Components of the Prokaryotic Cell and their Relationship to
advertisement

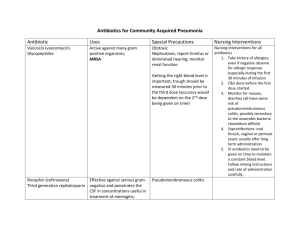
Components of the Prokaryotic Cell and their Relationship to Disease (Ability to cause, diagnose of, treatment, etc…) Glycocalyx o Capsule form prevents phagocytosis and therefore allows the bacterium to cause disease o Also may allow the bacterium to adhere to host tissues o Allows some cells to form biofilm Flagella o Allow cells to move to target tissues o The H antigen protein can be used to distinguish between strains for identification (E. coli H7:0157) Axial filaments of spirochetes allow the bacterium to move through bodily fluids Fimbriae function in attachment forming biofilm and attachment to bodily surfaces (N. gonorrhoeae and E. coli H7:0157) Conjugation pili allow cells to exchange DNA in a process called conjugation (may give antimicrobic resistance to the other cells) Cell Wall o Site of action of penicillin (prevents the formation of new peptidoglycan by interfering with the linkage of peptidoglycan rows by peptide cross-bridges) o Site of action of lysozyme (hydrolyzes the bonds between NAG and NAM o Other antibiotics, such as beta-lactams enter more easily through the OM of G- cell walls and are more effective than other antibiotics o Polysaccharides in streptococci group them into medically important types Gram + cell walls o Gram stain used to identify for diagnosis and treatment options o Teichoic acids are antigens and can be used to diagnose Gram + types of bacteria Acid fast cell walls (Mycobacterium) contain a waxy substance that can be differentially stained for diagnosis Gram – cell walls o Gram stain used to identify for diagnosis and treatment options o Outer membrane of Gram – bacterial cell walls Contains LPSs (an endotoxin) – Lipid A portion (embedded in lipid of OM) when released, causes fever, dilations of blood vessels, shock, blood clotting O polysaccharide (sticking out into outer environment) is an antigen and can be used to diagnose specific types of bacteria (E. coli H7:0157) o OM is another semipermeable structure capable of restricting the movement of antibiotics and other harmful substances from entering the cell o OM has a strong negative charge which helps the cell evade our defense system (inhibits phagocytosis and complement) Plasma membrane o A semipermeable structure that may prevent some antimicrobics from entering the cells o Detergents and some disinfectants (alcohols and quaternary ammonium compounds) disrupt the lipid bilayer o Some antibiotics (polymyxins) cause leakage through the plasma membrane and cell death o Glycoproteins and glycolipids serve as binding sites DNA: bacterial chromosome or plasmids o May contain genes for resistance or virulence factors o May be transferred to other cells through transformation or conjugation o May be the site of action of antibiotics or other antimicrobics (sulfa drugs)- prevention of DNA synthesis will not allow the cell to reproduce Ribosomes o Function in protein synthesis- many antibiotics function to prevent or disrupt protein synthesis specifically in bacteria (streptomycin, tetracycline) Inclusions o Specific inclusion materials may be specific to certain cells and therefore used for diagnostic purposes Endospores o Allow cells to survive in the presence of many substances and in environments that would normally kill the vegetative cell o Important in the food industry (for example, boiling does not destroy the endospore for many hours) Enzymes – Often the site of antimicrobic agents o Denature proteins o Enzyme inhibition