Meiosis & Mitosis Worksheet: Cell Division Stages
advertisement

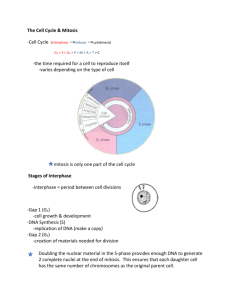
Meiosis Worksheet On the lines provided, order the different stages of meiosis I THROUGH meiosis II, including interphase in the proper sequence. 1. 4th metaphase I homologous pairs of chromosomes line up in the center of the cell th 2.5 anaphase I __ spindle fibers pull homologous pairs to opposite ends of the cell 3. 9th Telophase II 4 haploid (N) daughter cells form 4. 1st interphase _ cells undergo a round of DNA replication th 5.7 anaphase II _ sister chromatids separate from each other 6. 6th Telophase I _ 2 haploid (N) daughter cells form 7.3rd Prophase I __ spindle fibers attach to the homologous chromosome pairs th 8. 8 anaphase II individual chromatids move to each end of the cell 9. 2nd prophase I _ crossing-over (if any) occurs 10. Compare the number and type of cells that result from meiosis vs mitosis. Mitosis 2 diploid cells, that are somatic cells (cells that are not gametes) and identical to each other and to the parent cell __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Meiosis makes 4 haploid cells that are gametes and are all different from each other and from the parent cell __________________________________________________________________________________ 11. How do the genetic contents of cells resulting from mitosis and meiosis differ? Mitosis are identical, while meiosis is not identical _________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 12 If a diploid cell containing 28 chromosomes undergoes meiosis, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have? 14 ________________________________________________________________________________ In mitosis they would have 28 Read each statement, then on the line write down the phase of mitosis or meiosis that the action occurs. IF the action occurs in both, write both. The first one is done for you 1. _______________________metaphase I meiosis homologous chromosome line up in the center of the cell 2 anaphase II meiosis ; anaphase mitosis________ The duplicated chromosomes are split apart. 3. anaphase I meiosis _______________________ spindle fibers separate homologous pairs 4. Telophase II meiosis ______________________ 4 haploid (N) daughter cells form 5. interphase meiosis and mitosis _____________ cells undergo a round of DNA replication 6. metaphase mitosis/ metaphase II meiosis (no pairs) Individual chromosomes line up across the middle of the cell. 7. prophase I, Prophase II meiosis; prophase mitosis Chromosomes become visible. 8. anaphase mitosis; anaphase II meiosis _______ sister chromatids separate from each other 9. _______________________ Telophase I meiosis 2 haploid (N) daughter cells form 10. _______ anaphase II meiosis; anaphase mitosis Sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes. 11. _ Telophase I and II meiosis; Telophase mitosis Nuclear envelope re-forms. 12. _______________________ prophase I meiosis spindle fibers attach to the homologous chromosome pairs 13. _______ anaphase II meiosis; anaphase mitosis individual chromatids move to each end of the cell 14. ___ prophase I and II meiosis, prophase mitosis The nucleolus disappears 15. _______ prophase II meiosis; prophase mitosis Each chromosome is connected to a spindle fiber. On both sides of the centromere 16. _______________________ prophase I meiosis crossing-over (if any) occurs Directions: Write one clear sentence using all the words in the set that demonstrates your understanding of their relationship. Please underline the words in your sentence. 1. spindle, microtubules, centrosome (centriole) The centrosome (including the centriole in animal cells) produces the spindle which is made of microtubules 2. duplicated chromosome, sister chromatids, centromere A duplicated chromosome consists of 2 sister chromatids connected by a centromere 3. haploid, diploid, homologous pairs A diploid cell contains both chromosomes of a homologous pair, while a haploid cell contains only one chromosomes of a homologous pair 4. mitosis, meiosis, gametes Mitosis creates somatic cells, while gametes are produced by meiosis 5. cytokinesis, cleavage furrow, cell plate, Telophase Cytokinesis usually occurs during Telophase and starts when a cleavage furrow forms in animal cells or a cell plate forms in plant cells 6. prophase, spindle, nuclear membrane During prophase, the spindle is formed and the nuclear membrane breaks down. 7. interphase, G1, G2, S Interphase includes G1, G2, and S phases 8. Centrosome, Spindle, chromosomes The spindle originates from the centrosome and moves the chromosomes during mitosis/meiosis 9. mitotic phase, cell cycle, interphase The cell cycle include the main phases of interphase and the mitotic phase 10. Telophase, spindle, nuclear membrane During Telophase, the spindle breaks down and the nuclear membrane reforms 11. Checkpoints, cell cycle The checkpoints found in the cell cycle give the “go ahead” signal (G1) or stop the cell from continuing through the cell cycle if something is wrong (G2, M)