Climate and Vegetation
advertisement

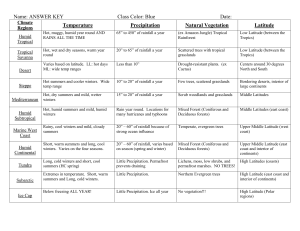
Chapter 3 – Climates of the Earth Earth-Sun Relationships A. ________________: condition of the atmosphere in one place during a short period of time 1. _______________: weather patterns typical for an area over a long period of time B. Earth’s position in relation to the _________ is the most important factor in climate 1. Earth is currently tilted about _________ on its axis 2. _________: an imaginary line that runs through the center of the Earth between the North and South Poles 3 Revolution: in astronomy, the Earth's yearly trip around the sun, taking _________ days a. Earth’s _________ creates seasons as it revolves around the sun b. Seasons in the ________________ and ________________ Hemispheres are reversed 4. ________________: one of two days (about March 21 and September 23) on which the sun is directly above the Equator, making day and night equal in length 5. ________________: one of two days on which the sun's rays strike directly on the Tropic of Cancer or Tropic of Capricorn, marking the beginning of summer or winter a. Tropic of ________________: latitude line at 23½° N b. Tropic of ___________________: latitude line at 23½° S 6. ___________________ __________: continuous daylight, or where the sun is visible at midnight during the summer in either the Arctic (66½° N) or Antarctic Circle (66½° S) C. ___________________ ______________: the capacity of certain gases in the atmosphere to trap heat, thereby warming the Earth Factors Affecting Climate A. Earth’s annual revolution around the sun creates ___________________ climate patterns that correspond with bands, or zones, of latitude. 1. Low latitude (_______________) zone: between 30° S and 30° N a. ___________ all year; precipitation varies with wind patterns 2. High latitude (_______________) zones: 60° N to 90° N and from 60° S to 90° S a. Long, cold winters; short, cool summers McGraw-Hill (2015) 1 3. Midlatitude (______________________) zones: 30° N and 60° N and 30° S and 60° S a. Four distinct seasons: ___________, summer, ___________, winter 4. ___________________ influences climate: thinning atmosphere causes temperatures to decrease 3.5°F for each 1,000 feet B. Winds and ocean currents distribute _____________ around the planet 1. ________________: cold or warm stream of seawater that flows in the oceans, generally in a circular pattern 2. ____________________ ____________: wind in a region that blows in a fairly constant directional pattern 3. ________________ ________________: the resulting diagonal movement, either north or south, of prevailing winds caused by the Earth's rotation 4. ___________________: a frequently windless area near the Equator 5. ______ _________: a periodic reversal of the pattern of ocean currents and water temperatures in the mid-Pacific region 6. Mountain _____________ affect climate: as warm, moist air is pushed upward, it cools and condenses which fall as precipitation on the windward side of the mountains a. __________________: being in or facing the direction from which the wind is blowing: b. ________________: being in or facing the direction toward which the wind is blowing c. __________ ________________: result of a process by which dry areas develop on the leeward sides of mountain ranges Climate Regions and Biomes A. __________ climate zones support different kinds of biomes: 1. ________________: a major type of ecological community defined primarily by distinctive plant and animal groups 2. _________________ ___________________: plant life that grows in a certain area if people have not changed the natural environment 3. Two main factors affect the distribution of Earth’s biomes: a. ________________ b. ________________: physical characteristics of the surface of the land McGraw-Hill (2015) 2 B. Tropical Climates: in or near _________ latitudes 1. Tropical __________ ________________: average daily temperature of 80°F; average annual rainfall 50-260 inches a. Average Daily ___________________: the average of the daily high temperature and the overnight low; often used for comparison across climate regions b. Thick ___________________ that grows in layers; tall trees form a canopy shading the forest floor c. Abundant wildlife; more than half of all of the ___________ and _________________ species exist in the tropical rain forests 2. Tropical ____________: pronounced dry and wet seasons; high year-round temperatures a. Called ___________________; fewer plants and animals; sunlight not blocked by trees C. Dry Climates: occur in _________ latitudes and midlatitudes 1. Semi-arid (_____________): away from large bodies of water; annual rainfall 10-30 inches a. ___________ summers and harshly ___________ winters; home to a diverse variety of grasses 2. Arid (________________): extremely dry; less than 10 inches of rain per year a. Support a small amount of ___________ and animal life b. Usually hot and dry; some do experience ___________ c. ____________: small area in a desert where water and vegetation are found D. Midlatitude Climates: ___________ temperate climate regions 1. ______________ ___________________: short, mild winters and nearly year-round rain a. ________________: an inland grass area b. ___________________ Trees: having cones and needle-shaped leaves, including many evergreens, that keep their foliage throughout the winter c. ___________________ Trees: falling off or shed seasonally or periodically; trees such as oak and maple, which lose their leaves in autumn 2. _____________ _____________ _____________: cool summers and cool, damp winters; abundant rainfall a. Mixed Forest: both coniferous and ___________________ trees 3. ______________________: mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers a. Natural vegetation includes thickets of woody ______________ and short trees McGraw-Hill (2015) 3 4. _____________ _____________________: no moderating effect of ocean winds because of inland locations a. Further north, winters become ___________ and more severe; summers ___________ and cooler b. ___________________ is similar to that found in marine west coast areas E. High-latitude Climates: ___________________ temperatures are common all year 1. Limited amount of ___________________ 2. ________________ Climate: just south of the Arctic Circle a. Bitterly ___________ winters; summers are short and ___________ b. ____________________: permanently frozen layer of soil beneath the surface of the ground 3. ________________ Climate: close to the poles a. Months of ___________________ and bitter cold; limited warming in summer b. ___________ cannot grow; low bushes, short grasses, mosses, and lichens 4. ___________ ___________ Climate: polar regions a. ___________ and ___________; often more than 2 miles thick b. ________________ are the only vegetation F. ________________ ________________: major changes in the factors used to measure climate over an extended period of time 1. Earth undergoes natural and predictable _____________ of cooling and warming caused by factors such as solar flares and volcanic activity McGraw-Hill (2015) 4