artificial neural networks The computational changes in the last
advertisement

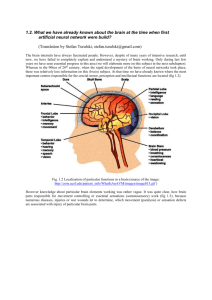
artificial neural networks The computational changes in the last several decades have brought growth to new technologies. One of these technologies is artificial neural networks (ANNs). Over the years, ANNs have given various solutions to the industry. Designing and implementing intelligent systems have become an important activity for the innovation and development of better products for human life. Examples might include the case of the implementation of artificial life and giving solution to interrogatives that linear systems are not able to resolve .An ANN is a mathematical model to deal with the information that is inspired by the way biological nervous system, such as the brain, performs in information processing. A key element in this model is the structure of this novel information processing system. The system is adaptive and is consisting of a large number of interrelated processing elements (neurons) working together to solve specific problems. Artificial Neural Networks can be viewed as parallel and distributed processing systems which consists of a huge number of simple and massively connected processors. Biological neural network The concept of ANN is basically introduced from the subject of biology, where neural network plays a important and key role in human body. In human body work is done with the help of neural network. Neural Network is just a web of inter connected neurons which are millions and millions in number. With the help of this interconnected neurons all the parallel processing is done in human body and the human body is the best example of Parallel Processing. A neuron is a special biological cell that process information from one neuron to another neuron with the help of some electrical and chemical change. It is composed of a cell body or soma and two types of out reaching tree like branches: the axon and the dendrites. The whole process of receiving and sending signals is done in particular manner like a neuron receive signals from other neuron through dendrites. The Neuron send signals at spikes of electrical activity through a long thin stand known as an axon and an axon splits this signals through synapse and send it to the other neurons artificial neural network module Artificial neural network is a massively parallel distributed processor that has a natural propensity for storing experiential knowledge and making it available for use. It resembles the brain in two respects: - Knowledge is acquired by the network through a learning process. - Interconnection strengths known as synaptic weights are used to store the knowledge. The basic unit of neural network ,the artificial neuron simulating a work of the neuron in human brain. The neuron consist of some inputs emulating dendrites of the biological neuron, a summation model , an activation function and one output emulating an axon of biological neurons. The importance of a particular input can be intensified by weight that simulate biological neurons synapses. Then the input signals are multiplied by values of weight and next the result are added in the summation part , the sum is send to the activation part where is processed by the activation function , thus we obtained neurons output for input signal ‘x’. Artificial neural network advantages Neural networks, with their remarkable ability to derive meaning from complicated or imprecise data, can be used to extract patterns and detect trends that are too complex to be noticed by either humans or other computer techniques. A trained neural network can be thought of as an "expert" in the category of information it has been given to analyze. Other advantages include: 1. Adaptive learning: An ability to learn how to do tasks based on the data given for training or initial experience. 2. Self-Organization: An ANN can create its own organization or representation of the information it receives during learning time. 3. Real Time Operation: ANN computations may be carried out in parallel, and special hardware devices are being designed and manufactured which take advantage of this capability. 4. Fault Tolerance : Partial destruction of a network leads to the corresponding degradation of performance. However, some network capabilities may be retained even with major network damage.