3.1 3.2 Air masses and fronts storms guided notes
advertisement

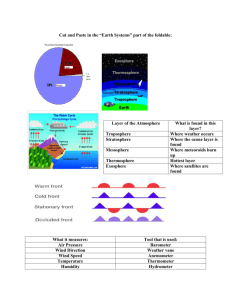
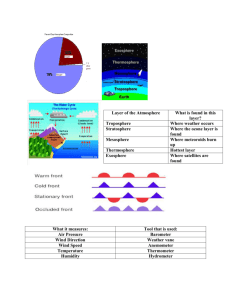
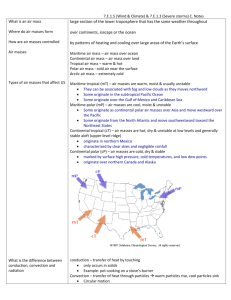
3.1 Weather changes as air masses move. Name __________________________________________ Vocab to remember _____________________________air mass--large volume of air with "same" temperature and humidity in locations at the same altitude _____________________--boundary between air masses ________________________________________________--formed when air moves around a high pressure center ______________________________________________--large weather system that surrounds a center of low pressure Weather changes as air moves—Air masses What was weather like yesterday? Weather changes as a new _______________________ moves into an area. An air mass can sit for many days over an area. As it sits, ____________________________________________________________________________________. Characteristics of an air mass Where did the air mass form? _____________________________________--air mass formed over land, becomes dry as it loses its moisture to dry land below it __________________________________--forms over water becomes moist as it gains water vapor from water below it Did it form near the equator? _______________________ --air mass formed near equator becomes warm as it gains energy ________________________--forms far from equator becomes cool as it loses energy Movement of air masses An air mass moves with _______________________________________ and can be influenced by ________________________________________. It carries its characteristics with it and _________________________________________________ as it moves. If the air mass moves _______________________, it changes the weather as it moves in. If the air mass moves ________________________, the mass may change its characteristics as it sits in a new area. ________________________________ are boundaries between air masses. As one air mass pushes another, the boundary ________________________ between them may be very different from either air mass. ______________________________________ weather can be expected as fronts pass over an area. When a cold, dense air mass pushes warmer air, it produces a _________________________ front. ________________________ move in quickly and are_____________________________________. The cold, dense air moves forward and pushes the warmer air ________________________. Water vapor in the warm air ____________________________________. Tall, cumulonimbus clouds and _______________________________ storms are likely. After the front moves through, the air is _____________________ and often very ___________________________. When a warm air mass pushes colder air, it produces a ____________________________front. Warm fronts move more ____________________________than cold fronts. Warm air moves up ______________________over the __________________, ___________________ air. The slope is less __________________________. High ___________________ clouds, then ______________________________clouds form. Warm fronts often bring hours of __________________________________________________, then the air is ________________________after the front moves. ____________________________ front forms when two air masses meet and stop ___________________. They may last of days with ______________________that cover the sky. The front becomes either a __________________front or a _____________________________ front depending on which mass pushes the other. High pressure systems High pressure centers have air that ___________________ slowly and ____________________________________ from the ___________________________________. It moves _____________________________in the Northern Hemisphere due to the Coriolis Effect. It usually moves slowly bringing ___________________________________________________________ air. Low Pressure System Develop around a center of low pressure. Air moves ____________________________________ toward the lowest pressure and then ___________________________________________ altitudes. As the air moves upward it __________________ the air pressure further and makes the air move ______________. It moves in a ___________________________________________ direction inthe Northern Hemisphere. It can develop along fronts between ___________________ air masses and _____________________air masses. It can become ____________________________. 3.2 Low Pressure systems can become storms. Vocab to remember ______________________________________--a low pressure system near the equator with winds at least 40 mph ______________________________________--a tropical low pressure system with winds at least 74 mph _______________________________________--a huge mass of ocean water pushed by a hurricane into a coastal area _________________________________--blinding snowstorm with winds at least 35 mph and temperatures usually below 20* F Hurricanes Warm ocean water near the equator can turn a __________________________________ into a violent storm. More and more energy is added as more ________________________evaporates and becomes part of the system. The Coriolis Effect causes the system to move in a _____________________________. The system becomes a tropical storm when winds reach at least ___________ mph. It becomes a hurricane when the winds reach ____________ mph. Tropical storms usually move ____________________________ due to ____________________________winds. As long as it stays over _________________water, it gains energy and becomes more powerful. As soon as it moves over ___________________________ water or _______________________________it loses energy and begins to die out. As the hurricane moves, a small area of clear weather moves through as the center passes over. This is called the _______________________________________. Hurricanes pound the coast with huge waves, strong winds, and heavy rains. ____________________can be produced. _______________________________ and ______________________________________ can happen. The _____________________________________________ can track progress of a storm and can warn if evacuation is necessary. Winter storms form as part of __________________________________ systems. They form when __________________ collide. When a ______________________________ air mass and a ____________________________________ air mass come together winter storms can happen. Three types of winter storms __________________________________--strong winds and very cold temperatures Northern and Central states _______________________________________--form east and south of the Great Lakes __________________________________freezing rain covers the ground, limbs, and power lines with ice 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms _______________________________________ can build up in the top and bottom of clouds as __________________ move up and down in the clouds. A spark moving between these charges causes ______________________________. The heating of the air causes a sharp wave of air to travel away from the lightning to cause the sound of ____________. Thunderstorms form in 3 steps. Step 1--Warm humid air is forced ___________________. As condensation occurs, energy is _____________________. A __________________________________________________ cloud forms. Step 2--_________________________ near the top of the cloud begin to fall, producing strong ____________________ next to the ____________________________. Winds and ____________________ or _______________ may fall. This is the most severe stage. Step 3--The _________________________ spread out and block the ________________________. The storm dies out. Effects of Thunderstorms (name them) Tornadoes form in severe thunderstorms. Sometimes the up-and-down motion of a ___________________________ may produce a ______________________. A tornado is a __________________________________________________________ between a cloud and the ground. Most tornadoes occur in North America in the __________________________, when wind conditions are just right. Tornadoes can tear off roofs and damage trees. The strongest tornadoes can lift cars or demolish buildings. 3.4 Weather forecasters use advanced technologies. Weather data comes from many sources. _____________________________are scientists who study the weather. Meteorologists develop weather forecasts by using data from: (use the space below to take notes on each) radar stations satellites ground stations weather buoys airplanes ships Meteorologists use ___________________________________ from other areas and from computer models to ___________________________ data and make forecasts. They use their expertise to make weather predictions. Scientists use instruments to measure factors that affect weather. The ______________________________ measures the amount of heat in the air. A ________________________________ measures the air pressure. An _____________________________________measures the speed of the wind. A _______________________________________ shows the direction of the wind. A ______________________________ measures the amount of precipitation that falls. Groundwater Groundwater has to ______________________________________________________ to continue in the water cycle. Dewpoint The _______________________________ temperature is the temperature at which the air can no longer "hold" all of the _________________________ which is mixed with it, and some of the water vapor must ______________________ into liquid water. The dew point is always lower than (or equal to) the air temperature. If the air temperature cools to the dew point, or if the dew point rises to equal the air temperature, then ___________________________________________________begin to form. At this point where the dew point temperature equals the air temperature, the ____________________________________________________________.