Course Outline Check-up Tool
advertisement
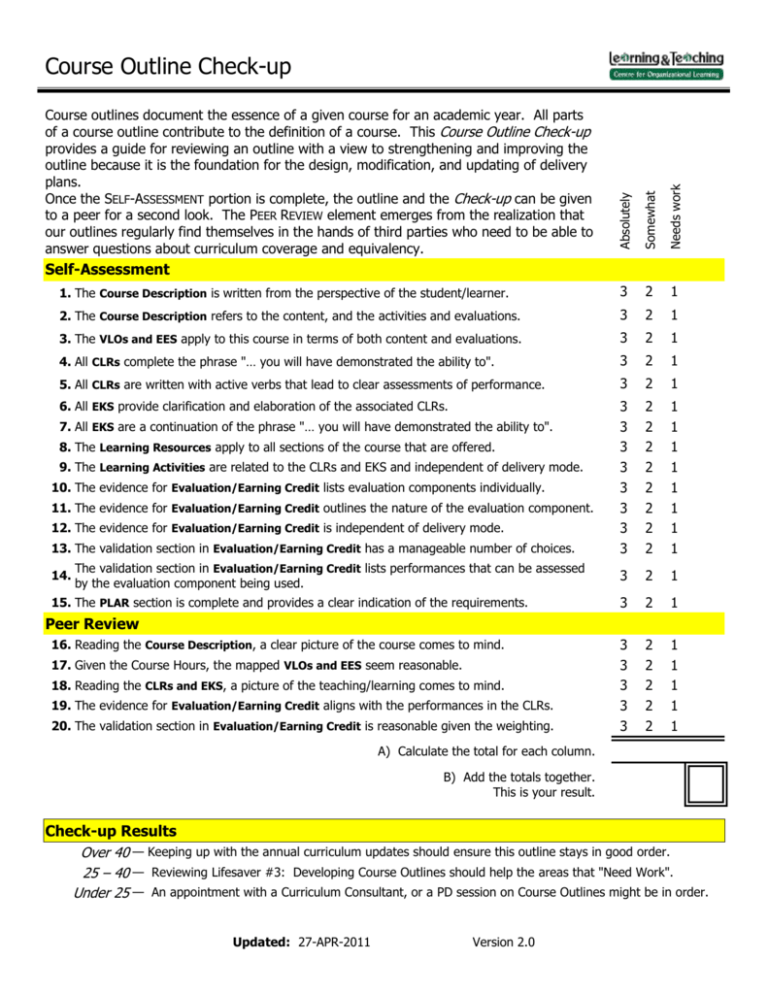
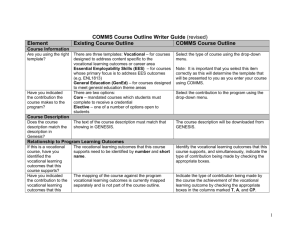
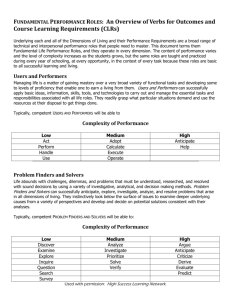
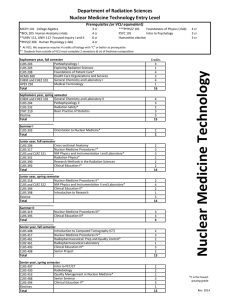
Course Outline Check-up Absolutely Somewhat Needs work Course outlines document the essence of a given course for an academic year. All parts of a course outline contribute to the definition of a course. This Course Outline Check-up provides a guide for reviewing an outline with a view to strengthening and improving the outline because it is the foundation for the design, modification, and updating of delivery plans. Once the SELF-ASSESSMENT portion is complete, the outline and the Check-up can be given to a peer for a second look. The PEER REVIEW element emerges from the realization that our outlines regularly find themselves in the hands of third parties who need to be able to answer questions about curriculum coverage and equivalency. 1. The Course Description is written from the perspective of the student/learner. 3 2 1 2. The Course Description refers to the content, and the activities and evaluations. 3 2 1 3. The VLOs and EES apply to this course in terms of both content and evaluations. 3 2 1 4. All CLRs complete the phrase "… you will have demonstrated the ability to". 3 2 1 5. All CLRs are written with active verbs that lead to clear assessments of performance. 3 2 1 6. All EKS provide clarification and elaboration of the associated CLRs. 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 2 1 3 2 1 3 3 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 Self-Assessment 7. All EKS are a continuation of the phrase "… you will have demonstrated the ability to". 8. The Learning Resources apply to all sections of the course that are offered. 9. The Learning Activities are related to the CLRs and EKS and independent of delivery mode. 10. The evidence for Evaluation/Earning Credit lists evaluation components individually. 11. The evidence for Evaluation/Earning Credit outlines the nature of the evaluation component. 12. The evidence for Evaluation/Earning Credit is independent of delivery mode. 13. The validation section in Evaluation/Earning Credit has a manageable number of choices. 14. The validation section in Evaluation/Earning Credit lists performances that can be assessed by the evaluation component being used. 15. The PLAR section is complete and provides a clear indication of the requirements. Peer Review 16. Reading the Course Description, a clear picture of the course comes to mind. 17. Given the Course Hours, the mapped VLOs and EES seem reasonable. 18. Reading the CLRs and EKS, a picture of the teaching/learning comes to mind. 19. The evidence for Evaluation/Earning Credit aligns with the performances in the CLRs. 20. The validation section in Evaluation/Earning Credit is reasonable given the weighting. A) Calculate the total for each column. B) Add the totals together. This is your result. Check-up Results Over 40 — Keeping up with the annual curriculum updates should ensure this outline stays in good order. 25 – 40 — Reviewing Lifesaver #3: Developing Course Outlines should help the areas that "Need Work". Under 25 — An appointment with a Curriculum Consultant, or a PD session on Course Outlines might be in order. Updated: 27-APR-2011 Version 2.0 Course Outline Check-up Glossary CLR: Course Learning Requirement Delivery mode: This is the method by which information is conveyed and interactions take place. At Algonquin, we have three delivery modes: online, hybrid, and in-class. EES: Essential Employability Skills EKS: Embedded Knowledge and Skills Evaluation Component: These are not the specific evaluation tools but rather broader evaluation strategies and methods that can be used to help students demonstrate their achievement of the CLRs and the Essential Employability Skills (EES) PLAR: Prior Learning Assessment and Recognition VLO: Vocational Learning Outcomes Notes on the parts of a Course Outline Academic Directive E33 – Course Outlines and Course Section Information identifies eight components in a course outline. This Course Outline Check-up looks at six of those components. 1. Course Description The course description begins the process of setting expectations for the course in terms of content, activities and evaluations. A good course description is written from the point of view of the student and should go a long way to ensuring that students are not surprised by anything that happens in the course. (Note: Course Descriptions can only be changed once a year.) 2. Relationship to program learning outcomes (VLOs and EES) This component lists the contribution(s) that the course makes to the program and the preparation of the students for graduation. As such, the list should be (1) reasonable given the course hours, and (2) applicable in the sense that the elements in the list can be seen explicitly in the CLRs and the Evaluation. 3. Course Learning Requirements (CLRs)/Embedded Knowledge and Skills (EKS) The statements or phrases in this component of the course outline provide a clear picture of the performances students complete to gain credit. As such, they begin with active verbs ("understand" is not an active verb), and are explicitly related to the VLOs, EES, and the Evaluation. 4. Learning Resources The learning resources component provides a list of resources (i.e., textbooks, readings, web sites, films, and so on) that are used in ALL sections of a course over an ENTIRE academic year. 5. Learning Activities This component provides a list of activities that students may experience when they are enrolled in the course. A good list of learning activities is connected to both the CLRs and the Evaluation, and presented in a way that includes in-class, hybrid, and online delivery. 6. Evaluation This area of the course outline provides important details about ALL sections of a course for an ENTIRE academic year: the evidence, the validation and the PLAR information. i. EVIDENCE: The evidence lists the individual evaluation components that assess the students' ability to complete the performance that is listed in the CLRs. Items that provide evidence should outline the nature of the component (i.e., written, oral, group and so on), and remain independent of delivery mode ( i.e., in-class, hybrid, or online). ii. VALIDATION: The validation lists the performance(s) that the evidence assesses. In this sense, evidence that contributes more towards the final grade validates a greater number of performances, and it is very unlikely that each item of evidence will validate all the performances in the course (CLRs and EES). iii. PLAR: The Prior Learning Assessment and Recognition (PLAR) area describes the process to be used for demonstrating achievement of the CLRs through life experience. The requirements, then, should be as clear as possible. Updated: 27-APR-2011 Version 2.0