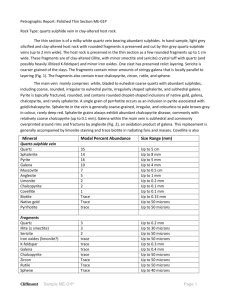
instructions to authors for the preparation - The Gibson Group
advertisement
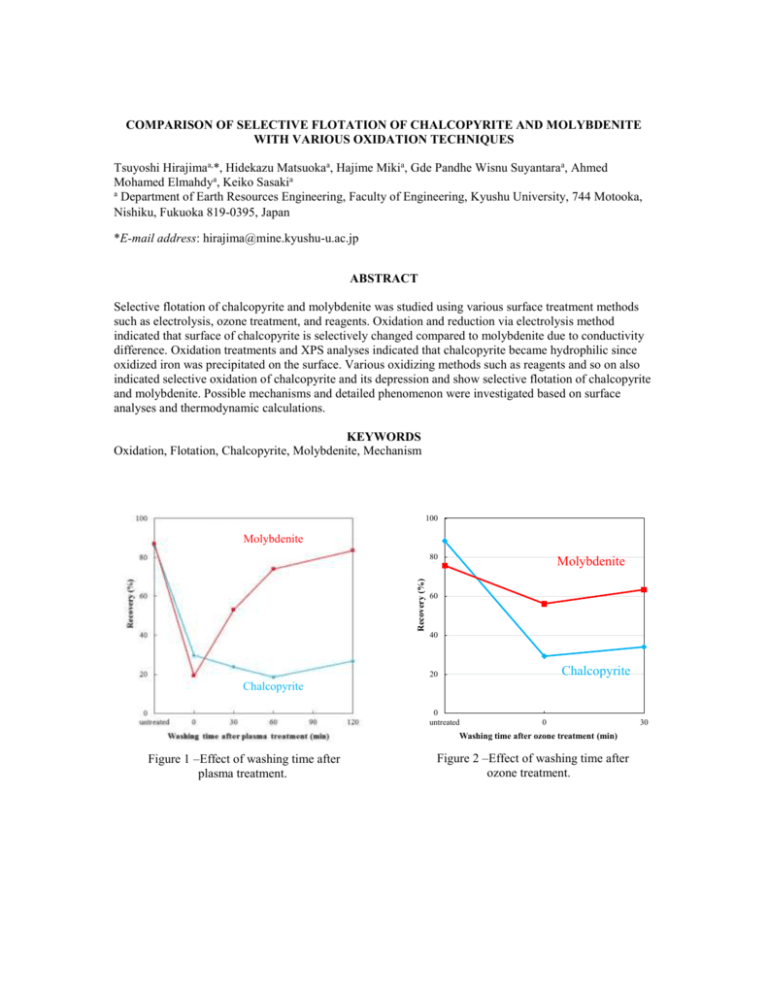
COMPARISON OF SELECTIVE FLOTATION OF CHALCOPYRITE AND MOLYBDENITE WITH VARIOUS OXIDATION TECHNIQUES Tsuyoshi Hirajimaa,*, Hidekazu Matsuokaa, Hajime Mikia, Gde Pandhe Wisnu Suyantaraa, Ahmed Mohamed Elmahdya, Keiko Sasakia a Department of Earth Resources Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, 744 Motooka, Nishiku, Fukuoka 819-0395, Japan *E-mail address: hirajima@mine.kyushu-u.ac.jp ABSTRACT Selective flotation of chalcopyrite and molybdenite was studied using various surface treatment methods such as electrolysis, ozone treatment, and reagents. Oxidation and reduction via electrolysis method indicated that surface of chalcopyrite is selectively changed compared to molybdenite due to conductivity difference. Oxidation treatments and XPS analyses indicated that chalcopyrite became hydrophilic since oxidized iron was precipitated on the surface. Various oxidizing methods such as reagents and so on also indicated selective oxidation of chalcopyrite and its depression and show selective flotation of chalcopyrite and molybdenite. Possible mechanisms and detailed phenomenon were investigated based on surface analyses and thermodynamic calculations. KEYWORDS Oxidation, Flotation, Chalcopyrite, Molybdenite, Mechanism 100 Molybdenite Recovery (%) 80 Molybdenite 60 40 Chalcopyrite 20 Chalcopyrite 0 untreated 0 Washing time after ozone treatment (min) Figure 1 –Effect of washing time after plasma treatment. Figure 2 –Effect of washing time after ozone treatment. 30