5.Study Design - TransCelerate BioPharma Inc.
advertisement

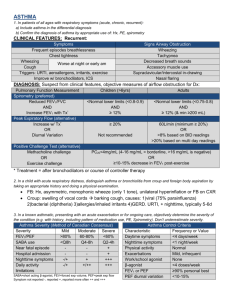
Common Protocol Template Asthma Library v2.0 Common Protocol Template Asthma Library v2.0 Section in Common Protocol Template (CPT) Library Content 1. Protocol Synopsis Objectives and Endpoints Protocol Synopsis Objectives and Endpoints 4. Objectives and Endpoints Objectives and Endpoints 5. Study Design Instructional text including Definitions of Common Assessments 10.3 Statistical Analyses Instructional text 11. References References applicable to the Asthma library Pulmonary Function Test Manual (not included with this template) Instructional text on suggested content for the Pulmonary Function Test Manual (not included with this template) 1. Synopsis Objectives and Endpoints and 4. Objectives and Endpoints (main body) Objectives Endpoints Primary To evaluate the efficacy of [x mg of Study Treatment] administered [frequency] to subjects with [severity of asthma] asthma Spirometry FEV1 The absolute change in the percentage of predicted FEV1 from baseline to [Week X] OR To evaluate the efficacy of [x mg of Study Treatment]administered [frequency] compared with [comparator] in participants with [severity of asthma] asthma © 2015 TransCelerate BioPharma OR The increase [magnitude of change] in FEV1 from baseline to [Week X] 1 Common Protocol Template Asthma Library v2.0 Objectives Endpoints Secondary To evaluate the efficacy of [x mg of Study Treatment] administered [frequency] to subjects with [severity of asthma] asthma To evaluate the efficacy of [x mg of Study Treatment]administered [frequency] compared with [comparator] in participants with [severity of asthma] asthma Forced Vital Capacity(FVC) The absolute change in the percentage of predicted FVC from baseline to [Week X] FEV1/FVC Ratio or % The change from baseline in FEV1/FVC (or change in the percentage from baseline) to [Week X] Asthma Symptoms Clinical Asthma Exacerbations (CAEs) The incidence of severe CAEs compared to control at [Week X] The incidence of moderate CAEs compared to control at [Week X] Examples of CAEs include the following: Hospitalization, emergency room (ER), or Urgent Care (UC) treatment with systemic steroids Initiation or increased dose (from a stable maintenance dose) of systemic corticosteroids (tablets, suspension, or injection) for at least 3 days to prevent a serious outcome Asthma-specific ICU admissions/intubations Asthma-related deaths © 2015 TransCelerate BioPharma Rescue Medication The reduction in number of rescue occasions compared to control at [Week X] 2 Common Protocol Template Asthma Library v2.0 Objectives Endpoints Exploratory To evaluate the allergic response to [x mg of Study Treatment to the skin prick test] Allergen Skin Test The response to the standard skin prick test at [Week X] 5.Study Design Definitions of Common Assessments Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second (FEV1) is the volume (L or mL) of air that is exhaled in the first second of a forced spirometry test. Percent Predicted FEV1 is the participant’s best FEV1 for the assessment divided by the participant’s predicted normal value multiplied by 100. Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) is the volume of air expired over the course of a forced, maximal exhalation after a full inhalation. It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and expiratory reserve volume. Percent Predicted FVC is the FVC value divided by the participant’s predicted normal value, multiplied by 100. Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) is the maximal flow rate (L/sec or L/min) achieved during a maximally forced exhalation. The PEF is quite variable and not recommended as a primary endpoint. Percent Predicted PEF is the maximal flow rate achieved during a maximally forced exhalation divided by the participant’s predicted normal value. FEV1/FVC Ratio (or percentage) provides a measure of the proportion of total FVC that is expelled during the first second of a forced exhalation. This measure is a good index of airflow obstruction. FEF25-75 is forced expiratory flow at 25% to 75% of vital capacity, also called maximal mid-expiratory flow (L/sec). Percent predicted FEF25-75 is the FEF25-75 value divided by the participant’s predicted normal value, multiplied by 100. © 2015 TransCelerate BioPharma 3 Common Protocol Template Asthma Library v2.0 10.3 Statistical Analyses 11.0 References Reddel HK, Taylor DR, Bateman ED, et al. An official American Thoracic Society / European Respiratory Society statement: asthma control and exacerbations: standardizing endpoints for clinical asthma trials and clinical practice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 180(1);59-99. Chung KF et al. ERS/ETS Guidelines on severe asthma Eur Respir J 2014; 43:343-373. Quanjer PH, Tammeling GJ, Cotes JE et al. Lung volumes and forced ventilator flows. Report Working Party Standardization of Lung Function Tests, European Community for Coal and Steel. Official Statement of the European Respiratory Society. Eur Respir J 1993; 6:Suppl. 16:5-40. Tojo N, Suga H, Kambe M. Lung Function Testing – The Official Guideline of the Japanese Respiratory Society. Rinsho Byori 2005 53(1):77-81. Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC), Version 1 of Therapeutic Area Data Standards User Guide for Asthma, November 26, 2013. © 2015 TransCelerate BioPharma 4