Send help fast!!!
advertisement

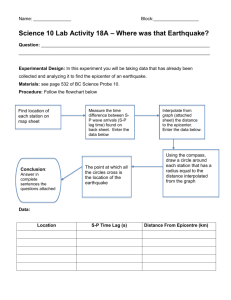
Send help fast!!! Virtual Lab Background There’s just been a serious earthquake! You are the seismologist on a team of professionals that needs to determine where to send rescue workers, ambulances, helicopters, and emergency supplies. I. Epicenter & Magnitude 4. Follow the directions on screen to find the epicenter of the earthquake. III. Summarize the steps you had to follow to find out where the epicenter was. What do you need to figure out in order to know where to send these resources? To Begin 1. Enable pop-ups on your browser. 2. Go to the Virtual Earthquake lab from CSU Los Angeles. (See the link on my web page.) Lag Time 3. Under Main Activities, click on “Travel Time.” Follow the directions on the screen to begin. a. E represents the epicenter of the quake. Place the seismograph stations (red numbers) in order from 1-5 from closest to farthest from the epicenter. b. Trigger the quake. c. Collect the distance and lag time data. II. What is the relationship between the distance from the epicenter and the S-P lag time? IV. Where should you send the disaster relief supplies and rescue personnel? Why? Vocabulary Word Bank: epicenter focus fault earthquake lag time Vocabulary seismograph 1. __________________ A break or crack in the ground that causes earthquakes when the rock moves 2. __________________The difference between the time when the fast P- Word Bank: epicenter focus fault earthquake lag time seismograph 1. __________________ A break or crack in the ground that causes earthquakes when the rock moves 2. __________________The difference between the time when the fast P- waves of an earthquake arrive and the time when the slower S-waves waves of an earthquake arrive and the time when the slower S-waves arrive at a seismograph station arrive at a seismograph station 3. __________________ The place underground where all the earthquake waves start 4. __________________ The place on the surface of the ground that is above where the earthquake begins 5. __________________ Shaking of the ground caused by sudden movement of rocks along a fault 6. __________________ A machine used to measure the waves caused by earthquakes 3. __________________ The place underground where all the earthquake waves start 4. __________________ The place on the surface of the ground that is above where the earthquake begins 5. __________________ Shaking of the ground caused by sudden movement of rocks along a fault 6. __________________ A machine used to measure the waves caused by earthquakes