SUPPORTING INFORMATION for Chad W. Johnston1, Alex D
advertisement

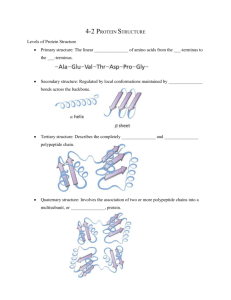
SUPPORTING INFORMATION for Chad W. Johnston1, Alex D. Connaty1, Michael A. Skinnider1, Yong Li1, Alyssa Grunwald2, Morgan A. Wyatt1, Russell G. Kerr2 & Nathan A. Magarvey1* 1 The Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Infectious Disease Research, Department of Biochemistry and Biomedical Sciences; Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada L8N 3Z5. 2 Department of Chemistry; Department of Biomedical Sciences; Atlantic Veterinary College, University of Prince Edward Island, Charlottetown, PEI, C1A 4P3 ‘ Supplemental Figures Figure S1. Diversity of peptaibol chemical families. Nearly 300 known peptaibols sorted by hierarchical clustering of chemical similarity reveals 8 dominant families. All structures share an initiating N-acetyl amino acid, a Cterminal alcohol, and extensive stretches of aminoisobutyric acid (Aib), aminoisovaleric acid (Iva), or alanine residues. Consensus sequences for each family were derived from comparisons of structures from each clustered group. Figure S2. Automated detection of trichopolyn 4. (a) iSNAP search result for MS/MS scan 1490 reveals a hypothetical variant structure that matches trichopolyn 4. (b) MS/MS data contains amide bond cleavage fragments that verify the amino acid sequence of trichopolyn 4. Figure S3. Automated detection of trichopolyn 2. (a) iSNAP search result for MS/MS scan 1510 reveals a hypothetical variant structure that matches trichopolyn 2. (b) MS/MS data contains amide bond cleavage fragments that verify the amino acid sequence of trichopolyn 2. Figure S4. Automated detection of trichopolyn 1. (a) iSNAP search result for MS/MS scan 1515 reveals a hypothetical variant structure that matches trichopolyn 1. (b) MS/MS data contains amide bond cleavage fragments that verify the amino acid sequence of trichopolyn 1. Figure S5. Automated detection of trichopolyn variant 1174. (a) iSNAP search result for MS/MS scan 1546 reveals a hypothetical variant structure of a new trichopolyn with a modification to AHMO observed in the related trichoderin family. (b) MS/MS data contains amide bond cleavage fragments that verify the amino acid sequence of this new variant. Figure S6. Automated detection of trichopolyn variant 1188. (a) iSNAP search result for MS/MS scan 1574 reveals a hypothetical variant structure of a new trichopolyn with a modification to AHMO observed in the related trichoderin family. (b) MS/MS data contains amide bond cleavage fragments that verify the amino acid sequence of this new variant. Figure S7. Automated detection of trichopolyn variant 1190. (a) iSNAP search result for MS/MS scan 1595 reveals a hypothetical variant structure of a new trichopolyn with a modification to AHMO observed in the related trichoderin family. (b) MS/MS data contains amide bond cleavage fragments that verify the amino acid sequence of this new variant.