2010 PALS Algorithms
advertisement

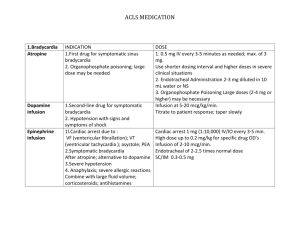
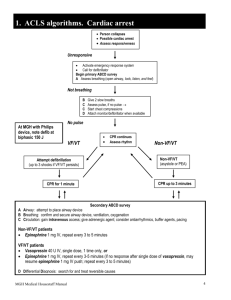
PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT 2010 Algorithms Florida Heart CPR* Wabasso, Florida 32958 866-388-5252 Web: floridaheartcpr.com Revised January 2011 1 Ventricular Fibrillation and Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia ↓ Start high quality CPR Give oxygen, attach monitor/defibrillator ↓ As soon as possible, measure child with BROSELOW tape Defibrillate 2j/kg ↓ Continue CPR (no pulse check) Obtain IV or IO access ↓ Epinephrine IV/IO: 0.01 mg/kg 1:10,000 *USE BROSELOW DOSE* Repeat q3-5 minutes If no IV/IO access, may give ET dose: 0.1 mg/kg (0.1mL/kg of 1:1000 concentration (consider advanced airway with capnography or capnometry) ↓ Defibrillate 4j/kg ↓ Amiodarone 5 mg/kg * USE BROSELOW DOSE* (may be repeated up to 2 times in refractory V-fib/PVT) ↓ Defibrillate 4j/kg ↓ Epinephrine ↓ Defibrillate 4j/kg ↓ Amiodarone Treat reversible causes Hypovolemia Hypoxia Hydrogen ion (acidosis) Hypoglycemia Hypo/hyperkalemia Hypothermia Tension Pneumothorax Tamponade, cardiac Toxins Thrombosis, pulmonary Thrombosis, coronary 5 mg/kg ↓ Defibrillate 4j/kg Never stop CPR for more than 10 seconds: If organized rhythm check pulse; if ROSC, start post-cardiac arrest care Revised January 2011 2 Pediatric Asystole/PEA Check pulse/begin high quality CPR ↓ Secure Airway Ventilate with 100% O2 ↓ Obtain vascular access, IV or IO ↓ As soon as possible, measure child with BROSELOW tape Epinephrine IV/IO: 0.01 mg/kg 1:10,000 *USE BROSELOW DOSE* (ET: 0.1 mg/kg 1:1,000) ↓ Repeat Epinephrine q3-5 minutes While providing high quality CPR ↓ Consider advanced airway w/capnography Identify & treat reversible causes: Hypoxemia Hypovolemia Hypothermia Hyper/hypokalemia & metabolic disorders Tamponade Tension pneumothorax Toxins/ poisons/ drugs Thrombosis-pulmonary Thrombosis-coronary **Patients who do not respond to several doses of epi with no extenuating circumstances should be considered for termination. Revised January 2011 3 Bradycardia Assess ABCs Maintain patent airway, assist breathing if necessary Administer 100% O2 Cardiac monitor, IV/IOaccess Assess BP, oximetry ↓ Cardiorespiratory compromise? Acutely altered mental status? Signs of shock? NO ←←←←← →→→ YES Support ABC’s, oxygen Observe, consider Expert consultation Begin chest compressions if pulse is ,<60bpm ↓ Epinephrine *USE BROSELOW DOSE* IV/IO: 0.01 mg/kg 1:10,000 ET: 0.1 mg/kg 1:1,000 ↓ (Repeat Epinephrine q3-5 minutes) ↓ For increased vagal tone or primary AV Block: Atropine (Max single dose: 0.5 mg for child) Consider transthoracic/transvenous pacing Treat underlying causes Toxins Tamponade Tension Pneumothorax Thrombosis Trauma Revised January 2011 Hypoxia Hypoglycemia Hypothermia Herniation of brain stem Heart Transplant 4 Stable Ventricular Tachycardia Unstable Ventricular Tachycardia (Child has normal v/s) (w/signs of poor perfusion) Assess ABCs ↓ Secure airway Administer oxygen ↓ EKG and pulse oximeter Assess vital signs ↓ Establish IV/IO Labs ↓ Consider ADENOSINE* *USE BROSELOW DOSE* Assess ABCs ↓ Secure airway Administer oxygen ↓ EKG & pulse oximeter Assess vital signs ↓ Establish IV/IO Labs ↓ Assemble code/suction equipment ↓ Immediate synchronized cardioversion 0.5- 1.0 j/kg if wide/regular QRS (monomorphic) ↓ Expert consultation advised; consider Amiodarone Procainamide If unsuccessful, increase to 2j/k ↓ (sedate if needed, but don’t delay cardioversion) ↓ Consult pediatric cardiologist! Details/doses Wide (>0.09 sec) Amiodarone IV/IO dose: Narrow (< or = 0.09 sec) 5mg/kg over 20-60 min. Adenosine IV/IO dose: Procainamide IV/IO dose: 1st dose: 0.1 mg/kg, max 6mg 15mg/kg over 30-60 min. 2nd dose:0.2 mg/kg max 12 mg Do not routinely administer Amiodarone and Procainamide together Revised January 2011 5 Unstable Stable Supraventricular Tachycardia Supraventricular Tachycardia Assess ABCs ↓ 12 Lead EKG Administer oxygen ↓ Vital signs, IV/IO, Labs ↓ Consider vagal maneuvers ↓ Adenosine* 0.1mg/kg IV rapidly followed by rapid flush (may double dose and repeat) ↓ Consider synchronized cardioversion or alternate medication ↓ Consult pediatric cardiologist Assess ABCs ↓ 12 Lead EKG Administer oxygen ↓ Vitals, IV/IO, Labs ↓ Consider vagal maneuvers ↓ Immediate synchronized cardioversion 0.5- 1.0j/kg Sedate if possible (but do not delay cardioversion) OR Adenosine* 0.1 mg/kg IV rapidly followed by rapid flush may double and repeat *USE BROSELOW DOSE Details Probable sinus tachycardia: Compatible history consistent with known cause P Waves present/normal Variable R-R; constant PR Infants: rate usually < 220/min Children: rate usually < 180/min Search for and treat reversible causes Revised January 2011 Probable supraventricular tachycardia Compatible history (vague, non-specific) History of abrupt rate changes P waves absent/abnormal HR not variable Infants: rate usually >220/min Children: rate usually >180/min Consider vagal maneuvers, consider Adenocard If IV/IO access not available, or if adenosine not effective, synchronized cardioversion 6 **CONSULT BROSELOW FOR DOSES*