AP Chemistry
advertisement

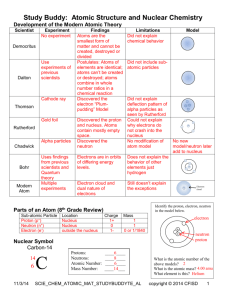
Chemistry Review 1 Name _________________________ Uncertainty in measurement Accuracy vs. precision accuracy (closeness) % difference: % = 100|mean – true| true A X Z ionic charge = p – e atomic symbol (# p) A value = p + n Z value = p Isotopes: same Z, different A Average atomic mass: 100mav = %1m1 + %2m2 + ... Forms of matter pure substances mixtures element compound homogeneous heterogeneous measurements mean Atomic symbol true value precision (spread) % deviation: % = 100 |trial – mean| N(mean) Significant figures: When are zeros significant? 0.00053000021000 never always with decimal Round off calculations never measurements x, : # of sf equals measurement with fewest sf +, –: decimal position same as measurement with highest Quantity of matter Measured as mass (definition) or volume (liquids, gases) Density: d = m/V Molar mass: MM = sum of atomic masses in grams Mole (6.022 x 1023 particles): n = m/MM Atomic structure scientists Dalton: atomic theory—elements made of indestructible, identical atoms that combine to make compounds J.J. Thomson: identified cathode rays as electrons and measured charge-to-mass ratio Millikan: measured electron charge with oil drops in a vacuum chamber Rutherford: characterized nucleus as dense and positive with gold foil and alpha () radiation Bohr: characterized electron region in terms of energy levels and concentric "orbits" Subatomic parts Diatomic elements: H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 Molecular compound vs. crystalline compound molecular: formula defines size crystalline: formula shows ratio of atoms Forms of natural radiation Mass # Charge Relative Type Symbol (A) # (Z) penetration 4 2 1 42He alpha 0 e – -1 100 0 -1 beta 0 e +1 destroyed 0 + 1 positron 0 0 0 10,000 0 gamma Balance nuclear reactions A and Z values are conserved Nuclear symbol based on Z value Nuclear decay Rate of decay: rate = kNt (k = rate constant, Nt = amount at time t) Calculating Nt at time t: ln(No/Nt) = kt Half-life: time when Nt = ½No: t½ = ln2/k Photon energy Light energy delivered as photon: Ephoton= hf = hc/ hc = 2.00 x 10-25 J•m Ephoton = 2.00 x 10-25/ (J) Energy proportional to frequency (color) Violet > Red (Inversely proportional to wavelength: Bohr model of hydrogen En = -2.18 x 10-18/n2 (J) Ephoton = 2.00 x 10-25/ (J) E = E2 – E3 < 0 (ground state) Particle proton neutron electron Location nucleus nucleus outside Charge + 0 – Mass 1 1 0 Symbol 1 p 1 1 n 0 0 e -1 (excited states) (n = : ionization, En = 0) Chemistry Review 1 Uncertainty in measurement Data "correctness" is measure by % ____________: % = _______________ Data "precision" is measured by % ____________: % = ______________ Significant figures are all ________ digits, ________ zeros, and trailing zeros when a decimal point is ______ Leading zeros are _________ significant Round off calculations never measurements x, : _________________________________________ +, –: _________________________________________ Multiple massing of an object using the same balance produces (12.3 g, 12.1 g, 11.9 g, 11.5 g, 11.3 g). a. What is the mean? b. What is the % difference (true value is 12.0 g)? c. What is the % deviation? d. Is the balance more precise or accurate? Explain Quantity of matter Measured as mass (definition) or volume (liquids, gases) Density: d _______ Mole: n = ___________ particles = __________ Molar mass: MM = __________________________ 12.0 g of CO2 has a volume of 6.11 L. a. What is the density of the CO2? b. What is the molar mass of CO2? c. How many moles of CO2? d. How many molecules of CO2? Atomic structure scientists ____________; elements made of indestructible, identical atoms that combine to make compounds ____________: identified cathode rays as electrons and measured charge-to-mass ratio ____________: measured electron charge with oil drops in a vacuum chamber ____________: characterized nucleus as dense and positive with gold foil and alpha () radiation ____________: characterized electron region in terms of energy levels and concentric "orbits" Subatomic parts Particle Location Charge Mass Symbol proton neutron electron Atomic symbol AZX Atomic number Z: number of _______ (defines element) Atomic mass A: sum of ________________________ Isotopes: ___________________________ Average atomic mass: 100mav = ___________________ Ions: # e # p (e > p = _________, e < p = _________) Magnesium has two common isotopes 24Mg, 25Mg. a. How many protons, electrons & neutrons are in 2512Mg2+? Name _________________________ b. What is the average atomic mass if the abundance of Mg-24 is 70.0 %? Forms of matter Pure elements: 1 type of atom diatomic: ____________________________ Pure compound: _______________________________ molecular: formula _________________ crystalline: formula _________________ Mixture: group of pure substances in a container or object ______________: microscopic solute particles (solution) ______________: visible solute particles Forms of natural radiation Mass # Charge Relative Type Symbol (A) # (Z) penetration alpha beta positron gamma Rank alpha, beta & gamma in terms of relative penetration: and mass: Balance nuclear reactions A and Z values are conserved Nuclear symbol based on Z value Complete the nuclear equations. 231 Th 231 Pa + 16 O + 1 H 13 N + 90 91 8 1 7 Nuclear decay Rate of decay: rate = kNt (k = _______________, Nt = __________________) Calculating Nt at time t: ln(No/Nt) = kt Half-life: time when Nt = ½No: t½ = ln2/k Co-60 has a half-life of 5.26 yrs. a. What is rate constant for Co-60? b. What % of Co-60 is present after 6 years? Photon energy Light energy delivered as photon: Ephoton= hf = hc/ hc = 2.00 x 10-25 J•m Ephoton = _______________ (J) Energy proportional to _________ (color) Violet > Red (Inversely proportional to _______________ What is the energy of a 4.34 x 10-7 m photon? Bohr model of hydrogen Electron occupies an orbit around the nucleus Orbits defined by energy level n: En = -2.18 x 10-18/n2 (J) Ground state—lowest energy level (n = 1) Excited state—electron absorbs photon energy and moves to higher (n > 1) energy level Eelectron = ____________ = _____________ +E when going to __________ energy level (-E when going to __________ energy level) Ionization—___________________ (n = ____, E = ____) An n = 2 electron absorbs the photon energy from 4.34 x 10-7 m photon. What energy level does the electron move to?