Long Term Plan Year 4
advertisement

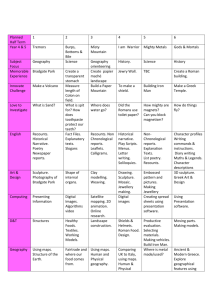
Year 4 Long Term Plan Sphinx HISTORY GEOGRAPHY SCIENCE AUTUMN 1 Life in Ancient Greece Ancient Greece – a study of Greek life and achievements and their influence on the western world. AUTUMN 2 Ancient Greek Culture Ancient Greece – a study of Greek life and achievements and their influence on the western world. SPRING 1 Legacy of the ancient Greeks A study of an aspect or theme in British history that extends pupil’s chronological knowledge beyond 1066: the legacy of Greek culture on later periods in British history, including the present-day. SPRING 2 Rome and it’s empire The Roman Empire and its impact on Britain: the Roman Empire by ad42 and the power of its army. SUMMER 1 Roman Britain The Roman Empire and its impact on Britain: Julius Caesar’s attempted invasion in 55–54bc; the Roman Empire by ad42 and the power of its army; successful invasion by Claudius and conquest, including Hadrian’s Wall; British resistance; ‘Romanisation’ of Britain and the impact of technology, culture and beliefs. SUMMER 2 Roman Britain The Roman Empire and its impact on Britain, including ‘Romanisation’ of Britain’: sites such as Caerwent and the impact of technology, culture and beliefs, including early Christianity; successful invasion by Claudius and conquest, including Hadrian’s Wall. Where on Earth? Our World from the International Space Station. Geographical skills and fieldwork Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied. Locational knowledge Name and locate counties and cities of the UK, and understand how some aspects have changed over time. Identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, equator, northern hemisphere, southern hemisphere, the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the prime/Greenwich meridian and time zones (including day and night). Human and physical geography Describe and understand key aspects of physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts. Describe and understand key aspects of human geography, including: types of settlement and land use and economic activity including trade links. Animals Including Humans Find out about food groups and healthy balanced diets. Study the human digestive system and how food is transported around Why Different weather? Weather around the world. Geographical skills and fieldwork Use fieldwork to observe, measure and record the human and physical features in the local area. Locational knowledge Locate the world’s countries, concentrating on their environmental regions. Human and physical geography Describe and understand key aspects of physical geography and human geography including climate zone biomes. Place knowledge Understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region. Who are the global caretakers? We are! Human and physical geography Describe and understand key aspects of human geography, including: economic activity and the distribution of natural resources including energy and water. Describe and understand key aspects of physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts. What can we discover about our local area? Human and physical geography Describe and understand key aspects of human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, and economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy. Geographical skills and fieldwork Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to describe features studied. Use the eight points of a compass, four- and six-figure grid references, symbols and key (including the use of Ordnance Survey maps) to build their knowledge of the UK and the world. Use fieldwork to observe, measure, and record the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs, and digital technologies. How do I impact on children and families far away? Geographical skills and fieldwork Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied. Human and physical geography Describe and understand key aspects of human geography, including: economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources. Catalonia - Here we come! Locational knowledge Locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe, concentrating on environmental regions, countries and major cities. Human and physical geography Describe and understand key aspects of physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers and mountains. Describe and understand key aspects of human geography, including: types of settlement and land use and economic activity including trade links. Geographical skills and fieldwork Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied. States of Matter Find out about the properties of the three different states of matter: solid, liquid and gas. Learn how to use Sound Show that sounds are made when objects vibrate and that sounds travel through solids, liquids and gases. Children Living Things & their habitats Remind children of the characteristics of living things and the basic needs their habitats supply. Establish why Electricity Children construct simple circuits and draw them. They find which materials are the best electrical conductors and Year 4 Long Term Plan Sphinx the body. Compare diets of herbivores, carnivores and omnivores. Investigate teeth and what causes decay. Look closely at food chains/webs. (Link to food) thermometers. Set up enquiries about matter changing from one state to another. Study the water cycle. Investigate air as an example of a gas. (Link to weather - Geography) ART Materials – Texture, pattern, experimenting Create visual texture using different marks and tools. Create patterns/ motifs with repeated mark making. Evaluate beginning to use artistic language. Explore Greek Art Ancient Greek Art: Greek craft / mythology Exploring Ancient Greek art and their use of repeating patterns to create a whole class fabric print, using stamps. Amphora vase – explore decoration and design to create a decorative Amphora vase using felt tip and collage. Pandora's box – design, plan, create a box using a net. Plan appropriate decoration for the shape/use. Painting 1: watercolours -observations, techniques and control Conduct an in-depth analysis of a watercolour painting. Comment on the form, line, technique and other observations. Form and discuss opinions. Begin to create a sketch book of what you have discovered. Evaluate beginning to use artistic language. Explore Greek Art Monet - Waterlillies D&T Food Prepare ingredients hygienically using appropriate utensils. Measure ingredients to the nearest gram. Assemble and cook ingredients (controlling the temperature of the oven or hob, if cooking). (Greek flatbread project) Textiles Select the most appropriate techniques to decorate textiles R.E. Belonging: Hinduism Teaching about God One God who takes many forms Worship in a Hindu home. In the home, a Hindu shrine Worship in a Hindu family Christmas No room at the Inn Feeling accepted or rejected P.E. Dance Demonstrate simple warm up Gymnastics Be able to select ideas, teach investigate how well sound travels through different materials and discover how instruments make sounds. Suggest how to change the pitch and loudness. (D&T Making a musical instrument project) Painting 2 – watercolour, experiment Plan, create and evaluate a painting using watercolours. Incorporate what you have found in Painting 1 into creating something. Students refer to the sketch book and use it for planning. Evaluate beginning to use artistic language. Explore Greek Art classification of plants and animals is important and classify minibeasts. Read and construct food chains and webs. Recognise that environments can change. use this information to make switches. Children wire plugs and find what happens to a bulb’s brightness when circuits are changed. They research scientists. Drawing – pencil, charcoal Children are to develop their drawing skills charcoal, pencils and sketching. Choose the appropriate techniques i.e. line, shape, colour and space. Introduce the concept of negative space. Evaluate beginning to use artistic language. (Sketches of tree through seasons throughout year) Explore Roman Art Olympics / action art Pencil sketches showing movement. (Greek) Explore artists: Edward Muybridge, Boccioni, Nolde, Robert Delaunay and Picasso. Showing how they created movement in their art. Create a pastel art showing movement, inspired by one of the artists. Computing Control and monitor models using software designed for this purpose (Probots, Logo, Scratch) Artists, architects and designers in history Continuously refer back to artists, architects and designers in history for inspiration or comparison. (Throughout Year) Explore Roman Art Andy Goldsworthy Natural Art (Link to Habitats) Explore Roman Art Roman mosaics- paper and scissor skills/ pencil design Roman artefact sculpturescreate a Roman artefact from clay and decorate with paints Roman myth –sketching, paint/ pastel Electricals and Electronics Create parallel circuits. (Link to science game project) Construction and Mechanics Strengthen materials using suitable techniques. Use scientific knowledge to choose appropriate mechanisms for a product. Belonging: Sikhism Welcoming new babies in Christian and Sikh communities Easter- How did Jesus share his last supper? Holy Communion, Easter foods Belonging: Sikhism Sharing Food as Part of Religious Worship The importance of sharing food Food as part of Christian worship The Langar, Kara Prashad (Sikhism) Sacred Writings and Stories Special books and sacred texts How holy books are regarded and handled Bible (Christianity) Guru Granth Sahib (Sikhism) Bhagavad Gita (Hinduism) Sacred Writings and Stories Hindu traditional tales Swimming Development to swim OAA/Games Use maps and diagrams to Games Play a game (pairs/small group) Athletics Understand & demonstrate Materials Measure and mark out to the nearest mm. Apply appropriate cutting and shaping techniques that include cuts within the perimeter of the material (such as slots or cut outs). (Link to Sound/Science: Making a musical instrument project) Year 4 Long Term Plan Sphinx activities and explore gestures and body actions e.g. flick, grab, float, strike. Be able to work in pairs or groups on a set dance. Be able to plan and perform a dance phrase in pairs including change of levels and direction. Make suggestions to improve quality of performance. COMPUTING PSHE FRENCH them to a partner and perform a 6 action sequence independently on floor and apparatus using speed and levels. Make suggestions to improve quality of performance. Demonstrate simple warm up activities and begin to describe changes in body. competently, confidently and proficiently over a distance of at least 25 metres Use a range of strokes effectively [for example, front crawl, backstroke and breaststroke] Perform safe self-rescue in different water-based situations orientate themselves around a simple course. Begin planning sensible responses to a challenge and can work and discuss problems as group. Recognise what tasks have demanded of them physically. Identify what parts of activity were successful. with rules and scoring. Kick/pass and control/catch a ball with feet/hands with accuracy and consistency. Understand how to position yourself when attacking/defending. Watch a partner and suggest improvements. Explain a warm up/cool down and give reasons why it is done. differences between athletic techniques – sprinting/running for sustained distance and show a range of throws and jumps while showing consistent technique and accuracy when performing all athletic actions. Play different roles when working as a group. Discuss how different warm ups affect heart rate and body temperature. Begin to evaluate own and others’ performances.