2-1 Physical Properties of Water
advertisement

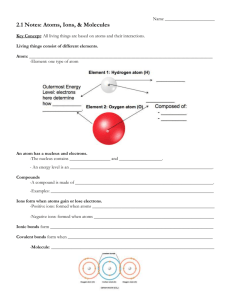
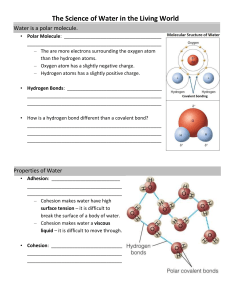
2-1 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF WATER Water All _______________ things depend on water for their existence. In most cells, water accounts for between _____% and _____% of the cell’s mass. o Exceptions include _______________ and _______________ that actually _______________ water. They can lie dormant for a long time, but _______________ will revive them. Proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids and membranes assume their characteristic _______________ because of water. Because water is an essential solvent and a substrate for many cellular reactions, much of the _______________ machinery of cells operates in an aqueous environment. Water is Polar Draw a 3D Lewis structure for water. Identify its molecular geometry and bond angle. Redraw it, and apply individual dipoles to the bonds. Does it have a net dipole? The presence of a net dipole means that the molecule is _______________. Hydrogen Bonding in Water Polar molecules exhibit _______________ forces, specifically _______________ _______________ forces. o If hydrogen is involved, it is called a _______________ bond. What conclusion can be drawn about the following enthalpy of formation values? Hf° Hydrogen Bond: –20 kJ/mol Hf° O–H covalent bond: –460 kJ/mol Hydrogen bonds are extremely important in biochemistry. For example, the attractions of complementary bases in a strand of DNA are H-bonds, which help hold DNA in its __________ __________ structure. Other intermolecular forces like __________ _______________ forces also play a role in the structures of biomolecules. The _______________ __________ of water is 4.184 J/g°C, which is high compared to many other liquids. A rather _______________ amount of heat is required to change the temperature of water. o Since 60-90% of a cell’s mass is water, this property allows temperature fluctuations to be _______________, a critical biological feature since reaction _______________ is sensitive to temperature changes. The heat of _______________ of water is 539.4 cal/g, which is another property that is much _______________ for water compared to other liquids. This means that water must absorb this much energy from its _______________ to evaporate. o This allows _______________ to be an effective method of _______________ body temperature since the water must remove heat energy from the body to evaporate. Water is an Excellent Solvent Solute and solvent interactions are governed by the simple rule “__________ _______________ __________.” Since water is polar, it will dissolve molecular substances that are __________ and __________ substances that have low _______________ energy. o These substances are called _______________ and are said to be _______________. Organic compounds that have polar functional groups will dissolve in water, and include _______________, _______________ __________, __________, _______________ and _______________ groups. o The more __________ groups on a molecule, the more soluble it will be. o The longer the _______________ chain on a molecule, the less soluble it will be. The behavior of solutes in cytoplasm is different than how they behave in water. o The _______________ of cytoplasm is higher than water because of the presence of sugars that contain many polar hydroxyl groups. o Charged molecules bind to each other momentarily inside cells, restricting their _______________. o Collisions with other molecules inhibit _______________ due to molecular _______________. Picture two aqueous solutions of different concentrations separated by a solventpermeable membrane. The dots represent the solute. o The solvent will pass from the lower-concentrated solution to the higherconcentrated solution in a process called _______________. o In order to prevent solvent flow, the _______________ of the system must be increased. This is called _______________ pressure. o In cells, the cell _______________ separates the highly-concentrated cytoplasm from the surrounding aqueous environment, and prevents water from entering the cell due to osmosis. To prevent cell bursting due to osmotic pressure, cells may _______________ many individual molecules into a larger _______________. For example, 50 000 glucose molecules can be stored as one _______________ molecule in animal cells. If enough water entered the cell to dissolve the 50 000 glucose molecules the cell would burst. Nonpolar Substances Nonpolar substances are _______________ in water. They are said to be _______________, and the interaction between nonpolar substances and water is called the _______________ __________. o This is critical for the _______________ of proteins and self – _______________ of biological membranes. Detergents (or surfactants) have a _______________ end and a _______________ end: O Ex: Sodium dodecyl sulfate + Na O - S O O o These molecules are said to be _______________. o Form micelles (shown below) – nonpolar ends trap grease and oils while the polar end remains hydrated, allowing them to be washed away. Some dissolved ions such as thiocyanate (SCN–) and perchlorate (ClO4–) called _______________ enhance the solubility of nonpolar compounds in water by disordering the water molecules.