Horse Test/Key
advertisement

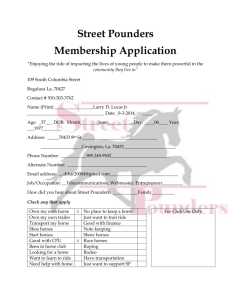
2013 FFA Horse Selection Team Written Test Fill out one scan card per team Multiple Choice (2 points each) _____ 1. In general, how many pounds of feed will a 1000 pound horse consume each day? a. 5 pounds b. 20 pounds c. 40 pounds d. 60 pounds _____ 2. Mastication refers to what? a. Chewing b. Digestion c. Rumination d. Swallowing _____ 3. Protein is broken down into what basic compounds before it is absorbed? a. Vitamins b. Minerals c. Amino acids d. Starch _____ 4. Which vitamin can the horse make in its body from sunlight? a. Vitamin A b. Vitamin D c. Vitamin E d. Vitamin K _____ 5. The main site where forage is digested in the horse is the: a. Stomach b. Esophagus c. Small intestine d. Large intestine _____ 6. What two minerals are present in salt? a. Sodium and Calcium b. Sodium and Phosphorus c. Sodium and Potassium d. Sodium and Chloride ______ 7. What is the most essential nutrient required by the horse? a. Water b. Protein c. Carbohydrate d. Vitamin _______ 8. Name the section of the small intestine closest to the stomach: a. Jejunum b. Ileum c. Duodenum d. Cecum ______ Which nutrient can supply the most energy per gram of feed? a. Protein b. Vitamin c. Carbohydrate _____ 9. 10. d. Fat If adequate forage is available, how many hours per day on average will free-ranging horses spend grazing? a. 1-2 b. 5-7 c. 10-12 d. 18-20 ______ 11. Which of the following is NOT a method for processing grain? a. Grinding b. Caking c. Pelleting d. Extrusion ______ 12. What product is commonly added to horse feed to reduce dust and improve palatability? a. Molasses b. Soybean meal c. Beet pulp d. Alfalfa meal ______ 13. Which of the following is NOT a cool-season grass used for horses? a. Red clover b. Orchardgrass c. Bromegrass d. Timothy _____ Body condition score is used to estimate fat cover on a horse’s body and is measured on a scale of what? a. 0-5 b. 1-5 c. 1-9 d. 1-10 14. ______ 15. Where is the primary site for fat digestion in the horse? a. Stomach b. Small intestine c. Cecum d. Large intestine ______ 16. Blister beetles are toxic when eaten by horses and can be found in: a. Alfalfa hay b. Corn c. Oats d. Beet pulp ______ 17. Which of the following is NOT a common grain fed to horses? a. Sunflower b. Oat c. Corn d. Barley ______ 18. Which classification has the highest daily energy needs? a. Average maintenance horse b. Early lactating mare c. Lightly exercising horse d. Late pregnancy mare ______ 19. Eating too much grain or lush forage at one time can lead to what disease of the horse’s foot? a. Navicular disease b. Colic c. White line disease d. Laminitis (founder) ______ 20. What behavior occurs when horses eat quickly and aggressively and do not thoroughly chew their food? a. Bolting b. Cribbing c. Weaving d. Slobbers ______ 21. Which vitamin is essential for the process of blood clotting? a. A b. C c. E d. K ______ 22. Horses should never receive less ____% of their body weight in forage per day. a. 0 b. 1 c. 10 d. 20 ______ 23. Which forage would be most likely to have the highest protein content? a. Alfalfa b. Bromegrass c. Timothy d. Tall Fescue Which part of the gastrointestinal tract has the largest capacity? a. Stomach b. Small intestine c. Cecum d. Large colon ______ 24. ______ 25. What hormone helps regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels? a. Oxytocin b. Insulin c. Glycine d. Gastrin 2013 State FFA Horse Evaluation Test Answer Key 1. B 2. A 3. C 4. B 5. D 6. D 7. A 8. C 9. D 10. C 11. B 12. A 13. A 14. C 15. B 16. A 17. A 18. B 19. D 20. A 21. D 22. B 23. A 24. D 25. B