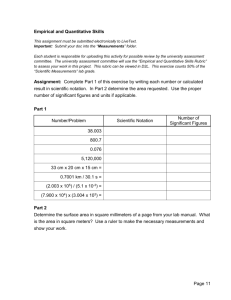
empirical data, knowledge
advertisement

Unit 1.2- Scientific Method 1.2 Scientific Method Empirical/ Non-empirical Data/ Evidence/ Knowledge Qualitative and Quantitative 4 Steps Observation Hypothesis Experiment Theory Scientific Law Formalized Hypothesis “If….then” method I Can Statements: 1. Define the word laureate 2. Explain the significance of the Nobel Prize 3. Explain what is meant by a Nobel Laureate 4. Explain the concept of and identify or state examples of empirical data, knowledge, or evidence” 5. Define and distinguish between the two types of empirical data, knowledge or evidence as well as identify or state examples of each A. Qualitative B. Quantitative 6. Explain the concept of and identify or state examples of Non-empirical data, knowledge, or evidence 7. Explain the concept of objective data, knowledge, or evidence and how it relates to empirical data, knowledge, or evidence 8. Explain the concept of subjective data, knowledge, or evidence and how it relates to nonempirical data, knowledge or evidence 9. Identify or state examples of subjective and objective data, knowledge, or evidence 10. List , identify, explain, and state examples of the 4 steps of the Scientific Method and explain what is meant by each step A. Observation B. Hypothesis C. Experiment D. Theory 11. Write a formalized hypothesis using the “If….then” method. 12. Define, explain, and state examples the difference between a scientific theory and a scientific law 13. Identify or state examples of scientific theories and laws 1 Vocabulary: Empirical data, knowledge, evidence Experiment Formalized hypothesis Hypothesis Laureate Nobel Laureate Nobel Prize Non-empirical data, knowledge, evidence Objective data, knowledge, evidence Observation Qualitative data, knowledge, evidence Quantitative data, knowledge, evidence Subjective data, knowledge, evidence Scientific Law Scientific Method Scientific Theory Achievement Scale: Goal 1.2 C Level B Level A Level Can define the word laureate Can explain the significance of the Nobel Prize Can explain what is meant by a Nobel Laureate Can explain the concept of empirical and non-empirical data, knowledge, or evidence Can define and distinguish between qualitative and quantitative empirical data, knowledge, or evidence Can explain the concept of objective and subjective data, knowledge, or evidence and how they relate to empirical and non-empirical data, knowledge, or evidence Can list and explain the 4 steps of the scientific method. Can write a formalized hypothesis Can define scientific theory and scientific law and explain the difference Can identify examples of empirical and nonempirical data, knowledge, or evidence Can identify examples of qualitative and quantitative empirical data Can identify examples of objective and subjective data, knowledge, or evidence Can identify examples of each of the 4 steps of the scientific method Can identify examples of scientific theories and laws Can state examples of empirical and nonempirical data, knowledge, or evidence Can state examples of qualitative and quantitative empirical data Can state examples of objective and subjective data, knowledge, or evidence Can state examples of scientific theories and laws Sample Questions: C Level: What is a Nobel Laureate? A person who has been honored by being awarded the Nobel Prize. What is empirical data, knowledge, or evidence and why is it considered to be objective data, knowledge, or evidence? Empirical data, knowledge, or evidence is gained through direct observation. It is objective because it does not depend on the view of the observer. 2 How is qualitative data, knowledge, or evidence different from quantitative data, knowledge, or data? Qualitative data, knowledge, or evidence is gained without benefit of measurements whereas quantitative data is always based on measurements. List the 4 steps of the scientific method and give a BRIEF description of each. Observation = notice the details of a particular phenomenon Hypothesis = ask a testable question about the phenomenon Experiment = collect data based on testable question Theory = attempt to explain phenomenon based on collected data Write a formalized hypothesis for the following statement. Temperature may cause leaves to change color. If leaf color change is related to temperature, then exposing a leaf to different temperatures will cause the leaf to change color. B Level: List the empirical and non-empirical data in the following: The white, crystalline solid melted at 750C. Non-empirical: white, crystalline Empirical: melted at 75oC Identify the objective and subjective information in the following: Sally said the test was difficult and that the average score was 72%. Subjective: the test was difficult Objective: average score was 72% A Level: Give an example of a scientific theory and a scientific law. THEORY: Galaxies may be moving away from each other due to momentum imparted to the universe during the Big Bang. Hubble's LAW: Hubble's law provides a concise method for measuring a galaxy's velocity in relation to our own. The movement of those galaxies can be traced backed to the Big Bang. 3