Ch.5 HW
advertisement

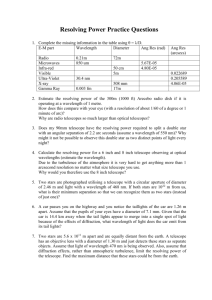
Name _____________________ Chapter 5 Homework 1. What technique allows scientists can use a few smaller telescopes to take images with the same resolution as a much larger telescope? 2. To triple the resolving power of a telescope, what must you do to its diameter? 3. What is the best way to observe a warm dust cloud in which stars are forming? 4. What is the best way to observe a galaxy with almost no starlight but plenty of cool clouds of hydrogen gas? 5. What is a false color image? Are the posters on the ceiling in my classroom false color? 6. Ignoring the effects of the atmosphere, what is the theoretical resolution of an 8 inch telescope (about 20 cm) if you are looking at visible light with a wavelength of about 500 nm? 7. If your pupils have a diameter of about 5mm, about how many times more light gathering power does a telescope with a diameter of about 20 cm (8 inches) have than your pupils? 8. What property of light affects the resolving power of a telescope? 9. What is one of the biggest problems for ground based astronomy today? 10. What are the two most important properties of any telescope? 11. Why does a pencil inside a water glass appears to be bent? 12. Why does the Sun look flattened near the horizon? 13. Why does the Moon appear bigger near the horizon? 14. What are the disadvantages of using a lens in a large telescope? 15. What do we call the ability of a telescope to show two very close objects separately? 16. Vining has a 5-inch refracting telescope and Hill has a 3-inch reflecting telescope. Whose telescope has a higher light-gathering power? Whose telescope has a higher resolving power? 17. In astronomy, what is "seeing"? 18. What is he best site for placing an X-ray telescope? Optical telescope? 19. An interstellar gas is emitting 10-centimeter wavelength radiation and a nearby star is emitting 10micrometer wavelength radiation. Which of these can you observe through an Earth-based telescope? 20. What prevents us from viewing objects that produce X-rays on the surface of the Earth? 5-1 21. Why do stars twinkle? 22. What is the most efficient detector for observing visible light through a telescope? 23. Which space telescope is observing X-rays? 24. What is an inherent disadvantage of radio telescopes? What do we observe with radio telescopes? 25. What is the most important quality of an astronomical telescope? 26. Compare the light-gathering power of a telescope with a 10-centimeter (about 4-inch) diameter mirror to that of the human eye. (Take the diameter of the pupil of the eye to be about 5 millimeters.) 27. Can the unaided human eye resolve a crater on the Moon whose angular diameter is 1 minute of arc (560 seconds of arc)? (Take the diameter of the pupil of the eye to be about 5 millimeters and the wavelength of the light to be 500 nanometers.) 28. Compute the collecting area of the 27 telescopes in the VLA radio interferometer if each has a diameter of 25 m. If this were a collecting area of a single dish, what would be its diameter? 5-2