File
advertisement

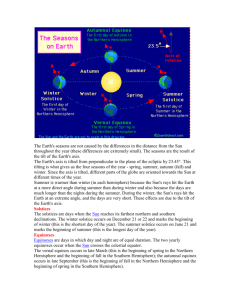
Astronomy- study of celestial bodies (moon, stars, comets, asteroids and other objects in the sky) Rotate- spin on its axis…rotation-is the act of rotating---the sun and ALL planets do this Revolve -move around another object…revolution act of revolving Orbit-the path an objects it takes as it revolves SUN: ...rotates approximately every 30 days …source of life on Earth EARTH: Earth’s axis– an imaginary vertical line through the center of Earth; connects the North Pole to the South Pole…is at a 23.5° angle Equator– is an imaginary horizontal line around the middle of Earth. Northern hemisphere– the half of Earth above (north) of the equator. North Pole– the northern most point on Earth. Southern hemisphere– is the half of Earth below (south) of the equator South Pole– is the southernmost point on Earth. Earth revolves around the sun-year 365 ¼ days---ACTUAL year 365 days—CALENDAR year 366 days----LEAP year: add up four ¼ days to get an extra day (Feb 29) Reason for leap year is to catch up with the calendar Rotate- spin on its axis…rotation-is the act of rotating--the sun and ALL planets do this Rotation of the Earth causes day and night Day & Night • The Earth's rotation causes the change of day and night. • The Earth rotates on its axis once every 23 hours and 56 minutes. • The rotation of the Earth is west to east, so the Sun is visible in the eastern sky first. • The Sun shines only on half of the Earth at any time, so that half the Earth is in daylight and the other half is in darkness. • The tilt on the Earth's axis causes day and night to be of different lengths in different parts of the world. • A solstice occurs twice a year. The summer solstice is the longest day (and shortest night) of the year. The winter solstice is the shortest day of the year. • An equinox occurs twice a year when day and night are of equal length. 12 hours of dark plus 12 hours of light = one day 24 hours Earth rotates and revolves counterclockwise-LEFT-Prograde Season– one of the major divisions of the year, usually based on regular weather changes. Why do we have seasons? Earth’s tilt and revolution around the sun…In most places, the year is divided into four seasons: winter, spring, summer, and autumn (fall). Each season is about three months long. In tropical regions, average temperatures do not change much during the year: Two seasons “rainy season” and the “dry season.” Seasons • Seasons are caused by the Earth's revolution around the Sun and the unchanging tilt of the Earth's axis. • The different distances to the Sun caused by the tilt do not cause the seasons. • The season depends on how much of the Earth's surface is covered by light rays, and at what angle they reach the Earth's surface. Head-on rays on a small area are strong and cause summer seasons. Slanting rays focusing on a large area are weaker and cause winter seasons Direct sunlight– is sunlight that strikes Earth’s surface at close to right angle (90° angle). Indirect sunlight– is sunlight that strikes Earth’s surface at an acute angle (less than 90 ̊). The Earth’s position in relation to the sun determines the angle and amount of sunlight an area receives A. Solstice– One of two days during the year when the direct rays of the Sun reaches farthest from the equator. 1. 2. Summer solstice– is the first day of summer - is the longest day of the year - it is also the day when the noon Sun is highest in the sky. -In the northern hemisphere the summer solstice occurs on/near June 21. -In the southern hemisphere the summer solstice occurs on/near December 21. Winter solstice– the first day of winter -is the shortest day of the year. -day when the noon Sun is lowest in the sky. -in southern hemisphere occurs on/near June 21 - in northern hemisphere occurs on/near December 21. B. Equinox-sun is directly above the equator -neither end of earth’s axis is pointed towards the sun: equal amount of daylight in both hemispheres - happens on March 21 and September 23 Tides • Tides occur because of the pull of gravity of the Moon and the Sun on the Earth's oceans. Because the Moon is closer to the Earth, it has the greatest effect on our tides. There are approximately 2 high tides and 2 low tides every 24 hours. • Spring tides (often called 'king tides' by fishermen) occur at New Moon and Full Moon when the Sun, the Moon and the Earth are in line. This forms extremely high high-tides and extremely low low-tides. • Neap tides occur at First Quarter and Last Quarter, when the Sun, the Earth and the Moon are at right angles. This forms quite low high-tides and quite high low-tides. Eclipses • Eclipses occur when a large shadow travels across the surface of the Earth. • Umbra - The Umbra is the darker part of the shadow. • Penumbra - The Penumbra is the lighter part of the shadow. • Total Eclipse - Observers on the Earth's surface who are shadowed by the darker umbra would see a total eclipse. • Partial Eclipse - Observers on the Earth's surface who are shadowed by the lighter penumbra would see a partial eclipse. • Solar Eclipses occur sometimes when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth at New Moon. The shadow of the Moon falls on the Earth appearing to block out (eclipse) the Sun. Lunar Eclipses occur sometimes when the Moon passes on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun at Full Moon. The Moon passes in the Earth's shadow. It appears dull and can only just be seen. Day & Night • The Earth's rotation causes the change of day and night. • The Earth rotates on its axis once every 23 hours and 56 minutes. • The rotation of the Earth is west to east, so the Sun is visible in the eastern sky first. • The Sun shines only on half of the Earth at any time, so that half the Earth is in daylight and the other half is in darkness. • The tilt on the Earth's axis causes day and night to be of different lengths in different parts of the world. • A solstice occurs twice a year. The summer solstice is the longest day (and shortest night) of the year. The winter solstice is the shortest day of the year. • An equinox occurs twice a year when day and night are of equal length.