Unit 1 - Broken Arrow Public Schools
advertisement

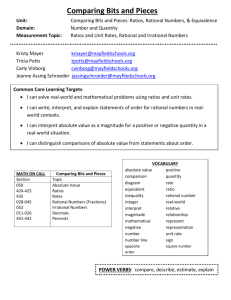
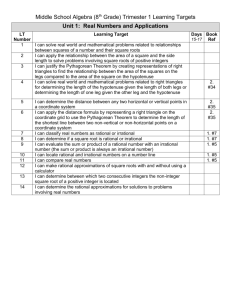
Grade/Course: Algebra I (First Semester) Instructional Unit 1: Understanding Quantities and Expressions Instructional Schedule: First Nine Weeks (suggested for 10 days) Adapted from Timothy Kanold Scope-and-Sequence documents Standards: Evidence Of Standard: (student should be able to…) Prerequisite Knowledge: (standards linked to content taught in previous grades) Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems. (supporting content) (BA/PASS 1.1c) Use units as a way to understand problems and to guide the solution of multi-step problems; choose and interpret units consistently in formulas of geometric models, science, and statistics to solve problems within an algebraic context; choose and interpret the scale and the origin in graphs and data displays. -Calculate unit conversions. -Recognize units given and/or needed to solve problems. (BA 1.1e) Define appropriate quantities for the purpose of descriptive modeling. Choose a level of accuracy appropriate to limitations on measurement when reporting quantities. -Define descriptive modeling: 1. Describing real-world events and the relationships between factors responsible for them. 2. Presenting main features and a summary of data. -Determine appropriate quantities for the purpose of descriptive modeling. -Use given units and the context of a problem as a way to determine if the solution to a multi-step problem is reasonable (e.g. length problems dictate different units than problems dealing with a measure such as slope). -Choose appropriate units to represent a problem when using formulas or graphing. -Interpret units or scales used in formulas or represented in graphs. -Use units as a way to understand problems and to guide the solution of multi-step problems. Assessment Tools: (formative assessments, quizzes, mastery tasks/activities) -Identify appropriate units of measurement to report quantities. -Determine the limitations of different measurement tools. -Choose and justify a level of accuracy and/or precision appropriate to limitations on measurement when reporting quantities. -Identify important quantities in a problem or real-world context. Interpret the structure of expressions. (key content) (BA/PASS 1.2a) Interpret parts of an expression, such as terms, factors, and coefficients. Simplify and evaluate linear, absolute value, rational, and radical expressions. (BA 1.2d) Interpret complicated expressions by viewing one or more of their parts as a single entity. For example, interpret 𝑃(1 + 𝑟)𝑛 as the product of P and a factor not depending on P. -For expressions that represent a contextual quantity, define and recognize parts of an expression, such as terms, factors, and coefficients as well as in terms of the context. - Simplify and evaluate linear, absolute value, rational, and radical expressions. -For expressions that represent a contextual quantity, interpret complicated expressions, that could include parentheses and exponents, by recognizing one or more of their parts as a single quantity. Use properties of rational and irrational numbers. (additional content) (BA 1.2) Explain why the sum or product of two rational numbers is rational; that the sum of a rational number and an irrational number is irrational; and that the product of a nonzero rational number and an irrational number is irrational. -Recognize the difference between rational and irrational numbers. -Use knowledge of properties of rational and irrational numbers to explain: 1. Why the sum or product of two rational numbers is rational. 2. Why the sum of a rational number and an irrational number is irrational. 3. Why the product of a nonzero rational number and an irrational number is irrational. Note: Any italicized text denotes portions of a given standard that do not apply to identified standard content in this unit. Resources/Exemplar Tasks: ( list possible task/activities students could engage in within this unit) Standards for Mathematical Practice: (highlight practice standards to be emphasized in the instructional unit) 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4. Model with mathematics. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 6. Attend to precision. 7. Look for and make use of instruction. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. ( BA: Broken Arrow rigor standard; PASS: Priority Academic Student Skills standard; BA/PASS: Combination standard )