September 21-25

Teacher: Amber Dale Grade: 4 th Mathematics Week: September 8-11
Monday MATH
Mathematics/4 th Grade/Multiplication
Subject/Grade/Unit
TEKS/ELPS
Duration
Number and Operations—4.4.D Use strategies and algorithms, including the standard algorithm, to multiply up to a four-digit number by a one-digit number and to multiply a two-digit number by a twodigit number. Strategies may include mental math, partial products, and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties
ELPS: 4.F.3, 4.F.8
90 min.
I can use the Distributive Property to multiply a 2-digit number by a 1-digit number?
Objective/Purpose
(I can statement)
Modifications/Differentiat ed Instruction
Key Vocabulary
Go Math
RTI: 37
Enrich: 32
Algorithm, approximate, associative property, Area model, array, base-ten place value system, commutative property, compose, compatible numbers, decompose, Distributive Property, equation, estimate, expanded notation, factor, length, multiple, multiply/multiplication, number sense, operation, pattern, place value, product, partial product, partial quotient, reasonable, remainder, round, whole numbers, width
Go Math 7.3
Materials/Resources
Anticipatory Set:
Hook/Prior
Knowledge/Focus
Lesson Components
Summative Assessment
1.
UPSE Warm-up
2.
Rocket Math
3.
Investigate Go Math p. 228
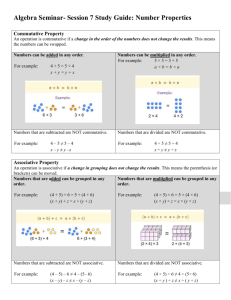
Students will use grid paper and draw a rectangular model to represent 6 × 13. When the squares of an array are pushed together, it is sometimes referred to as an area model.
A A rectangle can be drawn that is 6 units down and 13 units across.
B Students should draw a vertical line on the model to separate 6 rows of 13 into 6 rows of 5 and 6 rows of 8. • How does breaking apart the model help you multiply 6 × 13? Possible answer: I can break apart 13 into lesser numbers and use basic facts to multiply.
C Give students an opportunity to share the different ways they broke apart 13.
• Describe the number of rows and columns in each of your rectangles. Answers will vary. Some students will use 6 × 6 and 6 × 7. Share with students that they have just used the Distributive
Property. Read the definition of the Distributive Property again with students. Students should recognize that the vertical line they drew broke the larger rectangle into two smaller rectangles, each representing a product. The sum of the products of both rectangles is the product of 6 × 13.
4.
Students will complete an interactive journal entry that provides the steps and practice problems for distributive property.
5.
Independent Practs-Go Math p. 233-234
Stations
Go Math p. 233-234
Closure/Homework Choice Board and math fact log due today.
Tuesday
Subject/Grade/Unit
Mathematics/4 th Grade/multiplication
MATH
TEKS/ELPS
Duration
Number and Operations—4.4.D Use strategies and algorithms, including the standard algorithm, to multiply up to a four-digit number by a one-digit number and to multiply a two-digit number by a two-digit number.
Strategies may include mental math, partial products, and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties
ELPS: 2.C.2, 4.C.3, 4.F.9
90 min.
I can use expanded form to multiply a multidigit number by a 1-digit number
Objective/Purpose
(I can statement)
Modifications/Differentiat ed Instruction
Key Vocabulary
Go Math
RTI: lesson 38
Enrich: lesson 33
Algorithm, approximate, associative property, Area model, array, base-ten place value system, commutative property, compose, compatible numbers, decompose, Distributive Property, equation, estimate, expanded notation, factor, length, multiple, multiply/multiplication, number sense, operation, pattern, place value, product, partial product, partial quotient, reasonable, remainder, round, whole numbers, width
Go Math Module 7.4
Materials/Resources
Anticipatory Set:
Hook/Prior
Knowledge/Focus
Making Connections Invite students to tell you what they know about multi-digit numbers. What is a multidigit number? (A multi-digit number has more than one digit in the number.) What are examples of multidigit numbers? (Possible answers: 18, 350, or 5,748.)
Lesson Components
Summative Assessment
1.
UPSE Warm-up
2.
Rocket Math
3.
Whole Group-Go Math 7.4 Explore p. 235-236
Example 1 Students use expanded form and the Distributive Property to multiply a 3-digit number by a 1-digit number. Work through the steps with students.
• How can you write a number in expanded form? Possible answer: write the number as the sum of the value of each digit, starting with the greatest place value.
• How do you use the Distributive Property to multiply? Possible answer: multiply each addend in expanded form by the 1-digit number. Then add the partial products.
• How does the model relate to the Distributive Property? Possible answer: each rectangle represents multiplying an addend in expanded form by the 1-digit number.
• Why do you add in Step 4? Possible answer: after I find each partial product, I need to add the partial products to find the answer
Example 2
Read and discuss the problem. Then work through the example with students.
• When writing 1,250 in expanded form, why don’t you write anything for the ones place? Possible answer: the value of the ones digit is zero. Adding zero doesn’t change the sum of the partial products, so I don’t need to include it.
• How is multiplying by a 3-digit number similar to multiplying by a 4-digit number using expanded form? Possible answer: the steps are the same. Depending on the digits in the 3-digit and 4-digit numbers, you may have more or fewer partial products.
4.
Ind. Practice-p. 239-240 odds
5.
Stations
Go Math p.239-240 odds
Closure/Homework Choice Board and math fact log due Friday.
Wednesday MATH
Mathematics/4 th Grade/Multiplication
Subject/Grade/Unit
TEKS/ELPS
Duration
Number and Operations—4.4.D Use strategies and algorithms, including the standard algorithm, to multiply up to a four-digit number by a one-digit number and to multiply a two-digit number by a two-digit number.
Strategies may include mental math, partial products, and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties
ELPS: 4.F.3, 4.F.8
90 min.
I can multiply use place value and partial products to multiply by a 1-digit number
Objective/Purpose
(I can statement)
Modifications/Differentiat ed Instruction
Key Vocabulary
Go Math
Tier 1: lesson 39
Enrich lesson 34
Graph paper to line up numbers
Algorithm, approximate, associative property, Area model, array, base-ten place value system, commutative property, compose, compatible numbers, decompose, Distributive Property, equation, estimate, expanded notation, factor, length, multiple, multiply/multiplication, number sense, operation, pattern, place value, product, partial product, partial quotient, reasonable, remainder, round, whole numbers, width
Go Math 7.5
Materials/Resources
Anticipatory Set:
Hook/Prior
Knowledge/Focus
Invite students to tell you what they know about 3-digit numbers. What are examples of 3-digit numbers in the real-world? (Possible answers: number of students in a school, temperature of an oven.) 125 is a 3-digit number. Where would the 5 go in a place value chart? (ones) Where would the 2 go? (tens) What about the 1? (hundreds)
Lesson Components
Summative Assessment
1.
UPSE Warm-up
2.
Rocket Math
3.
Whole Group Instruction-Student will complete an interactive notebook entry that lists the steps for using partial products to multiply.
Also, use Go Math unlock the problem on page 241 to reinforce concept of partial products.
4.
Stations p. 242 odds
Closure/Homework Choice Board and math fact log due Friday.
Thursday MATH
Subject/Grade/Unit
Mathematics/4 th Grade/multiplication
TEKS/ELPS
Duration
Number and Operations—4.4.D Use strategies and algorithms, including the standard algorithm, to multiply up to a four- digit number by a one-digit number and to multiply a two-digit number by a twodigit number. Strategies may include mental math, partial products, and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties
ELPS: 2.C.4, 3.D.2, 3.E
90 min.
I can use mental math and properties to help you multiply numbers.
Objective/Purpose
(I can statement)
Modifications/Differentiat ed Instruction
Go Math
RTI-tier 1 lesson 40
Enrich-lesson 35
Key Vocabulary
Materials/Resources
Algorithm, approximate, associative property, Area model, array, base-ten place value system, commutative property, compose, compatible numbers, decompose, Distributive Property, equation, estimate, expanded notation, factor, length, multiple, multiply/multiplication, number sense, operation, pattern, place value, product, partial product, partial quotient, reasonable, remainder, round, whole numbers, width
Go Math 7.6
Anticipatory Set:
Hook/Prior
Knowledge/Focus
Making Connections
Invite students to tell you what they know about the various ways to multiply numbers.
Have you ever done a math problem in your head, without pencil, paper or a calculator? Tell us about it.
(Possible answers: Determining the total cost of two or more items, calculating how many hours it will take to complete homework in all your school subjects.)
How did you perform multiplication in these situations? (Possible answers: Estimated, used repeated addition.)
Lesson Components
Summative Assessment
1.
UPSE
2.
warm-up
3.
Rocket Math
4.
Go Math
Unlock the Problem p. 247
Students read the problem. Students should understand that they are multiplying the number of sections times the number of groups in each section times the number of seats in each group. sections × groups × seats
• Which factors were multiplied first? 4 and 25 • How can you use mental math to multiply 4 ×
25? Possible answer: I can skip count by 25s; 25, 50, 75, 100.
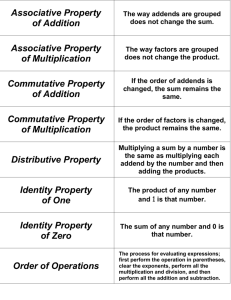
• How does the Commutative Property help you solve this problem? Possible answer: I can change the order of the factors to multiply factors that I know first. The product stays the same.
Try This!
Example A uses the Associative Property; the parentheses are moved to change the grouping of the factors.
• Explain how to multiply 10 times 10 mentally. Possible answer: skip count by 10s, 10 times
Example B uses the Commutative Property; the factors are written in a different order. It also uses the Associative Property; the parentheses are moved to change the grouping of the factors.
• Explain how to multiply 4 times 250 mentally. Possible answer: I can use 4 times 25 and then write a zero. Skip count by 25s; 25, 50, 75, 100. Then use a pattern of zeros to write 1,000.
• How does the Associative Property help you solve this problem? Possible answer: I can group the factors in different ways to multiply factors that I know first. The product stays the same.
Examples
Explain that the examples show different mental math strategies for multiplying.
Example A • You can break apart a number into hundreds and tens and ones. How do you break apart 625 into hundreds and tens and ones? 600 + 20 + 5
Example B • What expression are we using in place of 398? 400 – 2
5.
Stations p. 251-252 odds
Closure/Homework Choice Board and math fact log due Friday.
Friday MATH
Mathematics/4 th Grade/Multiplication
Subject/Grade/Unit
TEKS/ELPS
Number and Operations—4.4.D Use strategies and algorithms, including the standard algorithm, to multiply up to a four-digit number by a one-digit number and to multiply a two-digit number by a twodigit number. Strategies may include mental math, partial products, and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties
ELPS: 4.F.3, 4.F.8
90 min.
Duration
Objective/Purpose
(I can statement)
I can use the draw a diagram strategy to solve a multi-step multiplication problem.
Modifications/Differentiat ed Instruction
Key Vocabulary
Go Math
RTI: lesson 41
Enrich: 36
Algorithm, approximate, associative property, Area model, array, base-ten place value system, commutative property, compose, compatible numbers, decompose, Distributive Property, equation, estimate, expanded notation, factor, length, multiple, multiply/multiplication, number sense, operation, pattern, place value, product, partial product, partial quotient, reasonable, remainder, round, whole numbers, width
Go Math 7.7
Materials/Resources
Anticipatory Set:
Hook/Prior
Knowledge/Focus
Invite students to tell you what they know about using diagrams or pictures to solve problems. How can drawing a diagram or picture help you solve a one-step multiplication problem such as 8 × 4? (You can draw a diagram of 8 groups of 4 or 4 groups of 8 and find the sum of the items.)
Lesson Components
Summative Assessment
1.
UPSE Warm-up
2.
Rocket Math
3.
Guided Instruction- Go Math p. 253
Unlock the Problem
At the sea park, one section in the stadium has 9 rows with 18 seats in each row. In the center of each of the first 6 rows, 8 seats are in the splash zone. How many seats are not in the splash zone?
After students read the problem, discuss how they will use the information in the diagram to answer the question. Be sure students understand that they are looking for the number of seats that are not in the splash zone.
• Why do you multiply to find the number of seats in the splash zone? I know the number of rows and the number of seats in each row. I need to combine equal groups, so I multiply to find the total.
4.
Independent Practice-Go Math p. 257-258
5.
Stations
Go Math p. 257--258
Closure/Homework Choice Board and math fact log due today.