Regional Characteristics
advertisement

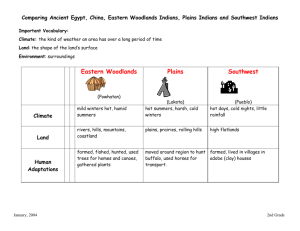
Northwest Coast Region • • • • • • • • Cold winters, cool summers heavy rainfall thick fur spruce and cedar forests Enjoyed seafood from the Pacific Ocean Built wooden houses with planked sides and gabled roofs. Had painted and carved tree trunks called totem poles. These poles honored their many gods and spirits. Each village was ruled by a few rich families. Wealth was measured by possessions such as canoes, blankets and slaves. California Region • • • • • • • Winter rains, hot dry summers coastal foothills, valleys, deserts, mountains oak trees with acorns – Great Basin Area – desert, low grasses, sagebrush – small animals, such as rabbit and lizards Houses were thatched or made of earth Hunted, fished, and collected wild plants, seeds and nuts. Acorns were ground to make flour and mush. Life was more difficult for those living away from the coast in the Great Basin area. Plateau Region • • • Cold winters, gentle summers large rivers abundant fish Southwest Region • • • • • • • • Canyons, mountains, desert, mesas dry, hot climate Colorado River and Rio Grande Huge dry region In the north are steep canyons South is flat, desert country. Early southwest Indians built cliff houses. Cliff dwellers built on the sides of cliffs to protect themselves from enemies. Later had many-storied houses made of adobe. People entered by climbing ladders to the roof. Ladders could then be taken up to keep enemies out. Great Plains Region • • • • • • • • • Treeless grassland dense grasses more water and softer soil in eastern part of the region. Before the arrival of Spanish explorers in the 1500’s few lived in this region. Women grew crops of beans, corn, squash, and tobacco. During the summer, men hunted deer, elk, and sometimes buffalo. Buffalo were difficult to hunt on foot. Natives tried to stampede herds over cliffs. Explorers came with both guns and horses. When they returned to Spain, they left their horses behind. Made hunting much easier. Other nearby tribes forced west by White settlers came and adopted the plains way-of- life. Apache, Arapaho, Blackfeet, Cheyenne, Comanche, and Sioux were some of those moving to the plains. Communication was difficult so they developed a system of sign language. Eastern Woodland Region • • • • • • • • Snowy winters, rainy summers thick forests many lakes Iroquois tribes controlled the Northeast area. The Iroquois League was the most powerful group. Had Iroquois Great Law of Peace. Enjoyed good fishing and hunted. Houses were domed-shaped wigwams covered with bark. Some were long. A number of related families would live together in the long houses. Among first Natives to meet Europeans Southeast Region • • • • • • Warm, humid summers, mild winters coastal plains, river valleys mountains, swamps Lived in thatched huts called chickees which had raised floors and open sides. Many groups were warlike. Before battle they painted themselves and held ceremonies worshipping their many gods. In peace celebrations the peace pipe was smoked. Far North Region • • • • Cold climate Few lived in this region Short growing season made food scarce. Fished, hunted caribou, moose, and deer.